-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Migraines
The Ultimate Guide to the Acupuncture Point on Head for Headaches
by Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.
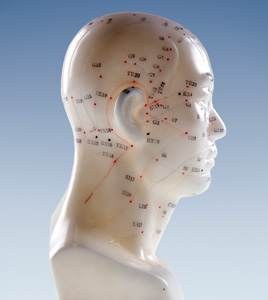
Why does the TCM doctor always put an acupuncture needle in top of head? If you’ve had acupuncture before, it’s likely that your acupuncturist used some acupuncture points on head during your treatments. Using pressure points on the head is something TCM doctors do often, because there are so many useful acupressure points on the head, especially acupuncture points top of head. There are head pressure points for headaches, points to relieve migraines, acupressure head points to help anxiety, fatigue, allergies, and many other conditions.
Even if you’re coming in for acupuncture to help some other condition, whether it’s chronic pain, an autoimmune disease, heart problems, or kidney problems, probably at some point your acupuncture practitioner is going to use acupoints on head to help you relax during your treatment. Every single person who comes into our office for acupuncture is suffering from some form of stress, and using certain points on the top of the head can help with stress relief right away.
Other common reasons to use pressure points in neck and head include:
- to fight fatigue
- headache and migraine
- allergies, asthma, hives, rhinitis, sinus problems, common cold
- anxiety
- nervous disorders
- thyroid disorders
- hormone imbalances
- more mental focus, improved memory and cognition
- tinnitus, ringing in the ears
- vertigo, Meniere’s disease
- toothache, dental pain, dental anxiety
Why are pressure points on the head so powerful? To answer this question, let us explain a bit about the meridian system in TCM.
TCM Meridian Head Points
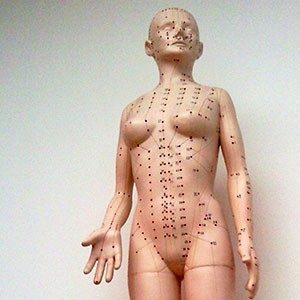
TCM is based on interdependent systems of organs and energy channels that run through the body. The channels are known as meridians, and along them flows Qi, the life energy that animates the body and all of its functions. There are 12 major meridians and 8 major vessels; the meridians are close to the surface of the skin, and the vessels, which essentially connect all the meridians, are deeper inside the body. While the way in which we think of the meridian pathways is more metaphorical than physical in nature, they can be considered roughly analogous to the circulatory system of blood vessels or the network of nerves of the nervous system as we think of them in conventional Western medicine.
Along the meridians lie acupoints, specific points that we stimulate with acupuncture needles during acupuncture treatment or with the fingers and thumbs during acupressure massage. The interconnectedness of the organs, meridians, and individual points is the foundation of acupuncture theory.
We use specific points on a meridian in order to address issues in a particular organ or organ system that corresponds (energetically) with that meridian. There are several pressure points for head and neck pain, points to help relieve allergies, pressure points for frontal headache, and more.
Several of the major meridians originate or end in the head:
- Gall Bladder (GB) meridian – points of the gall bladder meridian wrap around the side of the head, the forehead above the eyebrow, the temple, around the ear, and down the back side of the neck–just as the pain of a migraine often does. Then it continues down from the intersection of the neck and shoulder, zig-zagging across the torso, and finally running down the leg and ending in the fourth toe. This meridian is used to treat severe headaches, stress, tension that affects the shoulder and neck, and bile-related problems.
- Large Intestine (LI) meridian – begins at the points of the index finger, travels up the arm, through the shoulder and neck, then comes up to the lower corner of the nose. This meridian is involved in “letting go,” both from the eliminatory organs of the lower body, and exhalations from the nose.
- Stomach (ST) meridian – the ST meridian starts near the eye, swoops up to the side of the top of the head, comes down next to the mouth, and continues down through the neck, chest, center of the body, down the leg, ending at the point of the second toe. This meridian is used to treat Shen (spirit) disorders, like insomnia, anxiety, palpitations, memory problems, and blood deficiency.
- Small intestine (SI) meridian – originates in the little finger, runs up the arm into the shoulder and then branches out, some of it going into the major organs of the heart, stomach, and small intestine; then other branches go up into the face, by the cheekbone and right in front of the center of the ear. The SI is used to treat fevers and mental health conditions, among other things.
- Bladder (UB) Meridian – begins at the inner canthus of the eyes, goes up and over the top of the head, about an inch away from the midline on either side, and then all the way down the back and leg, ending in the little toe. Used to help with invasion disorders (wind, cold, heat etc.) that affect the eyes, sinus headaches, allergies, stuffy head, neck pain and stiffness.
- Triple burner meridian, also known as San Jiao (SJ) – begins at the tip of the ring finger, then goes up the arm, through the shoulder and chest, up the side of the neck and comes up around the ear, and into the temple and outer brow bone. The San Jiao head points are used to work on dizziness, headaches, eye twitching, and dental pain.
- Conception vessel – also known as the Functional Channel, or the Front Channel, or Ren Mai, this vessel originates at the navel, then drops down to the perineal area, and runs back up the center of the front of the body, ending in a point on the chin, in the dip just under the lower lip. This vessel controls the Yin energy of the body and is essential to the health of the reproductive organs and fertility.
- Governing vessel, also known as the Extraordinary vessel, the “Sea of Yang” or Du Mai – originates in the lower back near the kidneys, runs up the spine and around and over the top of the head, ending in the middle of the face. This vessel controls the Yang energy of the body, and in particular the kidneys, the back and spine.
