-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Uncategorized
How to Treat Glaucoma With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Dry eyes, blurred vision, or a headache behind eyes? Eye pain, redness, or pressure behind eye should not be ignored, as these symptoms may be a sign of deeper issues. Acupuncture and TCM offer an effective and holistic way to treat glaucoma, eye pain and headache, dry eye syndrome, and blurry vision in one eye or both eyes.
As a delicate organ that holds itself together in an orb shape, the eye requires the right amount of fluid to maintain tension and to keep its surface moist. Many eye problems are related to the balance, or imbalance, of fluids in and around the eyeball. Tears keep the eyeball lubricated, while a liquid called aqueous humor keeps the eyeball inflated. When there is not enough fluid, or when the fluid doesn’t drain properly and builds up in the eye, it can lead to eye disorders like dry eye and glaucoma.
TCM treatment for eye disorders work well as an alternative or adjunct to standard treatments for glaucoma or dry eye disease, as they focus on addressing the internal, root causes of these common eye issues.
What Causes Dry Eyes?
One of the most common eye problems is dry eye disease, which happens when you don’t produce enough tears, or if the tears you do produce don’t lubricate the eyes enough. Tears are made up of water, oil, and mucus. If the glands that produce tears are not functioning correctly, and/or the balance of water, oil, and mucus is not right, the tears may not protect the surface of the eyeball the way they’re supposed to.
The symptoms of dry eye syndrome include:
- Burning eyes, stinging eyes
- Thick, stringy mucus in the eyes or around the eye
- Extra sensitivity to light
- Red eyes, eye redness
- Watery eyes, watering eyes as reaction to dryness
- Eyes itching, rubbing eyes, feeling like there is something gritty or sand in your eye
- Blurred vision, blurry eyes, blurry vision in one eye, sudden blurry vision
- Eye fatigue, eyes tired when reading or looking at screens, eyelids feel heavy
- Difficulty driving at night
- Difficulty wearing contacts

Dry eyes can be caused by many different factors, from weather, environment, or humidity levels in your home or office, to allergies, hormones, medications like antihistamines, decongestants, birth control pills, antidepressants, and medications prescribed for high blood pressure and Parkinson’s disease. Some people may have dry eye after having LASIK eye surgery, or because of wearing contacts, or staring too long at their computer. Some health conditions that put you at higher risk for dry eye syndrome include: rheumatoid arthritis, ALS, lupus, and hyperthyroidism. Dry eyes can become inflamed, and make you more susceptible to infections. Over time, dry eye syndrome can lead to scarring of the cornea, which can permanently affect vision.
The typical treatment most people try for dry eye syndrome is the use of over the counter eye drops or artificial tears. There are various types of prescription medications that also aim to replace or increase the production of tears. Some doctors may recommend antibiotics to help reduce inflammation around the tear ducts, or special contact lenses that are designed to keep moisture on the surface of the eye. But none of these solutions treats the underlying cause of dry eyes.
Acupuncture has been shown to boost the efficacy of standard treatment for dry eyes by helping promote more tear secretion and improving the makeup of the tears themselves, so that they don’t evaporate so easily.
What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is an umbrella term for vision loss related to damage to the optic nerve. This often happens because of a buildup of too much fluid in the eye, which creates pressure. Often, a person has already had glaucoma for a long time before they begin to notice changes in their vision. The most common types of glaucoma do not cause eye pain but can cause loss of vision, usually beginning with peripheral vision.
Glaucoma is one of the top causes of blindness worldwide, and can begin at any time in life. African Americans have a much higher risk of developing glaucoma. Other people at higher risk for glaucoma include people over 60, people who have diabetes, and people who are already very near-sighted.
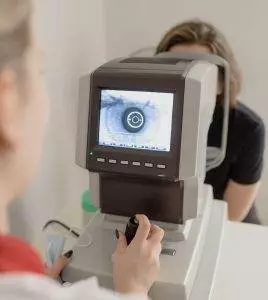
The most common type of glaucoma is primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), which is diagnosed when an eye examination finds damage to the optic nerve or retinal nerves. Most people with POAG demonstrate some level of elevated intraocular pressure, but some do not. Most types of treatment for glaucoma are focused on reducing this eye pressure, as it is one known factor. However, medical science is still unclear about exactly what causes glaucoma.
Medications to treat glaucoma try to remove the excess pressure built up in the eye by either increasing the flow of fluid out of the eye, or by decreasing the production of fluid within the eye. Combination medications do both. These medications may or may not be helpful for individual patients. For some people, they cause irritation or dry eyes (see above). They require frequent usage and can be expensive. Laser surgery is another alternative, but many patients begin having problems with eye pressure again after some time has passed.
Acupuncture treatment can improve blood flow to the eye and to the optic nerve, which can in turn help to reduce pressure behind the eye.
