-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Traditional Chinese Medicine
How to Treat Acne With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Acne breakout, pimples, blackheads? Painful cystic acne and acne scars can affect your confidence and even lead to depression. Acupuncture and TCM provide an alternative skin care option to treat hormonal acne and clear up blemishes.
What causes acne? Acne is a skin condition in which bumps on skin form when hair follicles become clogged with dirt and oil. Sebum, the natural oil produced by skin glands, builds up in the pores and causes blockages. Pimples may appear on the face or other parts of the body (back acne, chest acne, bumps on arms, pimples on scalp/scalp acne, etc.).
Acne is most common during the teenage years, but people of any age can experience skin breakouts. Acne is also influenced by fluctuations in hormones, reactions to cosmetics or foods, weather, and perhaps most commonly, stress.
Rosacea is another skin condition that typically causes redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels on the skin, but it can also cause red bumps to break out, similar to acne. This is known as “acne rosacea.”
Everyone gets a few pimples at some point in their lives. However, severe acne that causes scarring can have a serious impact on a person’s confidence in daily life, as well as being physically painful.
There are many types of products and acne medication available, both over the counter or with a prescription, including: benzoyl peroxide, retinol for acne cream, acne patch, and acne face wash.
Topical treatment for acne may clear blemishes on a skin-deep level. Acupuncture and other TCM skin treatments can help get rid of acne and other skin problems, like rosacea, dermatitis, and eczema by addressing the root causes: hormonal imbalances, inflammation, and stress.
Types of Acne

Acne blemishes can show up in different forms. The most commons types of acne include:
- Whiteheads – small, closed, white bumps that develop when a pore is clogged
- Blackheads – open bumps that are filled with oil and dead skin
- Red bumps on skin – papules are hard, red, inflamed bumps on skin
- Pustules – a papule that has a pus-filled tip
- Nodules – large, painful red bumps
- Fungal acne or bacterial acne – when red bumps are caused by bacteria or yeast clogging the follicles
- Acne rosacea – rosacea can cause acne-like breakouts in addition to red flushing
- Cysts or Cystic acne – large, painful, nodules that are deep down, under many layers of skin
Cystic acne is considered to be the most severe type of acne. The deep, inflamed cysts can get very big, last a long time, and leave permanent scars. Cystic acne may be genetic, as it tends to run in families.
Hormonal acne, which is also called “adult acne,” occurs because fluctuations in reproductive hormones like progesterone and estrogen and the stress hormone cortisol stimulate the overproduction of sebum. This kind of acne is most common among women in their 20s through their 40s.
Many women have breakouts that occur cyclically, coinciding with their PMS week or their period. Women may also experience pregnancy acne during the postpartum period. Women over 40 may have unexpected patches of pimples during perimenopause and menopause. Acne is also common among women with PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome).
Advanced Dermatology Acne Treatment

Dermatologists have tools that allow them to help remove pimples, known as acne extraction or blackhead extractions. Injections of corticosteroids can help reduce inflamed blemishes. Laser resurfacing can help minimize acne scarring.
A dermatologist can also provide acne medication. Cystic acne and hormonal acne will usually be treated with oral birth control pills to help manage hormone levels. Spironolactone is also sometimes prescribed; this is a diuretic, usually used to treat high blood pressure, that also has an effect on the hormones that control oil secretions.
Isotretinoin, also known as Accutane, is a medication used to treat severe acne, cystic acne, or nodules. Antibiotics are usually prescribed to help clear bacterial acne or fungal acne.
Many of these courses of treatment can cause unwanted side effects, and they do not get to the root cause of the hormone imbalance or internal toxicity.
TCM and acupuncture provide a way to get rid of acne that works from the inside out.
Can Acupuncture Help Acne?
According to TCM theory, skin problems reflect imbalances that originate deeper in the body. Heat and dampness are pathogenic forces that can take root in the organ systems. When heat “overflows” due to imbalances in the digestive or reproductive organs, the body tries to release some of the excess by allowing it to erupt out of the skin.
Acupuncture for acne can both help at the deeper, root level and on the surface of the skin.
We use meridian acupuncture points to target the internal organs that are creating toxic levels of heat or producing too much of some hormone. Then, we also use needles to stimulate the localized areas of the skin that are affected by the breakout and encourage healing.
Acupuncture treatment for acne will often focus on clearing heat from the stomach, intestines, liver, and lungs. This will help lead to fewer breakouts.