Top 10 Acupuncture Points on Head
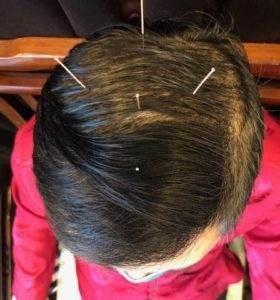
Of course, your acupuncturist will not only use acupoints on your head during a treatment session. We choose a variety of points that will work together to alleviate symptoms and help optimize the functioning of the organs. These specific head points may be used as part of a treatment to work on a specific symptom or condition:
- Yin Tang, or the “Hall of Impression” – this is what is called an “extraordinary point,” meaning it doesn’t really belong to a meridian; it stands on its own. Right in the third eye, it is used to reduce anxiety, vertigo (dizziness), help promote better sleep, clear wind and congestion, and relieve sinus pain and headache.
- DU21 – Shen Ting, “Spirit Court” – Right in the front middle of the top of the head, about an inch above the hairline. This is one of the pressure points for frontal headache, also good for sinusitis, nosebleeds, anxiety, panic attacks, and sleep problems.
- DU 20 – Baihui, or “The meeting of the 100s” – right in the very center of the top of the head, master of endocrine and nervous system, used for anxiety, fatigue, mental focus, relaxation, hypothyroid, adrenal problems, hormone imbalance, headaches.
- Si Shen Chong – “Four Alert Spirit” – this is actually a set of four “extraordinary points,” which surround DU20. Very helpful for sleep disorders, memory disorders, dizziness, and headaches.
- GB20 – Feng Chi, “Wind Pool,” low back of the head, where the skull meets the neck muscles, helps headaches, migraine, blurred vision, fatigue, neck pain and stiffness. We may use this point when a patient has a cold; this is a point where cold wind can get into the body, and why it is important to wear a scarf to protect your neck when it’s cold and windy out.
- Taiyang “Great Sun” – Right in the depression of the temple, this point can help dizziness, one-sided headaches, migraines, sensitivity to light, and jaw pain, TMJ.
- GV26 Shui Gou – in the mustache area, between the nose and mouth, right in the center of the crease, this point helps to calm the mind and restore mental focus. Also used as first aid when a person faints or is in shock. Helps stop hiccups. Helps with serious neurological disorders like epilepsy, seizures. Also good for low back strain.
- LI20 Ying Xiang “Welcome Fragrance” – located in the lower corner of the nose, right in the nasolabial groove, used to alleviate congestion, allergy itching in the nose, and to clear the nasal passages.
- ST8 – Touwei, about 5 finger widths above the eyebrow, dispels dampness, used for “splitting headaches,” frontal headache, migraines, headache with nausea and/or vomiting, vision problems, tearing eyes, eye twitching, dizziness/vertigo, hair loss. Helps with mental health, when a person is “overthinking” things, or having repetitive thoughts.
- BL2 – Zhanzhu – located at the inner corner of the eyebrow, good for itchy, watery eyes due to allergies, other eyes problems like glaucoma, night blindness, and sinus headache.
Facial Acupuncture Points

As we have mentioned, some pressure points on the face are used to help relieve sinus congestion, nasal congestion, and other issues related to common colds and flus or allergies. Points on the face may also be used to help the facial paralysis of Bell’s Palsy, or TMJ jaw pain.
Naturally, we also use acupuncture points on the face as acupuncture points for the face, that is, when we are striving for facial rejuvenation. This technique is sometimes called an acupuncture facial. Using points on the face can help to stimulate collagen production, help to tighten the skin, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and strengthen the facial muscles. People of all ages and genders can benefit from acupuncture skin care. Cosmetic acupuncture can treat signs of aging skin like sagging, puffiness under the eyes, and dryness.
Self-Care With Acupressure Head Points
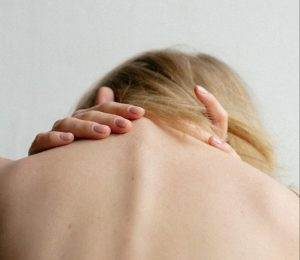
What is acupressure? Acupressure is a form of massage that goes back thousands of years in Chinese Medicine. Stimulating the same points we needle in acupuncture treatment with your fingers and thumbs can be beneficial for different types of headaches and neck stiffness, to calm anxiety, and bring more mental clarity.
Choose a time when your environment is quiet and free of distractions, the same as you would for a meditation practice or home workout. Be sure to breathe deeply and smoothly as you perform self-acupressure. Press firmly, applying deep pressure to a point in a small, gentle circular motion. Giving yourself an acupressure treatment only takes a few minutes, and it is a great way to take care of yourself between acupuncture sessions.
Acupuncture Near Me for Headaches and More
Every time you come in for acupuncture treatment, your TCM doctor is looking for ways to treat your overall condition, but also focusing on how you are feeling right now, today. Often, people are feeling tired and stressed, beyond and in addition to the health condition that caused them to seek out alternative medicine in the first place. Using points on the head that help fatigue, calm a racing mind, and reduce the physical effects of stress is one way that your acupuncturist is practicing preventative care, while at the same time, making sure you leave your treatment feeling rested and reenergized. The next time you come in for a visit, be sure to let us know how you’re feeling, and feel free to ask us, “What is that point on my head for?”