Acupuncture: A Natural Treatment for Dry Eye and Glaucoma
According to TCM, many eye disorders reflect other problems going on internally, dimming the life force energy that lights up the eyes. From the TCM point of view, eye problems like glaucoma and dry eye syndrome are due to lack of proper flow of energy, blood, and nourishment to the eyes.
In TCM, the liver is considered the storehouse and distributor of blood and other bodily fluids. If there is inadequate production of tears in the eyes, that is considered to be a reflection of some weakness or blockage coming from the liver system. The liver also contains the “spark of life” that shines out through the eyes. So, when there is not enough blood and Qi flowing from the liver to the eyes, there may be dryness and blurred vision. When there is too much fire energy coming from the liver, it can cause swelling that leads to pressure. This is what can cause the eye pressure of glaucoma, and also eye pain, or headache behind the eye.
Research has shown that acupuncture treatment can be effective for helping both glaucoma and dry eye syndrome:

- One study of patients treated for glaucoma showed reduced intraocular pressure both an hour after the treatment, and more generally, after having completed four treatment sessions.
- An analysis of studies showed that patients treated with acupuncture for glaucoma showed improved vision over those who did not.
- Another study showed that acupuncture treatment for glaucoma improved blood flow to the eye.
- A study done at the University of Pittsburgh compared patients treated with acupuncture for dry eye to those given “sham” acupuncture treatments over a six month period. Participants who had acupuncture reported improvement in symptoms of dry eye, such as less scratchiness and less redness. The results were still improved months after the treatment.
- A study that compared patients who received acupuncture treatment and used artificial tears to those who only used artificial tears found that the acupuncture recipients produced more natural tears of good quality, and experienced fewer symptoms of dryness.
Acupuncture Near Me for Glaucoma and Other Eye Disorders – Los Angeles Area
TCM has recognized and treated eye disorders for many centuries. Symptoms of dryness, itching, eye fatigue, pressure or headache behind eyes, and sore eyes can all be treated with acupuncture and herbs. Some changes in habits and nutrition will go even further to help people with glaucoma or dry eyes find relief. The doctors at Art of Wellness have over 35 years of experience in helping people get relief from dry eyes, restoring clearer vision, and bringing back the vibrant Qi that lights up your eyes.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Do you have joint pain, swelling or stiffness in the joints, especially finger joint pain or a swollen knee? Maybe you feel that the joint pain is moving to other parts of your body, or flares up sometimes, and then seems to go away. Joint pain accompanied by fever and fatigue may be a sign of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), an auto immune disease that causes inflammation and can lead to serious physical disability. Acupuncture and TCM offer a way to help people who suffer from Rheumatoid arthritis, as well as other types of arthritis and autoimmune disorders.
Arthritis is a general term that refers to all kinds of joint pain. Most types of arthritis begin to occur due to aging and the repeated “wear and tear” on the joints of the body that happens as we move through life. Any place in the body where two bones meet is considered a joint, so arthritis pain and inflammation can occur in the large joints of the limbs, causing shoulder pain or hip pain, in the spine, causing back pain, or in the extremities: arthritis in hands and feet. Rheumatoid arthritis most commonly shows up first as arthritis in fingers, hands, and knees.
RA can also be considered a connective tissue disorder, and, as such, bears similarities to Lupus and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS).
Rheumatoid arthritis used to be commonly known as “rheumatism,” and now may be referred to as “RA.” It is different from other types of arthritis because the joint pain is caused by immune system problems, not injury or overuse of the joint.
When a person develops an autoimmune disorder, their immune system is mistakenly attacking normal tissues in the body. In the case of RA, an immune response attacks the lining of the joints, a soft tissue membrane called synovium. This creates inflammation and can ultimately begin to cause damage to the bones themselves (osteoporosis). Affected parts of the body can begin to change shape, become weak, and eventually lose their ability to function properly.
In later stages of RA, other body systems can be affected, as well. The joint lining contains blood vessels and nerves, so damage to the synovium can also impact the cardiovascular system and the nervous system. People with RA are at greater risk for developing nerve damage, heart disease, lung disease, and problems with the eyes. People with Rheumatoid arthritis can also be more prone to getting infections like the flu or pneumonia, and certain types of cancers, like lymphoma.
RA can affect your body composition, leading to obesity. Some people may lose weight initially, but it is usually muscle mass that is lost, as RA makes exercise difficult. This means that people can end up with an unhealthy ratio of fat to muscle.
RA is different from osteoarthritis in that it can show up at any time in life. Sometime children develop Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis). Like RA in adults, this is an autoimmune disorder, and can cause other symptoms like fever and rashes. Some children will grow out of their RA symptoms; others may carry this disorder with them into adulthood.
Most people with RA begin to show signs in their middle age. Women are more likely to have RA than men. As with other autoimmune diseases, medical science has not determined the exact Rheumatoid arthritis causes, but they may be partly genetic, and partly having to do with hormones. Environmental factors may contribute to RA, as can stress and strong emotions. Past illnesses or viral infections, like Epstein Barr virus, can also be a factor.