Acupuncture needles can be placed on the face where blemishes occur. The tiny “wounds” created by the very thin needles bring blood flow to the area and encourage the body’s repair and rebuilding mechanisms. The thin needles create a micro-trauma that brings blood flow to the area and encourages the body’s repair and rebuilding mechanisms to kick in. This is why acupuncture is also effective as an anti-aging treatment and a good alternative to botox injections.
One study showed a 94% effective rate for patients given 10 sessions of acupuncture for acne. A systematic review of acupuncture treatment for acne concluded that TCM offered an alternative with fewer side effects than conventional medical treatment.
TCM skin care for acne is highly individualized. An acupuncturist finds clues about which organ system is out of balance by observing the placement and appearance of recurrent breakouts, in addition to other symptoms related to digestion, hormone cycles, and emotional health. Cupping is another TCM treatment that can help draw out toxins and excess heat and improve circulation. Herbal supplements and dietary recommendations will be based on each person’s individual situation.
Top 3 Tips to Get Rid of Acne Naturally

Reducing stress is probably the most important thing you can do to help stop breakouts from happening. It is also generally advisable to avoid or limit spicy or greasy foods. Here are some of our best tips for clear skin.
- Start your day by drinking a cup of warm water with slices of lemon.
- Eat cooling foods and avoid foods that produce heat. Melons, mung beans, and radishes are top choices, along with lots of greens and purple-blue berries and plums.
- Try a homemade skin mask made from cooked, mashed dandelion greens. Apply for 20 minutes to get rid of blemishes and redness. Dandelion is a natural antibacterial and antifungal herb and is also good for the liver.
Acupuncture Near Me for Acne in West Los Angeles
Acne affects almost everyone at some point in their life. Breakouts can have a negative impact on your self-esteem, especially when we live in a culture that is so focused on appearances. The best acne treatment involves reduction of stress and inflammation, good nutrition, and restoring internal balance. At Art of Wellness we have over 30 years of experience helping patients heal skin conditions of all kinds.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Encephalitis With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Headache, sensitivity to light, stiff neck, short-term memory loss? These could be signs of encephalitis, or inflammation in the brain. Infectious encephalitis can happen due to an infection; autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) is a type of autoimmune disorder. Acupuncture and TCM offer an adjunct treatment for encephalitis recovery.
What is encephalitis? Encephalitis refers to a serious condition in which the tissues of the brain become inflamed. It can happen to anyone, but is more common among children and older people.
The symptoms of encephalitis are sometimes ignored, because headaches, neck pain, and “brain fog” are so common and may not seem that serious at first. However, in combination, these signs should not be taken lightly. Like meningitis (inflammation of the membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis can cause serious complications if left untreated. Encephalitis needs to be caught early and treated in order for people to make a full recovery.
What causes encephalitis? Brain inflammation can be caused by the body’s immune response to an infection, or due to an autoimmune disorder, in which the body produces antibodies that attack the brain tissues.
Top 10 Causes of Encephalitis
Viral infections are the primary reason that people develop encephalitis. These could be viruses carried by insects, especially mosquitoes, which are then contracted by humans through bites. Other communicable viral infections that pass from person to person through bodily fluids or close contact can also cause infectious encephalitis.
Infections that can lead to encephalitis include:
- Mosquito-borne viruses such as: West Nile Virus, Eastern Equine encephalitis, Western Equine encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, LaCrosse encephalitis
- Tick-borne viruses
- Rabies virus – can be contracted through being bitten by an infected animal
- Polio virus
- Herpes Simplex, Type 1 and Type 2 (HPV1 and HPV2)
- Epstein-Barr virus (mono, mononucleosis)
- Varicella Oster virus (chicken pox, shingles)
- Measles (rubeola)
- German measles (rubella)
- Mumps
There have been cases of people developing encephalitis as a complication of a COVID-19 infection.
Some cases of encephalitis can be caused by bacterial or fungal infections, or by a parasite. It could also be caused by exposure to some sort of allergen or toxin in the environment.
People with weakened immune systems—for example, due to HIV/AIDs—or who take immunosuppressant medications are at a higher risk for developing encephalitis.
Immunotherapy used to treat certain kinds of cancer, such as melanoma, ovarian cancer or lung cancer, has been shown to cause encephalitis in some cases.
Some cases of autoimmune encephalitis, called Anti-NMDAR encephalitis, appear to be related to a certain kind of tumor called a teteroma. In women and young women, especially, this can be an ovarian tumor that produces the antibodies for NMDAR.