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Musculoskeletal Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Do you experience unexplained pain all over the body? Muscle pain and tenderness, along with feeling tired all the time and having mood issues? Widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue or feeling exhausted may be a sign you have fibromyalgia. Alternative medicine methods like Acupuncture and TCM offer a way to help ease the chronic pain, sleep problems, and emotional disturbances caused by fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia (sometimes referred to as “fibro” or FM) is one of the most common chronic pain conditions worldwide, affecting an estimated 10 million people in the United States alone. Still, this chronic condition is still not well understood by medical science. There are no definitive tests to show whether or not fibromyalgia is the cause of pain all over the body along with chronic fatigue, so many people go on having musculoskeletal problems and hurting all over without being diagnosed or treated. There are many people who have fibromyalgia who also suffer from depression and anxiety related to the illness. Fibromyalgia can dramatically impact a person’s quality of life. While people of ages and genders can have fibromyalgia, it is much more prevalent among women.
Fibromyalgia is considered to be a syndrome: a collection of symptoms that often occur together. Fibromyalgia is associated with other conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), myofascial pain syndrome, and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). It may coexist with these other chronic conditions, or sometimes be mistaken for one of them. However, fibromyalgia is now understood by medical professionals to be its own distinct condition with specific manifestations.
People who have RA have been shown to have an increased risk for also having fibromyalgia. But the quality and location of the musculoskeletal pain differentiates the two conditions. The pain of fibromyalgia shows up in the musculoskeletal system in the areas where there are large muscles, causing pain that may move around throughout the torso, back, hips, thighs and arms. Fibromyalgia pain is often described as a kind of “tenderness,” or when the body aches all over. “Tender points” all over the body are specific to fibromyalgia. This is different from arthritis, which generally causes swelling and pain in the joints. Both RA and lupus are understood to be caused by inflammation, while fibromyalgia is believed to be caused by a problem with the central nervous system (CNS), in which pain signals are amplified, causing extreme sensitivity and pain, even when there is no seeming reason for that area of the body to feel pain.
Some of the fibromyalgia symptoms are very similar to those of myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME), which is also known as chronic fatigue (CFS). As with RA and lupus, the two conditions can overlap. The difference is that the overwhelming symptoms of ME/CFS are related to fatigue or post-exertional malaise (PEM), while the predominant symptom of fibromyalgia is widespread muscle pain and tenderness.
Fibromyalgia seems to show up in some people due to a traumatic or triggering event. There can then be a fibromyalgia flare up due to the presence of other triggers later.
Fortunately, acupuncture, herbs, and other forms of alternative medicine that fall under TCM can approach all of the different symptoms of fibromyalgia holistically. Acupuncture is widely accepted to be effective for helping musculoskeletal conditions of all kinds, as well as neurological problems, rheumatological conditions, sleep issues, and emotional and mental health disorders.
Top 10 Symptoms of Musculoskeletal Pain

As a syndrome, fibromyalgia may manifest as any combination of a few or several of a variety of symptoms. The most common symptoms of fibromyalgia include:
- Widespread musculoskeletal pain: pain, tenderness, and/or stiffness in the muscles all over the body that may come and go or migrate from one area to another
- Fatigue, exhaustion, extreme tiredness
- Emotional and/or mental issues: depression, anxiety, PTSD
- Sleep problems, insomnia
- Cognitive issues: difficulty concentrating, memory problems, “fibro fog”
- Headaches, migraines
- Neuropathy: tingling or numbness in the hands and/or feet
- TMJ, jaw pain
- Digestive problems: irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), abdominal pain, bloating
- Bladder pain, interstitial cystitis
Other more subtle signs of fibromyalgia can include: itching all over, a skin crawling sensation (like bugs crawling on skin), extra sensitivity to smells or temperature, a tendency to shiver, or dry eyes or eye pain.
Top 5 Causes Musculoskeletal Pain Flares
The symptoms of fibromyalgia tend to come and go. Some days a person might feel almost totally fine, then other days, the fibromyalgia flares, causing more pain, exhaustion, and sometimes other symptoms. What triggers a fibromyalgia flare up?
- Hormonal changes during menstrual cycle, miscarriage, pregnancy, or postpartum
- Prolonged stress
- A sudden traumatic event, PTSD trigger, panic attack
- Changes in weather: temperature, humidity, barometric pressure
- Lack of sleep
When one of the 18 tender points of fibromyalgia is touched, it can trigger more widespread pain. These points include areas like: the front and sides of the neck, the base of the skull, the elbow, and the backs of the knees.
What Is the Treatment for Fibromyalgia?
Medical treatment for fibromyalgia typically involves a combination of medicine to alleviate pain with psychological support and lifestyle management. Drugs like Lyrica, Cymbalta, and Savella are approved for prescription for patients with fibromyalgia. Lyrica and Cymbalta are also used to treat conditions that involve nerve damage or nerve pain, like diabetes, neuropathy, shingles, while Savella works in a way that is similar to antidepressants. Other pain relievers and/or antidepressant medications may also be prescribed to help people manage pain of fibromyalgia, help them sleep better, and boost mood. All of these medications can come with unwanted side effects, and they do not help to relieve pain in every case.
People with FM pain will often receive counseling on how to manage their condition by being very careful not to exert themselves or become exhausted. Getting quality sleep and reducing stress can help to prevent fibro flare up. It can be hard for people to follow guidelines that ask them to make major lifestyle changes. Fortunately, acupuncture, herbs, and the patient support of a TCM practitioner can offer more help for people with fibromyalgia.
Acupuncture for Musculoskeletal Pain
Can acupuncture help fibromyalgia? Yes. TCM offers a comprehensive system for managing musculoskeletal pain and chronic pain, helping to heal nerve damage and restore central nervous system function, supporting mental health, relieving anxiety and depression, and addressing sleep problems. Whereas with conventional medicine, a patient might go from one doctor to another to handle all of these issues, the acupuncturist can address them all at once. The TCM point of view always takes into consideration the connection between what is going on physically with what is going on emotionally in each individual, so it is really an excellent way to help patients with fibromyalgia.