TCM and acupuncture treatment for Rheumatoid arthritis works on multiple levels. Acupuncture can help to reduce inflammation and stiffness in the joints. TCM treatment with herbs helps to improve and balance immune function. Acupuncture can also relieve emotional symptoms related to stress, fatigue, and depression.
Top 10 Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms

For some people the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis may develop slowly over many years; for others, they may start suddenly. People will experience RA symptoms as different sensations, in different parts of the body, which is part of what makes it difficult to diagnose. The most common symptoms of RA include:
- Joint pain that starts in the smaller joints: pain in hands, pain in knees, pain in toes
- Redness and swelling in joints: swollen fingers, swollen knee, hands swollen, ankle swollen
- A sensation of heat or warmth in the joints
- Stiffness first thing in the morning that gets better as the day goes on
- Fatigue, feeling exhausted, tired all the time
- Pain in same joint on both sides, for example, pain in both knees
- Hard lumps under the skin near the painful joints (Rheumatoid nodules)
- Eye pain, dry eyes, blurry vision
- Low grade fever
- Depression, feelings of frustration or hopelessness
People with RA that affects their hips, knees, or ankles may begin to walk with a limp. Diminished function of the joints may cause a person to lose their grip strength and coordination. Over time, the hands and fingers or feet and toes may begin to become disfigured, as loss of soft tissue and bone changes their shape.
People with Rheumatoid arthritis are also more likely to experience Raynaud’s syndrome, a condition that constricts blood vessels in the fingers and/or toes when exposed to cold, causing numbness and a whitening of the skin as blood circulation slows.
In some cases, RA can also cause an enlarged spleen.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
At this time, treatments for rheumatoid arthritis are mainly directed towards relieving pain, reducing chronic inflammation, and slowing down the progression of this inflammatory disease.
A primary care physician will probably refer patients to a rheumatologist for rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and treatment. Rheumatologists specialize in joint diseases and all types of arthritis, so they treat joint pain related to conditions like osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, musculoskeletal pain related to fibromyalgia, tendonitis, and autoimmune diseases like lupus.
Typical medical options for RA include NSAIDs and corticosteroids, to quickly reduce pain inflammation. Anti-rheumatic drugs, known as DMARDS, have both anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. They work more slowly, but if started soon after diagnosis, they can help to prevent more damage to joint tissues, and relieve RA symptoms.
Unfortunately, all of these medications carry side effects. In the case of DMARDS, some patients experience gastric upset, headaches, and fatigue. They can also increase chances of infections, which is already a problem for people with RA.
Biologics are another type of injectable medication used to help relieve chronic inflammation by suppressing certain immune responses. These can also put people at higher risk for infections and certain cancers.
Acupuncture and TCM offer a way to reduce inflammation and pain without side effects.
Can Acupuncture Help Rheumatoid Arthritis?
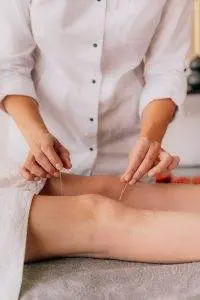
TCM has its own way of categorizing diseases. According to TCM theory, Rheumatoid arthritis falls under the category of “Bi” disorders. In TCM, environmental factors like cold, wind, heat, and dampness can invade the body and affect the organs, ultimately causing organ systems to malfunction. When they manifest in the body, pathogenic factors like cold and dampness can slow down or block the flow of blood and Qi (life force energy) through the body.
“Bi” conditions involve obstructions of Qi and blood that then lead to stiffness, swelling, soreness, redness, and heat in the joints. The famous TCM medical text known as “The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine,” which was written a few centuries B.C., recorded identification of Bi syndromes. Bi syndromes can certainly be in part related to outside environmental conditions, such as living in a cold, wet, windy place. They can also be related to a weakness of protective Qi that would translate into conventional terms as being a weakened immune system. Thus, Bi syndromes include rheumatoid arthritis, other types of arthritis, and other painful joint conditions like gout, lupus, and neuralgia.
A review of studies conducted on patients who received acupuncture treatment for Rheumatoid arthritis concluded that TCM is a good method for helping patients with this type of condition. TCM acknowledges that within one disease, different people may have very different symptoms, due to their genetics, or what we sometimes call “constitution.” One person will show hot symptoms like redness, swelling, and fever. Another person may find that their joint pain is particularly affected by cold, wet weather. An acupuncturist near me will look and listen to see what sort of pattern has developed, and will treat each individual accordingly with acupuncture points for joint pain.
Acupuncture Near Me for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Greater Los Angeles
TCM offers a framework in which we are able to see autoimmune disease as a collection of issues that can all be addressed in concert. With acupuncture and herbs, we can help relieve pain and inflammation, while also building back up of the systems of the body that have become weak. At Art of Wellness in West LA, we have many years of experience helping people manage autoimmune disorders and get relief from joint pain.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Celiac Disease With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Do you have digestive problems like a bloated stomach, diarrhea, and abdominal pain? Unintentional weight loss, fatigue, skin rashes? These can all be signs of Celiac disease. Different from food allergies, Celiac is a serious autoimmune disorder that can lead to malnutrition and other debilitating health problems. TCM herbs and acupuncture treatment offer a good alternative way of managing Celiac disease and gluten intolerance symptoms.