Symptoms of Encephalitis

A mild case of encephalitis might only cause some flu-like symptoms that clear up within a few weeks. These types of symptoms include:
- Headache
- Stiff neck, neck pain
- Muscle aches, joint pain
- Fever
- Fatigue, feeling tired and weak
- Sensitivity to light
More severe symptoms of encephalitis can affect both cognitive and motor function:
- Mental confusion, brain fog, difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems, short term memory loss
- Hallucinations
- Seizures
- Severe headache
- Trouble with coordination or balance
- Loss of sensations in parts of the body or face
- Loss of muscle control in parts of the body or face
- Problems with speaking or hearing
- Mood swings, changes in personality
Anti-NMDAR encephalitis (when there may be an ovarian tumor involved, especially) can cause symptoms like pro-domal headache, nausea, and fever, which may then progress to more severe complications, including involuntary movements or tremors, urinary incontinence, rapid heartbeat, and psychiatric symptoms like anxiety, paranoia, or mania.
In severe cases, encephalitis can cause loss of consciousness and even cause a person to go into a coma. It is very important to seek urgent medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Treatment for Encephalitis

Blood tests can confirm whether a viral or bacterial infection is causing encephalitis. Imaging tests like an MRI or CT scan may show the inflammation in the brain. A spinal tap may show an imbalance in cerebral fluids, or an EEG may show unusual electrical impulses in the brain.
However, there are times when these tests will not show exactly what is causing the encephalitis. As with many autoimmune disorders, it can be hard to pinpoint a clear diagnosis for autoimmune encephalitis (AIE).
Medical treatment for encephalitis will depend on what type it is determined to be. Mild inflammation will usually be treated with over the counter anti-inflammatory medications. Antivirals or antibiotics will be prescribed if a specific infection is found to be the cause. Steroids will often be used to help reduce inflammation. In more serious cases, a person may require breathing assistance or anti-seizure medications.
In cases where the cause is believed to be an autoimmune response, immunotherapy is used to try to interfere with the antibodies that are attacking the brain tissues. Steroids will be usually used in combination with other treatments. Plasmapheresis, or plasma exchange, removes some of these antibodies from the blood. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy introduces healthy antibodies to block the action of the malfunctioning antibodies.
In cases of anti-NMDAR encephalitis where a tumor is present, treatment will include the removal of the tumor in addition to immunotherapy. Patients with this type of encephalitis may also be prescribed antipsychotic drugs to relieve psychiatric symptoms.
Immunotherapy works for some patients, but not all. Many patients will be offered second-line treatments such as monoclonal antibodies or antimetabolites. In some cases, people may seem to recover from encephalitis for a while, and then have a relapse in which the inflammation flares up again.
Most people will need significant time and rehabilitation to help them make a full recovery from encephalitis. Some people will have long-lasting effects, such as memory problems, balance and coordination issues, speech problems, and emotional volatility.
Many of the pharmaceutical treatments available for encephalitis cause significant side effects and can even lead to more physical, emotional and mental health issues. Fortunately, acupuncture and other TCM modalities offer a way to reduce inflammation in the brain and help relieve encephalitis, as well as helping to offset any side effects from other medical interventions.
Can Acupuncture Help Encephalitis?

With acupuncture and Chinese herbs, we seek to treat the root cause and the various symptoms and complications of each condition according to recognizable patterns. This allows us to effectively treat some conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions that may not readily respond to conventional medicine.
In the TCM view, inflammation occurs because there is too much heat in the body. Yang energy provides the “fire” we need to keep the body warm and energetic. But, if there is an imbalance, and too much heat, this leads to conditions like fever, infections, and inflammation. So, we see pathogenic internal heat as contributing to encephalitis, in addition to outside pathogens like viruses or bacteria. To clear heat that is trapped or stagnant in the body, we will use specific herbs and cooling foods, along with acupuncture treatment and lifestyle changes to reduce physical and mental stress. TCM herbs can also be highly effective against bacterial and viral infections.
The motor control and cognitive problems that can result from encephalitis occur because the inflammation in the brain is affecting the functioning of the central nervous system. With acupuncture, we can help to reestablish connections and neural pathways.
Autoimmune disorders are still not well understood by Western medicine, but with acupuncture we can help to balance and regulate the immune system, so that it is not being inappropriately triggered. This is why acupuncture works well as an adjunct treatment for encephalitis and many other autoimmune disorders.