Like Western medicine, TCM recognizes that sometimes fibromyalgia can be originally caused by a traumatic event or an extremely stressful time in one’s life. Emotional upheavals cause stress to the liver, which in turn causes stagnation of blood and Qi. TCM also sees coldness and dampness as pathogenic forces that can have a profound effect on overall health. According to TCM, widespread musculoskeletal pain falls under the category of Bi Syndrome. In Bi Syndromes, cold and damp get into the body and take hold on a deep level, causing pain and stiffness. With acupuncture treatment for fibromyalgia, we seek to clear cold and damp, and restore good flow of Qi and blood throughout the body.
Acupuncture has an analgesic effect, relieving muscle pain without side effects. Moxibustion may be utilized to bring warmth to areas of the body. Cupping is another modality used to draw out damp cold and improve blood flow. Tai Qi and Qi Gong, gentle therapeutic movement practices that have been developed over 1000s of years as part of TCM, also may offer great benefits for people with FM.
A systematic review of over 400 studies of fibromyalgia treatment with TCM, acupuncture treatment was found to be effective for reducing both short term pain and long term pain.
Another review found that acupuncture and herbs worked better to reduce pain than standard medication therapy.
Top 5 Tips for Managing Fibromyalgia

Dealing with fibromyalgia and seeing significant improvement in fibro pain will probably involve making some lasting lifestyle changes. Making adjustments to your sleep habits, food choices, and your exercise routine can make a difference in preventing the next FM flare up.
- Choose a gentle, enjoyable form of exercise. Start slowly, and gradually increase the amount you can exercise over time. Walking outdoors is a great option, as are Tai Qi and Qi Gong.
- Limit or eliminate caffeine and alcohol. These substances can interfere with getting good sleep and exacerbate liver problems. Alcohol is not safe to consume if you are taking medications for fibromyalgia like Lyrica, Cymbalta, and Savella.
- Avoid sugar, which may give you a short-lived good feeling, but will lead to a “sugar crash,” and feeling more exhausted than before. Any kind of simple carbohydrates, like foods made of white flour, or bottled fruit juices, can cause highs and lows in blood sugar. Avoid sugar substitutes and food additives like MSG, which can trigger reactions in some people.
- Focus on eating complex carbohydrates, especially vegetables. These help you have a more sustained energy throughout the day. Nuts and seeds are also good.
- Warm baths with Epsom salts can be very soothing.
Getting enough sleep at night, and even resting or napping during the day, may be essential to your well-being if you have fibromyalgia. Develop habits that allow for plenty of rest and set yourself up for a good night’s sleep.
Acupuncture Near Me for Musculoskeletal Pain
Many people who have fibromyalgia choose to try alternative medicine as a way of managing FM pain. Physiological conditions that stem from emotional stress are often not resolved through the use of medications. Acupuncture and TCM have a long history of helping people to heal from emotional disturbances that cause physical pain. Acupuncture treatment works to increase the flow of energy through the body and improve the connections between the brain and nerve endings. If you or someone you know suffers with fibro, consider acupuncture as a way to find relief from musculoskeletal pain and constant fatigue.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How To Treat Dizziness With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Feeling light-headed and dizzy? Maybe you feel like your head is spinning, or that the world is spinning around you? Headache, nausea, dizziness, and vertigo are symptoms that can be caused by a variety of health problems. Acupuncture and TCM offer vertigo treatment that can help relieve that sense of dizziness and nausea, or feeling light-headed and tired all the time.
Feeling dizzy is one the most common reasons that people go in for a doctor’s visit, or even visit the emergency room. Dizziness is a fairly general term that can mean anything from feeling light-headed, woozy, faint, off-balance, or unsteady to feeling nauseated or like you’re about to pass out.
Vertigo is a specific type of dizziness that refers to a sensation of spinning, as if the room around you is moving. You might feel like you’re leaning to one side, or about to fall over. It can make you feel sick to your stomach, similar to motion sickness. In popular culture, the word “vertigo” is sometimes used to mean a “fear of heights,” but that is actually called “acrophobia.” The sensation of vertigo can be triggered by looking down from above, or looking up at something very tall, but this is not the cause of most episodes of vertigo.

Vertigo causes include migraines and problems with the inner ear. The inner ear and eyes both relay information to the brain about a person’s spatial relation to the environment, so when the functioning of the eyes or ears is disrupted, it can cause a sense of imbalance, and even nausea. Migraine headaches, particularly a specific type called a vestibular migraine, can cause pressure in the head and dizziness and nausea.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is one type of vertigo that causes short-term bouts of sudden dizziness. Benign positional vertigo is caused by the shifting of calcium crystals (canaliths) in the inner ear. This can happen due to a head injury or simply aging.
Other inner ear problems that can cause signs of vertigo include Meniere’s disease and Labyrinthitis. Meniere’s disease is a chronic disorder related to abnormal amounts of fluid (endolymph) collecting in the inner ear. The exact cause of Meniere’s is unknown, but it develops more frequently later in life. Meniere’s disease causes attacks of vertigo that can last from a few hours up to 24 hours. Like migraines with an aura, there is often a period of time during which a set of “warning symptoms” begin to occur, such as: a feeling of uneasiness, being off-balance, headache and dizziness, queasiness, hearing loss or ringing in the ears, or extra sensitivity to sound. Once an attack of vertigo hits, it can be quite severe, causing intense pressure in the ear, blurred vision, vomiting or diarrhea, cold sweats, rapid heart rate, and feelings of fear and panic. There is currently no cure for Meniere’s.