In recent years, you have probably heard a lot of people saying they are switching to a gluten free diet because they have a gluten allergy or gluten intolerance. Sometimes people may just be trying to see if they feel better when they cut out wheat products, or they are going on a low carb diet to help them lose weight. Other people may be experiencing symptoms like diarrhea and nausea and hope that going on an IBS diet will help.
What is gluten? Gluten is a protein that is present in some grains, including wheat, barley, and rye. When a person has Celiac disease, gluten is perceived by the immune system as a dangerous foreign substance, triggering an immune response. Antibodies (white blood cells) are produced as a reaction to gluten entering the body, and the antibodies end up causing inflammation and damage to the inside of the intestinal tract.
This damage to the small intestine is called villous atrophy, and this is what causes inflammation and malabsorption of nutrients, leading to the myriad symptoms of Celiac. Celiac symptoms vary widely, and can include both digestive problems, and other conditions, like anemia, that stem from the lack of proper nourishment to the body.

There is such a thing as a true wheat allergy, which for some people causes respiratory problems like difficulty breathing and nasal congestion, and other allergy symptoms like swelling and itching around the mouth and throat, hives or other itchy skin rashes, and headaches. Wheat allergies are a response to chemical compounds in wheat, which is found in a wide variety of food products. In some cases, exposure to wheat can cause anaphylaxis, which requires emergency medical attention because it can involve trouble breathing and swallowing, chest tightening, throat swelling, dizziness, and fainting.
Some doctors now recognize gluten intolerance or non-celiac gluten sensitivity as a separate condition from Celiac disease. For some people, gluten causes an immune response and symptoms, but not the same kind of damage to the intestines that Celiac does. If gluten intolerance is suspected, then following a gluten free diet for a period of time and noticing if symptoms clear up is usually the recommended course of action.
Celiac disease tends to run in families, and so is considered to be passed genetically. People can begin to show signs of Celiac at any age. It is estimated that at least 1% of the population has Celiac disease, but that number may be significantly higher, as it is still not a very well understood condition. Many people who have Celiac disease are unaware of it, or have been misdiagnosed with other conditions. Researchers believe that the incidence of Celiac disease is increasing worldwide, probably due to some environmental factors.
Acupuncture and TCM herbs provide a holistic way to treat Celiac disease, relieving the painful symptoms and providing detailed guidance for lifestyle and dietary changes that can help people manage Celiac and gluten intolerance. Nutrition is considered to be one of the primary branches of TCM, along with acupuncture and herbs. A TCM practitioner will be able to give you dietary recommendations far beyond just telling you to eat gluten free foods.
Top 10 Celiac Disease Symptoms
People can experience a variety of gluten intolerance symptoms, including digestive problems, allergy symptoms like skin rash, and other symptoms related to nutritional deficiency, like anemia and weight loss. Signs of gluten intolerance may be different in children, who are more susceptible to malnourishment that can lead to a failure to thrive.

Celiac symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea, pale colored stools, foul-smelling, fatty, greasy stool
- Abdominal bloating, bloated stomach, gas, stomach pain, abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting
- Constipation
- Headache, headaches, migraines, migraine headaches
- Skin rash, mouth ulcers, mouth sores, canker sores
- Neuropathy, numbness or tingling in hands and feet, problems with balance, joint pain
- Cognitive problems, foggy head, difficulty concentrating
Celiac can lead to SIBO, anemia, iron deficiency, loss of bone density (osteoporosis), weak bones, soft bones, bone loss (osteopenia), joint pain, or arthritis. People can also have liver problems, including fatty liver.
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a specific type of skin rash that causes itching and blisters to appear, primarily on the knees, elbows, torso, top of the head, and buttocks.
Women may find that celiac disease affects their hormones, menstrual periods, and can have an impact on fertility, even causing recurrent miscarriages.
Celiac disease can also contribute to infertility and low sperm count in men.
When a child develops celiac disease, the inability to absorb nutrients from food can cause problems with normal growth, such as short stature, delayed puberty, and damage to tooth enamel. Developmental disorders and behavioral issues can also be related to celiac, like ADD/ADHD and irritability.
In extreme cases, Celiac can cause seizures.
Celiac Disease Diagnosis and Treatment

Going through the process of being diagnosed with Celiac disease or gluten intolerance is quite complicated and involves multiple tests. From the medical standpoint, it is best that you do not eliminate gluten or change your diet before the testing, so that it can accurately show how gluten is affecting your immune system and your intestines.