Acupuncture Near Me for Encephalitis in Los Angeles and West Los Angeles
It can be very difficult when you or someone you love is facing a serious illness and a long, difficult recovery. TCM offers a healthcare option that treats each person in a highly individualized and caring way. At Art of Wellness, we have over 30 years of experience helping people gain back their strength and mobility after suffering from conditions like encephalitis, meningitis, Lyme disease, Guillain Barré Syndrome, Myasthenia Gravis, and many others.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Muscular Dystrophy With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Progressive muscle weakness and muscle atrophy (loss of muscle mass) are the primary symptoms of Muscular Dystrophy. Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative treatment to prevent muscle atrophy and treat complications of muscular dystrophy.
Muscular Dystrophy refers to a group of genetic muscle diseases that cause damage to muscles and lead to decreased flexibility and movement.
There are several types of Muscular Dystrophy. Some types of muscular dystrophy are more likely to show up during childhood, while others may develop later in life.
The most common type is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). Duchenne muscular dystrophy can lead to muscle wasting, limited mobility, and other complications with breathing and heart function. Duchenne most often affects boys and starts showing up in early childhood.
Becker muscular dystrophy is similar to Duchenne, but less common, and generally leads to milder symptoms of muscular dystrophy.
Muscular dystrophy of all types is caused by genetic mutations, usually inherited. These mutations affect muscular development and growth by blocking certain proteins in the body from performing their usual functions of building and maintaining muscle mass.
Muscular dystrophy is a progressive disease, which means that trouble with walking and other complications will get worse as a person gets older. Muscle weakness can affect the limbs and trunk, and can also affect the major internal organs, like the heart, lungs, and the muscles involved in swallowing. Muscles can shorten and tighten (contractures), causing them to pull on tendons and cause joint problems.
Both conventional medical treatments and alternative treatments are aimed at helping to slow the progress of the disease, maintaining maximum motor control, and keeping organs as healthy as possible.
Symptoms of Muscular Dystrophy
The signs and symptoms of muscular dystrophy vary, depending on the type of genetic mutation, and therefore, the type of muscular dystrophy.
The most common signs of muscular dystrophy include:
- Difficulty getting up from sitting or lying down
- Trouble walking, walking on toes, or waddling gait
- Falling frequently, stumbling
- Muscle pain, stiff muscles
- Enlarged calf muscles
- Learning difficulties, delayed development, difficulty concentrating
- Breathing problems, shortness of breath
- Heart problems, myocardiopathy
- Trouble swallowing
- Curved spine, scoliosis
- Drooping eyelids, vision problems, cataracts
Big calf muscles are common among people with DMD and Becker type muscular dystrophy. This is known as pseudohypertrophy, or calf hypertrophy, and is an abnormal development of the lower legs that happens in conjunction with the wasting of other muscles in the pelvis and thighs. With muscular dystrophy, healthy muscle can go through a pattern of inflammation that replaces healthy muscle cells with fat and scar tissue.
As people with muscular dystrophy age, they may begin to have more problems with respiratory function and/or heart problems like cardiomyopathy (scar tissue damage to the heart muscles) or arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). Because the lungs are weaker, a person may be more susceptible to serious respiratory infections, like pneumonia.
Some kinds of muscular dystrophy can cause digestive problems, infertility, and cataracts.
Even amongst people who have the same type of muscular dystrophy, the symptoms and complications can look very different in each individual.
Top 6 Types of Muscular Dystrophy

The different kinds of muscular dystrophy are caused by different genetic mutations that affect muscle development and function in different areas of the body. Some types show up early in life, and others may not develop until well into adulthood.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) – This is the most common type of muscular dystrophy, and occurs most often in boys, becoming apparent in early childhood. As a result, many young patients with DMD will show slow growth and motor development; they may walk late, tend to fall often, and have to use their hands more than usual to help them get up again.
- Becker Muscular Dystrophy – This type tends to begin the late teen or early adult years. Similar to DMD, a person will first notice weakness in the muscles, leading to more and more difficulty getting up and walking. Later, it can lead to heart problems.
- Myotonic Dystrophy – also known as DM (dystrophia myotonia). Categorized into 2 separate genetic disorders, DM1 (once known as Steinert disease) and DM2 (also known as Ricker syndrome, proximal myotonic dystrophy, or PROMM). DM develops in stages, and can affect the eyes, causing cataracts, and droopy eyelids. Uncontrollable muscle contractions (myotonia), muscle pain, and fatigue are other possible symptoms of myotonic dystrophy, as are hair loss, loss of facial expressions due to flaccid muscles in the face, and slurred speech.
- Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy (FSHD) – a specific type of dystrophy that often develops slowly and can be difficult to diagnose. It can involve loss of muscle mass, starting in the face and spreading to the upper body, especially the shoulder blades, often affecting the body asymmetrically. People with FSHD may have trouble with small motor functions, like pursing their lips to drink, closing eyes all the way, weakness in the hands, difficulty picking up the feet when walking (foot drop).
- Congenital Muscular Dystrophy – CMD is a more general term referring to different kinds of muscular dystrophy that are apparent at birth, causing lack of muscle tone (hypotonia, or “floppy baby” syndrome), atrophy, contractures (shortening of muscles), scoliosis (curving of the spine), as well as respiratory problems.
- Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy (LGMD) – a group of muscular dystrophies that primarily affect the muscles around the shoulders and hips.
Medical Treatment for Muscular Dystrophy

Muscular dystrophy can sometimes be difficult to diagnose. Other diseases, like ALS, multiple sclerosis, may also cause muscle weakness and atrophy.
People with muscular dystrophy need continual monitoring, and treatment options aim to manage the various symptoms and complications. Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy can help people maintain as much flexibility, strength, and functionality as possible.
Steroids are often used to help maintain muscle and respiratory function, but many people with muscular dystrophy will end up needing to use aids, such as a cane or wheelchair, or a ventilator to help with breathing. Patients may need to be on heart medications to control blood pressure or arrhythmia. In some cases, surgery may be needed to correct severe contractures or scoliosis.
Acupuncture and TCM can be used as an adjunct to conventional treatments, and may help to maintain muscle mobility, improve pulmonary function, nervous system function, cognitive function, and to reduce inflammation.
Can Acupuncture Help Muscular Dystrophy?
TCM offers a different way of looking at disease. The conventional medicine view of muscular dystrophy is that it is an incurable genetic disease, and the progressive worsening of symptoms and complications stems from that.
In the TCM view, we see patterns of symptoms that show up in different ways in different people, according to their constitution. Long before we had a modern understanding of genetics, TCM observed that some people are born with deficiencies of certain types of organ Qi.
So, the TCM practitioner is looking for a pattern of symptoms, and how that interplays with a person’s foundational health. In the case of muscular dystrophy, it is not just that problems in the organ systems occur because of the progressive muscle atrophy; the dysfunction in the organs is occurring due to an inherited deficiency, and contributing to muscle atrophy.
When we see weak muscles, diminished muscle mass, and even paralysis, this falls under the category of Wei Zheng conditions.
Other Wei Zheng illnesses include:
- Ataxia
- Myelitis
- Myasthenia gravis
- Multiple sclerosis
Although they may have similar symptoms, different Wei Zheng illnesses can arise from problems with varying organs, including the liver, spleen, stomach, or kidneys. So, according to TCM, different types of muscle diseases require differentiated treatments.
TCM views muscular dystrophy as being related to an innate deficiency of Yuan Qi, or kidney energy. In Western medicine, the kidneys are thought to mainly have to do with the urinary system, but in TCM, “Kidney Qi” is a much broader concept.
Kidney Qi is inherited from our parents; it governs the growth and strength of the body. Kidney deficiency is also considered to affect cognitive function and memory, infertility, and hair loss.
Kidney problems are common among adults with DMD, but in medical science, it is considered to be a long-term complication of muscular dystrophy, as opposed to being foundationally related to it.
So, TCM diagnosis and treatment for muscular dystrophy will aim to strengthen the kidneys, spleen, and other organs, while also stimulating and nourishing the muscles, tendons, and nervous system.
The acupuncturist will look at the specific range of symptoms presenting in each person, and plan a treatment course to include modalities such as acupuncture, tuina massage, herbal supplements, and nutrition.
Everything is also affected by the environment and lifestyle. Foods that nourish the Kidney Qi, a regimen of gentle exercises, and meditation can help maintain better overall functioning.
A case study involving a woman with FSHD showed a significant improvement in facial muscle coordination after a course of acupuncture treatment.
A research study showed that acupuncture helped to slow the loss of muscle mass.