Labyrinthitis refers to inflammation of the small parts of the inner ear, or around the nerves of the inner ear that can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, such as: a flu, measles, herpes, hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, chicken pox, or childhood ear infections. Symptoms of labyrinthitis can include: dizziness, nausea, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and difficulty concentrating.
Lightheadedness is a similar sensation to dizziness in some ways, but is usually caused by a sudden change in blood pressure or the flow of blood to the head. You have probably experienced feeling light headed and dizzy when you get up too fast from sitting or lying down. Other causes of lightheadedness include: allergies, anxiety, anemia, hyperventilating, arrhythmia, or heavy bleeding (as during menstruation).
Dizzy spells happen to everyone once in a while. But recurrent headache and dizziness should be addressed. Acupuncture and TCM have been used to help dizziness for thousands of years and offer natural solutions to the underlying causes of vertigo.
Top 10 Causes of Dizziness

Feeling light headed and dizzy, or having headache, nausea, dizziness, can occur as symptoms of a variety of imbalances. Reasons for dizziness may include:
- Inner ear imbalance, or labyrinthitis
- Meniere’s disease
- Sleep apnea, snoring
- Migraine – vestibular migraine
- Dehydration – alcohol, diuretics
- Sinus issues
- Ear infection
- Low Blood Sugar – diabetes, hypoglycemia
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Prescription Medication side effects
Dizzy spells that occur first thing in the morning are common for some people. This can be simply due to the change in pressure in the ear when you get out of bed. Waking up dizzy due to sleep apnea occurs because this condition obstructs your breathing during the night, and you may have lower oxygen levels when you wake up. Being dehydrated is another common cause of dizziness, which is exacerbated by drinking alcohol before bed. In general, drinking too much caffeine, too much alcohol, and not enough water, or taking diuretics can all lead to dizzy spells. Low blood sugar, whether due to diabetes, or simply not eating regularly enough, can also be a cause of light-headedness. Hepatitis, HBV, or HCV can also cause dizziness.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) causes dizziness when moving from a seated or position or lying down to standing up.
Cervical vertigo, or cervicogenic dizziness, is another type of vertigo caused by the positioning of the neck or cervical spine; in this case, the feelings of imbalance and spinning may be accompanied by neck pain. This type of vertigo may happen, for instance, after a whiplash injury.
Treatment for Vertigo
The medical treatment for dizziness and vertigo depends wholly on the underlying causes for the symptoms. If a bacterial infection in the ear is confirmed, then antibiotics may be used. In cases of BPPV, a canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is a non-invasive technique that can help the crystals within the inner ear move back into their proper place. Migraine-related vertigo may be treated with the medications typically prescribed for migraines. Anti-nausea drugs like Dramamine may be suggested. Patients suffering from cervical vertigo may be referred to physical therapy to help improve the positioning and strength of their neck/cervical spine.
Can Acupuncture Help Dizziness?

One of the central concepts of TCM is that of the root and the branches. The branches are the visible, outward signs or symptoms of a problem, while the root refers to what is going on deeper in the organ systems of the body. In the cases of dizziness and vertigo, there is deficiency in the root and excess in the branches.
Pathogenic factors involved in dizziness and vertigo are phlegm, wind, fire, and deficient Qi. When there is weakness in organs like the spleen, stomach, kidney, or heart, pathogens like wind, heat, and phlegm can take hold. The San Jiao, also known as the “triple burner,” is another important concept in TCM; one of its primary functions is to control the movements of fluids in the body so that they don’t collect and build up inappropriately. In case of vertigo, phlegm and heat develop to the point of causing stagnation and malfunctioning of the Jiao, pushing phlegm upwards in the body. An acupuncture practitioner will carefully listen and observe to discover which organ systems are out of balance, and work to strengthen those areas. For example, dizziness combined with emotional disturbances like anger and depression is a sign of too much wind or heat in the Liver. Weakness in the heart or spleen may follow a long illness or period of stress and anxiety. Too much phlegm, heat, and dampness in the stomach and spleen can result from an improper diet and too much stress.
Acupuncture and herbs to tonify these organs and clear heat and phlegm will take care of the root of the dizziness. Meanwhile, specific acupuncture points can have an almost immediate effect at relieving immediate discomfort, facilitating a natural vertigo cure.
A study conducted at a hospital in Taiwan used acupuncture to treat patients with dizziness and vertigo. The findings conclusively showed immediate improvement in symptoms.
A study of 60 patients who were admitted to an emergency room suffering from vertigo from a variety of causes, including Meniere’s and BPPV, showed that acupuncture treatment provided immediate relief of symptoms and is therefore a good alternative for dizziness due to various causes.
Top 5 Tips to Get Rid of Dizziness
Depending on the cause of the vertigo, there are different ways to manage with TCM techniques, including vertigo exercises, acupressure for dizziness, moxibustion, and foods to avoid.
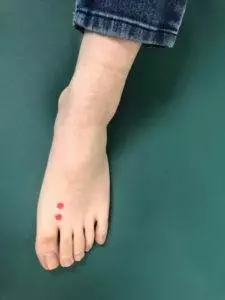
Major 4 types of Vertigo/Dizziness presentation:
- Hypertension type – When a person has high blood pressure, too much liver yang, and is overheated, it can cause dizziness. For this, we use acupressure Liver points 2 and 3 on the toes.