First, you will probably have a blood test that looks for certain antibodies that would indicate an autoimmune reaction to gluten. Some people may test negative for antibodies, and yet still have Celiac, though, so this blood testing is not enough to be conclusive. Genetic testing may be done, which looks for specific antigens to rule out Celiac. If testing shows that a person has antibodies, and they also have a specific type of skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis), that is usually enough for a doctor to give an official diagnosis of Celiac disease.
Endoscopy is an imaging test which uses a little camera to see if there is damage to the intestinal lining. They will also take some tissue samples from the lining of the intestine to check for inflammation and damage. The results of these tests may lead to a formal Celiac diagnosis. People will often need to have an endoscopy to find out if they have Celiac disease, and then possibly repeated endoscopies to see if the inflammation is getting better or worse.
Sometimes people will try figuring out what is going on themselves with a food sensitivity test or food intolerance test kit that you can do at home and send in for results. Food allergy testing may give you some information as to whether you have a reaction to a specific allergen (egg allergy, milk allergy, peanut allergy, shellfish allergy) or have a food sensitivity, but they cannot tell you if you really have Celiac disease or gut inflammation.
Going through the diagnostic process for autoimmune diseases like Celiac disease can be exhausting in and of itself. Meanwhile, you aren’t yet getting treatment for your symptoms. The only treatment available in conventional medicine for Celiac disease really is to follow a gluten free diet. Most doctors are not able to do much beyond give you a list of foods you shouldn’t eat, or refer you to a dietitian.
TCM has the ability to provide more comprehensive care for people with Celiac disease, and many other autoimmune conditions. Acupuncturists are highly trained professionals when it comes to offering patients detailed guidance for following an effective Celiac disease diet.
Can Acupuncture Help Celiac Disease and Gluten Intolerance?

TCM has more to offer than just acupuncture treatment and herbal medicine. Nutrition is one of core competencies every TCM practitioner must master.
Acupuncture treatment can help relieve digestive symptoms like abdominal pain and bloating, and also have a positive impact on the system malfunctioning that leads to autoimmune reactions. With Chinese herbs, we are able to get very potent nutrients into the body that wouldn’t normally come from food. For people with Celiac, or other problems like food allergies or sensitivities, malnutrition due to malabsorption is a real problem.
A TCM nutrition approach can help restore the body’s health with foods and herbs better than a simple elimination diet for Celiac disease can. An acupuncturist listens carefully to the particular symptoms and sensations you describe. These provide important clues as to which organ systems are involved, and where yin and yang are out of balance. Then TCM provides a framework for tailoring the treatment and food plan for Celiac disease to each individual’s needs.
According to TCM theory, the stomach and spleen are responsible for digesting food. Celiac disease symptoms are, according to a typical TCM diagnosis, related to a spleen deficiency. When Qi in the spleen is weak, the body is not getting the nutrients it needs. Building up the strength of the spleen will often be the focus of the acupuncture portion of the treatment. Herbs and specific nourishing foods will be recommended, which will help anemia and soothe the digestive tract.
Acupuncture Near Me For Celiac Disease, West Los Angeles
Autoimmune diseases like Celiac disease can be especially frustrating because they seem to take over your whole life. Not only physical health, but mental health is compromised. Treatment options are limited. Fortunately, TCM offers a complementary form of medicine that is able to provide multi-faceted care for autoimmune disorders like Celiac, including: Crohn’s disease, Type 1 diabetes, hyperthyroidism, Lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, and multiple sclerosis (MS). Acupuncture treatment can help reduce feelings of anxiety and depression as you learn to manage your illness.
If you or someone you know has been suffering from digestive issues, and you suspect it may have something to do with gluten intolerance or Celiac disease, be prepared to go through testing, but also give some thought to adding a TCM provider to your health care team. At Art of Wellness, we have over 35 years of providing excellent care through TCM treatments, including expert nutrition services. It is like getting an acupuncturist and dietitian in one.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Addiction With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac, Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Are you, or is someone you love, struggling with alcohol addiction or some other substance abuse problem? Alcoholism, drug addiction, and other issues like porn addiction problems or food addiction can be helped with TCM treatment. Acupuncture for addiction can help people overcome the physical symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, and help them deal with the mental and emotional aspects of substance abuse recovery.
Drug use, drinking, and smoking are behaviors that are widely practiced and deeply ingrained in our modern society. If we consider tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption in addition to “harder” drugs, then over 60% of the population uses some type of addictive substance on a regular basis.
Substance use disorders (SUDs) are a major health concern worldwide. It is estimated that over 20 million Americans are currently suffering from some type of addiction to drugs or alcohol. While addiction can happen to people of all ages, young people are especially at risk for substance abuse. When teens and young adults start binge drinking or abusing drugs, it can have a serious effect on their brain development and increase their chances of developing a substance abuse problem.
More recently, the surge of opioid use has dramatically increased the number of people who are dangerously dependent on prescription painkillers or deliberately misusing opioid medications like fentanyl or Oxycontin. People can become addicted to opioid medications in a short period of time. Accidental overdose is one of the leading causes of death in the U.S., which has contributed to the recent decline in average life expectancy.