Acupuncture Near Me for Muscular Dystrophy in Los Angeles, Westside
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture and TCM in West L.A., we have over 30 years of experience helping people manage musculoskeletal pain and weakness of all kinds. Acupuncture treatment can help prevent the worsening of degenerative disease and improve well-being for people suffering from many types of chronic illness.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How To Treat Claustrophobia Anxiety Disorder With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Claustrophobia is a specific kind of anxiety disorder in which fear of being in an enclosed space can bring on symptoms similar to those of panic attacks. Claustrophobic feelings like being anxious, hyperventilating, sweating, shaking, and rapid heartbeat can be eased with acupuncture and TCM.
Claustrophobia is actually quite common; at least 10% of people report experiencing some claustrophobic feelings. Women report having a fear of confined spaces more often than men do. Phobias are sometimes rooted in a childhood experience, but they can arise in anyone, at any age, and are considered mental health issues or psychiatric disorders.
Phobias are distinct from regular fears because of their intensity and, to some extent, irrational nature. Phobias are unreasonable fears; feeling very afraid, to the point of physical and emotional distress, of something that isn’t really happening. Claustrophobia becomes a serious mental health problem if it interferes with a person’s daily life or relationships.
Sometimes claustrophobia can get in the way of a person getting help for other health problems. For example, it may cause them to avoid undergoing an MRI. Some people might fear visiting a doctor’s office, which often means facing elevators, public restrooms, and other small rooms without windows. Some women report feeling claustrophobic during pregnancy, as if they are “trapped” inside their own bodies.
Other common triggers of claustrophobia include: airplanes, trains, tunnels, small cars, revolving doors, or amusement park rides with restraints. Even thoughts of having to be trapped in one of these situations can be enough to bring on symptoms of claustrophobia. Signs of claustrophobia can be similar to those of a panic attack.
Top 10 Symptoms of Claustrophobia:
- Sweating
- Shaking or trembling
- Trouble breathing
- Rapid heartbeat, fast heart rate, high blood pressure
- Tight feeling in chest, chest pain
- Flushed face, feeling hot
- Dizziness, feeling lightheaded or faint
- Ringing in ears, tinnitus
- Butterflies in stomach feeling, nausea, queasy feeling
- Numbness or tingling in parts of the body
Other signs of anxiety due to claustrophobia could include: dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, choking, chills, confusion, or disorientation. In addition to physical symptoms of panic, claustrophobia may cause a person to cry, yell, or to be overwhelmed by a desire to get out of a situation because they feel that they are in serious danger, even if it seems irrational.

Cleithrophobia is another type of anxiety disorder that is sometimes confused with claustrophobia. Cleithrophobia specifically refers to the fear of being trapped or confined with no way to escape. Claustrophobia is a fear of the small space itself. These two phobias can exist together. Either one could cause serious anticipatory anxiety, for example, if a person has to have an MRI.
Cleithrophobia is related to other “winter phobias,” which may include “cabin fever,” which is a sense that one is stuck inside, or a fear of being literally trapped in the ice or snow. Many people feel an extra sense of sadness or dread during the winter months; this kind of depression is known as SAD (seasonal affective disorder).
Over time, repeated panic attacks or bouts of intense anxiety brought on by claustrophobia can create long-term stress that is harmful to overall physical and mental health. Acupuncture and TCM offer an adjunct or alternative treatment for claustrophobia which can help reduce symptoms and offset the effects of stress.
What Causes Claustrophobia?
Phobias can be triggered by some event or experience in which a person felt endangered and was traumatized, similar to PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder). Like other mental health conditions, claustrophobia is influenced by brain chemistry. Imbalances in the neurotransmitters in the brain can cause some people to experience symptoms of anxiety or panic attacks even if nothing scary is really happening. Then, they may associate those physical and emotional feelings with a specific place or situation, which causes the anxiety to be triggered whenever they approach that place or even think of that situation.
People can perceive things differently. One research study suggested that people with claustrophobia may have a different perception of how near something, like a wall, is to them. In other words, they underestimate distances, or their sense of “personal space” is different from other people’s.
The amygdala is the part of the brain that processes incoming sensory information from the environment and signals the autonomous nervous system if it detects danger. This is essentially the neurological pathway of fear. Some research has suggested that people who experience panic disorders are more likely to have a smaller-than-average amygdala.