- Qi and Blood deficiency – if a person shows signs of anemia, or has heavy periods, hemoglobin is low, or if a person has chronic conditions, or has suffered a major injury, or recently given birth, experienced major blood loss. For this we want to ensure a good diet with plenty of soups and easy to digest foods. Moxa on the back can help to strengthen the body’s Qi and produce enough blood. Qi Gong exercise of squeezing the earlobes and outer ear up and down is helpful.
- Kidney essence deficiency – this could be due to some constitutional weakness, or due to old age, or someone who tends to have chronic illness, diarrhea. The kidney essence can’t support rising essence to the head. For this, acupressure for Kidney 1 – on the bottom of the foot.
- Phlegm stagnation – when the middle jiao is not working due to stagnation of phlegm creating blockage so Qi cannot ascend. This happens when people are overweight, or have poor digestion, diarrhea. Avoid dairy and fried foods, which encourage phlegm. Moxibustion treatment to the back is helpful, and applying pressure to Stomach-36 acupressure point can help the middle jiao open up.
- Neck Pain – if a neck problem is causing a blockage, due to a neck disease or bulging disc, unhealthy cervical disks, compression, tension, and muscle spasms can block upwards energy. Exercises to encourage the health of the neck discs, loosen up the muscles and allow flow of Qi and blood up to the head. Your acupuncture practitioner will recommend neck exercises to help with this.
Acupuncture Near Me for Dizziness
Vertigo and dizziness may not be life-threatening symptoms, but they can have a big impact on your daily life. Frequently being blindsided by unexpected dizziness, spinning sensations, nausea, and headaches is unsettling and debilitating. Medications can be helpful in some cases, but they can also cause unwanted side effects. Getting to the root cause of vertigo with acupuncture and TCM will help get rid of dizzy spells so they don’t keep coming back.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat TMJ With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
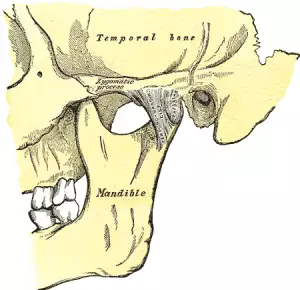
What is TMJ? “TMJ” is an acronym for “temporomandibular joint,” which is the double joint structure that attaches the lower jaw to the skull. “TMJ” is also used as a general term to refer to disorders of the jaw joint. Popping or clicking of the jaw joints, tension or pain in the jaw, grinding teeth, headaches, neck pain, and shoulder pain can all be signs of a TMJ disorder, or TMD. Acupuncture and TCM offer relief from TMJ jaw pain and inflammation.
The jaw joint is totally unique among joints in the human body in a few ways. It is really two joints that must always work together; you cannot choose to just move one side of your jaw. Also, the temporomandibular joint has two ways in which it moves; it “hinges,” and then, it “slides.”
Hinge joints, like the knees and elbows, allow flexion and extension on one plane, while remaining stabilized by a complex group of muscles, ligaments, and other connective tissues. Most of these joints are made of bones that are “molded” to fit and move together. Gliding joints, also called plane joints, like those in the ankles, wrists, and vertebrae, have flat sides that slide alongside each other when they move. The jaw joint combines both of these actions. Essentially the movement of the jaw is a kind of dislocation by design. Small discs of cartilage help to cushion the areas where the jawbone interacts with the sides of the skull in front of the ears.
It can be difficult to determine the exact causes of “TMD,” or temporomandibular disorders that cause pain and dysfunction. Injury to the jaw, dislocation of the jaw, inflammation of tissues, arthritis, and bruxism (clenching or grinding the teeth and jaw) can all potentially lead to jaw pain or clicking in the jaw. Erosion or damage to the cartilage sometimes causes TMD, impacting the usually smooth motion of the opening and closing of the jaw. Structural issues like missing teeth or an uneven bite can cause jaw problems. Dental and orthodontic work that requires the patient to hold the mouth open for long periods of time can sometimes lead to TMJ pain. Habitual movements like teeth grinding, biting on things like pencils, nail biting, or leaning your chin on your hand can also contribute to TMJ pain. Chronic pain syndromes like fibromyalgia can also cause jaw pain.
Most cases of TMJ disorders resolve themselves over time, usually within a few to several months. Resting the jaw and eating soft foods is usually recommended. Medical treatment usually involves medications to reduce inflammation and relieve pain while waiting for the jaw joint to gradually regain its normal function. Only in rare cases is surgery necessary to get rid of jaw pain.
TMJ, or myofascial pain in the muscles around the jaws, is experienced by a third or more of all adults at some point in their lives. TCM modalities like acupuncture can help alleviate the pain and impeded mobility of the jaw joint caused by TMJ disorders.
Top 10 Symptoms of TMJ

Pain around the jaw joints that comes and goes is the most common complaint of people with TMJ disorders. However, problems with the jaw can contribute to pain and tension in other parts of the head and shoulders, too. The most common signs of TMJ include:
- Pain in cheeks, tension in the jaw
- Jaw clicking, popping of jaw bones
- Limited movement of jaw, can’t open jaw normally
- Clenching of jaw, grinding teeth at night
- Tooth pain, pain in the back teeth
- Ear pain, ringing in the ears, tinnitus
- Headaches, migraines, pain behind eye, sensitive to light
- Stiffness in shoulders or neck, pain in neck, shoulder pain
- Numbness or tingling in arms, hands, or fingers
- Dizziness, vertigo
The combination of hard bony structures, muscles, and cartilage that are all involved in TMD causes TMJ pain that is hard to pinpoint because it may move around, and come and go. Most people describe the sensation as a dull ache. Some people don’t experience pain, but still have trouble with jaw clicking or opening and closing the jaw.