Even moderate drinking and use of recreational drugs can affect a person’s overall health, sleep habits, and fertility. There are many benefits to reducing your alcohol consumption, or choosing to go through an alcohol detox or a designated period of sobriety, like “Sober October” or “Dry January.” A TCM herbal detox with acupuncture treatment can help improve your vitality and get rid of nagging health issues.
If you know you have a serious problem with addictive behaviors, though, you will probably need some sort of treatment and support system to help you get sober and recover physically and mentally from substance use disorder.
What Causes Addiction?

When we talk about addiction, we are usually referring to the relationship of the body and mind to psychoactive substances such as: alcohol, nicotine, marijuana, heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine, hallucinogens, etc. The chemical composition of these substances causes them to have a profound effect on the brain chemistry of human beings.
Unfortunately, many drugs that are prescribed by doctors to help relieve pain and other symptoms of illness are habit-forming, too. When people try to stop taking the medication they’ve been using to help with post-surgical pain, for example, or to help them sleep, or to relieve situational depression and anxiety, they find they can’t just “quit.”
Even “milder” substances like caffeine and sugar, which many people consider to be a regular part of their daily diet, can be abused to the point that they become detrimental to your health. And, of course, we all know how hard it is for people to quit smoking. Nicotine is one of the most addictive substances out there.
Most of these drugs affect the way the brain produces dopamine and other neurochemicals. When you stop drinking or using the drug, the brain is not ready to go back to its old ways of creating and releasing dopamine. There is a period of adjustment, during which symptoms of withdrawal can make a person very uncomfortable, or even violently sick.
Certain behaviors, like scrolling through social media websites on your phone, or looking at pornography, or even engaging in sexual activity, can also be addictive because of the way they impact dopamine production and other brain activity.
There has been a lot of shame and stigma attached to alcoholism and addiction. Sometimes, people live in denial of the fact that they are too heavily reliant on drinking or using drugs to help them cope with stress. Alcohol abuse or drug abuse are still considered by some people to be personal problems, having to do with a lack of willpower or gratitude.
We now understand that addiction is a disease, and that it can be difficult and actually dangerous for people to try to stop using some drugs without some form of treatment. Doctors and mental health professionals are trained to help people safely recover from substance abuse, and treatments exist to provide relief from drug withdrawal symptoms. In addition to the 12 step program Alcoholics Anonymous, which provides emotional support through group interactions, many other clinics and rehab centers provide care for those trying to stop using drugs and alcohol.

Still, most people find that recovering from addiction is extremely difficult, probably the hardest thing they have ever tried to do. Many people, no matter what kind of treatment they receive, or how many times they go through a 12 step program, still relapse. First a person needs to decide that they are ready to commit to recovery. Then, finding the right support is crucial to success.
TCM methods of acupuncture and herbs offer an alternative or adjunctive treatment for addiction. Acupuncture treatment has been shown to help patients suffering from alcoholism and depression, reducing cravings and symptoms of withdrawal and improving mental health.
Acupuncture can help people overcome substance abuse, addressing both the physical effects of drug use with an effective alcohol detox or drug detox, and the emotional problems most people face when they begin recovery treatment.
Top 10 Symptoms of Withdrawal from Alcohol Dependence and Drug Abuse
Withdrawal is the body’s reaction when a person stops using drugs or alcohol after having been ingesting them regularly for a significant period of time. When the body and brain have become addicted to a substance, the physical and emotional need for that substance can cause a severe reaction when a person stops abruptly, making it very difficult for a person to resist using again. Withdrawal symptoms can vary, depending on what type of substance you’ve been using, and how long you’ve been using it.
Symptoms of withdrawal include:
- Tremor, hands shaking, body shaking, seizures
- Anxiety, depression, agitation, feeling jumpy, irritability, delirium, hallucinations
- Watery eyes, tearing, runny nose
- Hot flashes, chills, hot flushes, hot and cold, sweating, clammy skin
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Muscle cramps, muscle aches, muscle pain, muscle tension
- Dehydration
- High blood pressure, fast heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, palpitations
- Anxiety, depression, overwhelming negative emotions
- Insomnia, trouble sleeping, restlessness
Other signs of withdrawal can include: trouble concentrating, memory loss, foggy headedness, pupils dilated, loss of appetite.
Some medical detox programs are designed to help people gradually taper their use of drugs like amphetamines or sleep medications so as to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Treatment centers, such as a methadone clinic, may use certain approved medications to help relieve cravings when people are coming off of heroin or prescription pain medications.
Acupuncture, a TCM detox program, and other TCM treatments can serve as an alternative or adjunct treatment to help alleviate withdrawal and help people survive through the toughest parts of recovery.
Top 5 Ways Acupuncture Can Help Addiction

The relationship between Chinese medicine and alcohol goes back many centuries. As early as 1600 B.C., we have records of alcohol being used in medicinal preparations and for its anesthetic properties. Problems with overuse of alcohol, however, are also a longstanding part of Chinese culture, so TCM has developed treatments to help people reduce their consumption of alcohol.