Treatment for Claustrophobia
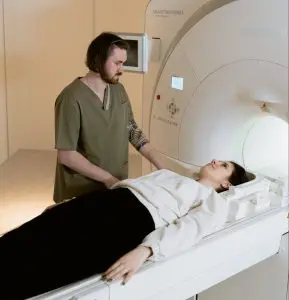
To be diagnosed with claustrophobia, a person will need to explain to their doctor that they have been having these intense feelings for a while and that they are having a negative impact on their lives. This could mean that they go out of their way to avoid certain places or situations. A mental health professional will try to determine whether these fears are normal, or could be attributed to some other condition.
Some doctors may prescribe SSRIs like Zoloft or Lexapro, which influence serotonin levels in the brain, to help patients who are suffering from claustrophobia or anxiety. Often therapy is recommended to help patients learn to cope with their feelings. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and/or exposure therapy aim to retrain the mind and may help people learn to get used to being in a small space without feeling so anxious.
Psychiatric medications can have unwanted side effects and may create a sense of dependence. Some people will avoid therapy because it can be very confronting and become another source of fear.
Acupuncture and other TCM modalities, including herbs and movement techniques like Tai Chi, may offer an alternative solution for panic attacks due to claustrophobia, without side effects or having to work through the problem with uncomfortable talk therapy sessions.
Can Acupuncture Help Claustrophobia?
According to TCM, the organ systems closely associated with fear are those of the kidneys, liver, and heart. Kidney deficiency, in particular, can cause fear and mental disturbances. These types of mental disorders can also be related to imbalances in Yin and Yang energies, and blood deficiencies. An acupuncture practitioner’s approach to treatment for claustrophobia may, therefore, focus on strengthening and nourishing the kidneys, while soothing the liver and heart.
One study compared patients who knew they had claustrophobic feelings going into an MRI; some were treated with acupuncture based on TCM acupoints. Control groups patients were given sham acupuncture (not really the points that would correspond with TCM theory). They concluded that the real acupuncture treatment did offer a therapeutic effect for claustrophobia, with a 92% rate of effectiveness; meaning, the patients were able to remain calm during the MRI.
A case study of a woman who had experienced bouts of claustrophobic symptoms since her teenage years, including shortness of breath, trembling, sweating, and loss of motor control in her hands and feet. After six acupuncture treatment sessions, she reported much improvement: feeling calmer, no headaches, palpitations, or anxiety. Chinese herbs can also be used, in conjunction with acupuncture treatment, help a person overcome claustrophobia.
Acupressure Points for Claustrophobia
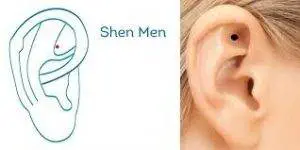
In between acupuncture sessions, you can use self-care acupressure to relieve claustrophobia.
Shen Men is a Master point, located in the valley of the upper part of the ear. This is a classic point to help feelings of anxiety.
Shoujie, which is located on the palm of the hand between the metacarpals of the fourth and fifth fingers, along the topmost crease, helps relieve palpitations and dizziness.
Acupuncture for Claustrophobia Near Me in Los Angeles Area
TCM is an excellent way for people to find relief from mental health issues of all kinds, including depression, anxiety, panic attacks, and phobias. We will do all we can to make sure that you are comfortable in one of our larger treatment rooms with a window, and to make your acupuncture treatment experience relaxing and pain-free. If you or someone you know is finding that the thought of enclosed spaces is creating anxiety in day-to-day life, please do not hesitate to try acupuncture for claustrophobia.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Ataxia With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Ataxia is a general term that covers many conditions involving muscle weakness or lack of coordination. Ataxia causes can include: infections, neurological disorders, degenerative brain disease or tumors, some autoimmune disorders, stroke, or alcohol addiction. Acupuncture can help with the muscular weakness and balance problems of cerebellar ataxia and sensory ataxia.
Ataxia can affect the limbs, leading to difficulty with balance and walking. It can also affect the muscles involved in speech, chewing and swallowing, and eye movements.
Different types of Ataxia include:
- Cerebellar ataxia – The most common types of ataxia are related to some sort of problem with the cerebellum, the part of the brain in the back of the head, which regulates muscle activity, balance, and equilibrium. Damage or dysfunction of the cerebellum can also cause tremors and difficulty in judging distance (dysmetria).
- Sensory ataxia – Ataxia may also happen due to issues with other parts of the brain and nervous system, such as damage to the somatosensory nerve, the brain stem, posterior lobe, cerebral cortex, the spinal cord, or the peripheral nerve. These kinds of ataxia can affect the gait and walking.