What Is the Treatment for TMJ?

A doctor or dentist may check for signs of TMJ by observing and manually examining the movement of the jaw joint. Dental X-rays may be used to help determine the cause of jaw pain. CT scan or MRI may be recommended to get a more detailed look at the bones and cartilage.
The primary recommendations for jaw pain and clicking is to rest the jaw as much as possible and eat only soft foods. Physical therapy (PT) can help strengthen the muscles of the face and encourage people to change habitual behaviors that might be contributing to TMJ. Wearing a splint or bite plate keeps the mouth and jaw in place and prevents grinding teeth in the night. This combination of PT and splinting is called stomatognathic treatment. If pain is serious enough to require further medical treatment, doctors will usually prescribe either pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants, or some combination of these. Surgery is only used in rare cases when the jaw has become “locked,” or TMJ inflammation and pain has become chronic.
Acupuncture and TCM treatment offer a way to reduce inflammation and pain related to TMJ disorders without risky surgical procedures or the adverse side effects sometimes caused by corticosteroids and other medications.
Acupuncture Treatment for TMJ
Acupuncture can work to reduce inflammation and pain from many different conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders like TMD. Acupuncture is effective at reducing sensations of pain, both by reducing inflammation in areas from which the pain is originating and by stimulating the release of endorphins and other neurotransmitters that help boost feelings of well-being. Acupuncture treatment can also help the muscles involved with jaw function to relax, alleviating the “clicking” or “popping” associated with TMJ disorders.
In TCM theory, TMJ is often related to what we call different types of “obstruction” syndrome. Stress and trauma, both physical and emotional, can cause Qi stagnation and/or blood stagnation. Pathogenic forces like cold, heat, wind, and damp can cause painful obstruction, or blockages of energy and blood in certain areas of the body. People suffering from TMJ do not necessarily only have dental pain or myofascial pain, a clicking jaw, or limited movement. They may also be experiencing a variety of other symptoms that are actually related. A TCM practitioner will look at the whole picture of what each patient is feeling, and treat accordingly.

For example, a person with Liver Qi stagnation may have:
- tension in the facial muscles
- neck pain
- feelings of anger or anxiety,
- ringing in the ear, tinnitus
- headaches
A person with a Wind/Cold Bi Syndrome presentation might feel:
- acute onset of pain
- pain moves around from one area to another
- aversion to wind and cold
- fever, chills
- ear ache, ringing in the ears
As a holistic form of medicine, TCM works not only to relieve jaw pain and swelling, but to get to the root of the problem.
A comparative study designed to evaluate TCM treatment for TMJ found that patients who received acupuncture treatment reported less pain and muscle tenderness than those that did not.
A clinical study that compared groups of patients who received acupuncture treatment for TMJ pain and limited motion to patients treated with decompression splints. Both groups experienced reduction in pain and increased mobility, and the researchers concluded that acupuncture can be considered beneficial as either an adjunct or alternative treatment.
In some cases, a stiff, painful jaw joint can be a secondary symptom of another, more systemic problem like rheumatoid arthritis or fibromyalgia. These conditions can also be addressed with acupuncture.
Acupuncture Near Me for TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders interfere with a person’s most basic activity: eating. While most cases of TMD improve within a matter of months with the proper rest, they can cause a lot of pain and frustration while a person is waiting to heal. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help relieve TMJ pain and restore normal jaw function, helping people get back to normal more quickly than rest alone. At Art of Wellness, we have over 30 years of experience helping patients with musculoskeletal disorders and pain of all kinds find relief and a return to their usual mobility.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Migraine with TCM and Acupuncture
By Xiaomei Cai L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Migraine is a disorder that affects about 10% of people worldwide; women are three times more likely to suffer migraine headaches than men. A migraine is an intense headache that lasts anywhere from several hours to three days and is severe enough to impede normal activities. The throbbing, pulsating, or stabbing pain in the head typical of a migraine is usually accompanied by a variety of other symptoms, including nausea and increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli. Migraines develop in stages over several hours or days, and the exact nature of the experience differs widely from person to person.
Migraine is a recurrent condition, and patients are typically diagnosed with migraine if they have experienced at least five of these types of headaches in their lifetime. Some people suffer from chronic migraines that cause them to be debilitated several times per month.
There are different types of headaches, but migraine headaches are distinct from tension headaches, sinusitis headaches, and cluster headaches in key ways. Sinus headaches, for example, are related to a sinus infection.
Although much research has been done, the physiological processes that cause migraines are still not completely understood. There is no cure for migraines, and treatment methods focus on preventing migraines from beginning or fully developing, and alleviating the symptoms until the attack abates.
While more research is needed to demonstrate exactly how acupuncture impacts brain chemistry, studies have made it clear that TCM methods and acupuncture treatment are an effective alternative for relieving migraine.
What Causes Migraine?
Current medical theory generally attributes migraines to abnormal neurological functions in the brain cells. This may be due to genetics, as susceptibility to migraines does tend to run in families, especially from mothers to daughters. A cascade of chemical activity, possibly caused by fluctuations in hormones, causes the blood vessels to constrict, which leads to the pressure in head, throbbing pain and elevated nerve sensations. Migraines have also been linked to carpal tunnel syndrome, a nerve condition in which the median nerve is compressed. TMJ, or disorders of the jaw, can also contribute to migraines. Meniere’s disease, an inner ear problem that causes vertigo, dizziness, ringing in the ears, and nausea, has also been linked to migraines. Occipital neuralgia, which occurs when the occipital nerves are compressed or irritated, can cause migraine-like pain in the back of head and neck.