According to TCM philosophy, too much alcohol creates excessive heat in the body, and disturbs the balance of Yin and Yang. In conventional medicine, the focus tends to be on how alcohol abuse impacts the liver. In TCM, we see that binge drinking also taxes the stomach and spleen, and encourages dampness to take hold. Thus, acupuncture treatment for alcohol addiction will often focus on clearing heat and dampness from the organ systems, while strengthening the stomach and spleen.
TCM takes a holistic approach to treating Substance use disorders, meaning we focus not only on the physical symptoms of withdrawal, but also on the emotional, mental, and spiritual problems associated with addiction.
Most people become dependent on drugs or alcohol because they are already experiencing some form of emotional struggle or mental health issue. When the substance is taken away, those feelings come up to the surface again, demanding attention. For many people, the anxiety and depression they face when they quit drinking or using drugs is overwhelming.
Some people may avoid 12 step programs, an AA meeting, alcohol rehab, drug addiction centers for substance use disorders, or even one-on-one talk therapy because they are not ready to talk about the trauma that triggered their anxiety or depression. Acupuncture treatment can be very helpful for anxiety and depression, without having to delve into these conversations.
TCM treatment for addiction works on multiple levels:
- Detox – TCM has a history going back for many centuries of actively seeking to remove toxic substances from the body to improve both physical and mental health. The practice of using Chinese herbs used in combination has been developed to be highly effective as a detox from all kinds of drugs. A TCM detox treatment program uses acupuncture treatment as well as herbs taken internally (as a tea or capsule) and used externally (detox patches) to draw toxins from the body, providing a deep cleansing for the liver and other organ systems.
- Reduces cravings – whether the problem is nicotine, alcohol, opiates, food, or some behavior like engaging with porn, the use of auricular acupuncture and applying pressure to acupressure points on the head and ears for cravings can be very effective.
- Withdrawal Symptoms – Acupuncture has been shown to help people with symptoms of opioid withdrawal, heroin withdrawal, and prevent relapses.
- Mental Health – people who were treated with acupuncture for addiction reported that it helped them feel more confidence in their ability to quit. Acupuncture helps relieve anxiety and the negative effects of stress.
- Sleep aid – many people start using drugs in the first place because they have trouble sleeping. When people quit drinking and using drugs, they can suffer from insomnia and restlessness. Acupuncture is an excellent modality for helping people to relax and experience deeper, higher quality sleep.
Acupuncture has been shown to have an effect on neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are involved in the brain processes that make certain substances so addictive.
Several types of Chinese medicines based on herbal formulation have been tested and approved for treatment of opiate addiction in China.
Studies have shown that electro-acupuncture, and auricular acupuncture can reduce cravings, and alleviate anxiety related to drinking cessation.
Acupuncture for Addiction Treatment Near Me in Los Angeles Area
Addiction can be devastating for individuals and their loved ones, but substance abuse and other kinds of addictions can be overcome with time, dedication, and the right treatment plan. At Art of Wellness, we are ready to become part of your support team, providing consistently excellent health care through acupuncture and herbs, as well as being there for you when you need emotional support. We want our patients to think of our clinic as a second home, where they can find peace and strength to help them overcome their substance use disorder.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Essential Tremor With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac, Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Shaking hands, body shaking for no reason, head shaking, feel wobbly when you’re walking, maybe your voice quivers when you speak? These could be signs of Essential Tremor (ET). Essential tremor is a neurological condition, often mistaken for Parkinson’s disease, which causes rhythmic shaking of parts of the body, especially the hands. Acupuncture and TCM are an effective way to treat symptoms of essential tremor.
Essential Tremor (ET), also called “kinetic tremor” or “benign essential tremor,” is a chronic nervous system disorder that causes hand tremors, trembling hands, head shaking, body tremors in the arms or legs, and can also affect the voice. The hand shaking most often happens when you try to perform some simple, yet specific task that requires coordinated movements or using tools, such as shaving, writing, or pouring liquid into a glass.
Essential tremor is the most common type of movement disorder, affecting about 4% of older adults, although it can happen at any age. The causes and progression of ET are not fully understood by medical science.
Tremors are categorized into two main types of tremors: resting or active. A resting tremor is when the body shakes even at rest. Active tremors are when there is shaking when a person is attempting to make voluntary movements. Essential tremor is a type of active tremor.
“Postural tremor” refers to an active tremor that occurs when a person is trying to maintain a position, like standing with the arms outstretched, and cannot do it without shaking. An “internal tremor” is a person’s feeling that a quivering or shaking sensation is taking place inside their body, that cannot be seen by others.