- Vestibular ataxia – Inner ear problems can cause ataxia that affects balance and can cause vertigo, dizziness, nausea.
- Hereditary ataxias – While they are rare, some people are born with hereditary forms of ataxia. These are classified as autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive, and they may begin to show up at any point in life. These types of ataxia are usually degenerative, meaning the symptoms are chronic and get worse over time. Autosomal dominant ataxias used to be called “Marie’s ataxia,“ and autosomal recessive ataxias used to be called “Friedrich’s ataxia.”
Ataxia may be acute or chronic, with symptoms that last for hours, days, weeks, or years, depending on the root cause. An infection, for example, could cause a temporary episode of ataxia. Ataxia can be triggered by an autoimmune flare-up.
Acupuncture and other TCM modalities are uniquely helpful for all kinds of neurological problems, including ataxia symptoms. Acupuncture can help to restore communications between parts of the nervous system and repair damaged nerve cells.
Top 10 Causes of Ataxia:
Ataxia can be caused by a wide variety of health issues that affect the brain and nervous system:
- Stroke, brain aneurysm
- Brain tumor or lesions on the spinal cord
- Alcohol abuse
- Some medications or chemotherapy
- Toxins, heavy metal poisoning
- Severe vitamin deficiency
- Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid problems
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Celiac Disease
- Encephalomyelitis (Chronic fatigue syndrome, ME/CFS)
Ataxia can also result from serious infections like Lyme disease, Chickenpox, HIV, or COVID-19.
The severity and duration of ataxia symptoms can vary, depending on the cause of ataxia, and the type.
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment for Ataxia
It can be challenging to get a clear diagnosis when a person shows symptoms of Ataxia. Testing for Ataxia often involves performing the Romberg Test. This is a fairly simple, physical test, often used by both doctors to measure a person’s balance and coordination. It is sometimes used by police officers to determine if someone is under the influence of alcohol.
The patient undergoing examination stands in various positions, closing and opening the eyes, and shaking the head from side to side. The changes in their ability to balance and maintain their position can help a doctor quantify their equilibrium in order to diagnose sensory ataxia, or vestibular ataxia, for instance. It can also help determine if a patient suffers from vertigo.
Other physical testing involves studying a person’s gait, or mode of walking. A person with sensory ataxia, for example, often demonstrates a particularly heavy, high-stepping gait due to the lack of sensation of the bottoms of their feet when they touch the ground.
Blood tests, spinal tap testing, or MRI imaging may show if ataxia is due to some sort of damage to the brain or spinal cord, or if there are lesions, tumors, or possibly some sort of infection causing the problem.
For most ataxia symptoms, however, there is no specific medical treatment. Patients who are having trouble with walking or moving their hands and facial muscles, may be referred to physical therapy or occupational therapy. Some people will need walkers or other physical aids.
Acupuncture offers a way to help people with all kinds of ataxia to improve their muscle coordination, balance, and other problems.
Can Acupuncture Help Ataxia?

Acupuncture treatment and other TCM modalities are suited to helping patients with all kinds of neurological conditions, by enhancing connections between the brain and the nervous system, and helping to restore the healthy development of nerve and neural cells. For patients with ataxia, this means an improvement in muscle coordination and limb function. Similar to the way that acupuncture helps Bell’s Palsy,Trigeminal Neuralgia, Myasthenia Gravis, and Parkinson’s, it may be able to improve eye problems and problems with eating due to nerve damage.
One case study followed a man who had suffered a stroke and was experiencing sensory ataxia. After regular rehab, he regained some of his muscular strength, but still had trouble with balance and perception. Acupuncture helped him regain his sense of spatial awareness and coordination of his lower limbs.
Another study found that acupuncture treatment helped increase connectivity between different parts of the brain and motor function in patients who were recovering from a stroke.
Formulations of traditional Chinese herbs are also a key part of TCM treatment for ataxia.
Tai Chi movement practice can also benefit people with ataxia, promoting better dynamic balance.
Acupuncture Near Me for Ataxia in West Los Angeles
Conditions like ataxia can be difficult to treat with conventional medicine. Neurological disorders, autoimmune disorders, stroke recovery, the long-term effects of a serious infection; these are all situations in which a person may be helped by trying acupuncture and TCM as an alternative or adjunct to traditional treatment. Drs. Tan and Cai at Art of Wellness in Los Angeles, CA have over 30 years of experience helping people regain muscular strength and motor function.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.