Essential tremor is often misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s disease, but, in fact, essential tremor is much more common than Parkinson’s (20 times more common). Like Parkinson’s, essential tremor causes hand shaking, but ET is different in that symptoms usually occur when you’re actively trying to do something, whereas Parkinson’s tremor occurs even when your limbs are at rest. Parkinson’s also typically involves non-motor symptoms as well as motor symptoms.
Other conditions can also cause hand tremors. Vascular parkinsonism, a neurological disorder that is the result of small strokes, causes blockage of blood flow in the brain. Both Parkinson’s and vascular parkinsonism can cause a distinct type of tremor that involves the thumb and fingers brushing together slowly, sometimes called a “pill-rolling tremor.” Asterixis is another kind of motor control disorder that causes muscles to jerk, resulting in a characteristic hand-flapping gesture, sometimes referred to as “liver flap.”
There are many other conditions that can also cause tremors, including: hyperthyroidism, multiple sclerosis (MS), stroke, liver or kidney disease, and alcohol addiction. Anxiety or panic attacks can also cause a temporary tremor or shakiness.
Essential tremor seems to run in families sometimes, but many people begin to experience tremors for no apparent reason. It is theorized that ET may be caused by something genetic, or it may be caused by neurodegeneration–the gradual degradation and death of cells in the brain.
Acupuncture, combined with other TCM modalities such as moxibustion and herbs, is a good method for reducing hand tremors and other symptoms of essential tremor, as it has been demonstrated to have positive effects on the generation of cells in the brain and nervous system, as well as reducing stress and anxiety.
Top 5 Essential Tremor Symptoms

Very mild symptoms of essential tremor, such as having trouble threading a needle, often begin to show up when a person is in their 40s. Then, as time goes on, the symptoms of ET become more obvious:
- Tremor, especially in hands, that is most noticeable when you’re trying to do something
- Head nodding that you can’t control
- Shaking on one side of the body more than the other
- Voice quivers or voice is shaky when you speak
- Tremor gets worse over the years
Some medications (amphetamines, corticosteroids, or asthma medications) or stimulants like caffeine may make the tremors more noticeable. Some people find that the tremor lessens when they drink a moderate amount of wine or other alcohol. Stress, strong emotions, too much exertion, low blood sugar, or being dehydrated can make the tremor more pronounced.
Essential Tremor Treatment
There is no specific test that shows whether a person has essential tremor. Diagnosis is based on observation of symptoms, and the use of testing to rule out other disorders, such as thyroid disease or Parkinson’s.
Medications are used to treat tremors with varying levels of success. Propranolol and Atenolol are beta-blockers that can be helpful for some people with ET. Primidone or Topamax are anti-seizure (anti-epileptic) drugs that can also be prescribed to help relieve shaking. In many cases, these medications are not very helpful for relieving the tremors. Doctors may try anti-anxiety medications like Valium, Ativan, or Klonopin. Botox injections have also been tried as a medical treatment for essential tremor.
In some cases surgery to remove parts of the thalamus has helped stop severe tremors, but there is a high risk with this type of brain surgery. Nowadays, when drugs do not seem to provide relief from tremors, people may be referred for a thalamic deep brain stimulation therapy, in which electrodes send an electrical impulse to the brain to interrupt the faulty signals leading to involuntary shaking.
Acupuncture treatment is another way to stimulate brain activity, having a positive effect on neurotransmitters in the brain and reestablishing connections throughout the nervous system.
Can Acupuncture Help Essential Tremor?

According to TCM theory, the symptom of hand tremors generally originates from the liver and kidney systems. Liver blood deficiency and kidney deficiency are closely related, and can lead to rising Liver Yang, and Liver Wind. It is the pathogenic factor of wind that causes the hand shaking. We use acupuncture treatment and herbs to nourish the liver and kidney so that wind is subdued and yin and yang energies are balanced.
One study compared groups of people with ET who were treated with medication (Propranolol) versus patients treated with both acupuncture and medication. The results showed better results for the patients who received the combined therapies.
A hospital study in China showed that a combination of acupuncture treatment and herbal formulation had an over 80% efficacy rate for patients with benign essential tremor.
A recorded case study of a woman treated with acupuncture for tremor showed that she was better able to write and hold objects, and that the improvements were maintained even a year after she had completed acupuncture treatment.
Best Exercise for Hand Tremors
Regular exercise is important for everyone, especially as we age, in order to keep our physical and mental faculties strong and agile. Exercises that can be beneficial for people with essential tremor include:
- Regular cardiovascular exercise and light strength training
- Tai Qi
- Yoga
- Meditation
- Puzzles, math games, brain teasers, word searches, etc.
Acupuncture Near Me for Essential Tremor in West Los Angeles, Brentwood area
If you’ve started to notice your hands shaking, voice trembling, or that you’re feeling unsteady on your feet, don’t wait until the situation gets worse. Acupuncture treatment can help reduce the frequency and severity of hand tremors, and prevent essential tremor from progressing. The TCM doctors at Art of Wellness have over 35 years of experience treating all kinds of neurological disorders and helping people maintain their quality of life as they get older.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.