Stages and Symptoms of Migraine
Migraines do not simply cause a severe headache. Migraine episodes go through a pattern of stages, during which a variety of symptoms come and go. While a person may not be able to predict when a migraine will come on, once he or she is familiar with these stages, the course of the migraine attack is somewhat predictable.
- Premonitory or Prodrome Stage of Migraine – In the early part of the migraine, a person might experience physical signs such as stiffness in the neck (cervicogenic headache), especially on one side, frequent yawning, cravings for certain foods, marked thirstiness, and increased urination. Emotionally and mentally, a sense of fatigue, irritability, depression, or confusion might pervade. Some people feel hyperactive or even euphoric. This period can last for hours or days.
- Aura – Not everyone who has migraines experiences what is known as the Aura phase, which produces unusual sensory distortions. In other cases, people may experience the Aura phase, but not the subsequent headache pain phase. Some examples of migraine with aura symptomology include: Allodynia (hypersensitivity to touch, so much that it is painful), Metamorphopsia – a profound change in perception of the size of objects, including one’s own body, altered spatial awareness, Aphasia – impairment in the language center of the brain that causes forgetting words, feeling generally unable to express oneself verbally, Visual – seeing wavy lines or flashing lights (phosphenes), “blind spots” or reduced field of vision (scotoma), Auditory – loss of hearing, auditory hallucinations, Headache and dizziness or vertigo.
- Headache – Some people may have only mild pain during this phase, and therefore do not recognize they are having a migraine. Many migraine sufferers, however, experience severe throbbing headache, sharp pain in head, or stabbing pain (ice pick headache), often on one side of the head, headache back of head, headache behind eyes, or in the temples on head. The pain is usually worse if one is active. Heightened sensitivity to light, sounds, and smells are common, and people usually feel like retreating to a dark, quiet room to lie down. During this phase, people may also experience nausea and/or vomiting, dehydration, dizziness, hot flashes and/or chills, and strong emotions such as anxiety, fear, and depression. This phase can last anywhere from several hours to three days.
- Postdrome – The final phase of migraine is sometimes likened to a “hangover.” People generally feel low energy and low mood, as well as fatigue and compromised cognitive function. This phase, too, can last several hours to a few days.
Migraine episodes have a devastating impact on people’s ability to function normally. More than half of migraine sufferers miss at least two days of work per month, and many more try to get through their workdays even though they are in the middle of a migraine.
Are Migraines Related to Hormones?

While anyone can have migraines, women are three times more likely to experience them, especially during their reproductive years. Many women perceive their migraine to be a PMS headache or period headache, because it occurs prior to or during the menstrual period. These types of migraine can be particularly debilitating. The cause of headache is believed to be due to a sudden drop in estrogen. This same mechanism can cause frequent headaches during perimenopause or early menopause due to fluctuations in estrogen levels.
Sometimes women are prescribed the use of continual oral contraceptive medication (i.e., skipping the placebo week of pills) in order to prevent drops in estrogen that may be causing migraine. This treatment does not work for everyone, though, and obviously is not helpful for women who may wish to get pregnant.
Serotonin levels have also been linked to migraine. Research has shown that fluctuations in neurotransmitters and vascular functions in the brain are part of the migraine pathology, but it remains unclear exactly how this plays out. Triptans, drugs which act upon the serotonin receptors in the brain, are currently the most common treatment for acute migraine, as in some cases, they will stop a migraine attack from progressing. These medications do not work for everyone, though, and they cause constriction of blood vessels, which can lead to other problems, such as tightness, tingling, and hot flushes in various parts of the body.
Targeting the production and function of one of two specific hormones may produce some positive results, but as migraines appear to stem from a complex combination of hormonal, vascular, and metabolic malfunctions, a more holistic approach may be indicated. Acupuncture has been shown to help regulate hormones like estrogen and serotonin, specifically, but TCM achieves those results by observing and treating the whole person, emotionally, mentally, and physically; not only focusing on one or two isolated chemicals.
Acupuncture and TCM for Migraine Help
TCM theory is based on the concept of Qi as a life force energy which flows through the body along channels called meridians. Qi and blood move through these channels, several of which meet in the head. Blockages and stagnation in one organ system can impact other organ systems. Recurrent migraines are considered to be caused by stasis and deficiencies in the liver, spleen, and kidney, which cause yang energy from the liver to rise to the head. Overconsumption of the wrong kinds of foods can cause phlegm build-up in these organs, while alcohol and pungent foods can create excess heat energy. A typical TCM treatment protocol might involve using specific acupuncture points and herbs to quench liver fire and eliminate phlegm.
Acupuncture can work on migraine pain with its natural analgesic effects, while also helping to prevent future attacks by resolving these deeper organ system imbalances. One study showed that migraine patients given acupuncture treatment experienced fewer episodes and missed fewer days of work than those given medications. The results also indicated that acupuncture was more cost effective than the medications. A review of randomized trials involving thousands of patients concluded that acupuncture is effective at reducing the number of days lost to migraines and should be considered a valuable treatment option.
Top 5 Home Remedies for Migraine Headaches

Migraines appear to be triggered by various stressors, lack of sleep, and certain foods. Aside from seeking acupuncture near me for migraine, there are several things you can do to prevent and relieve severe headaches. Natural remedies for migraines involve simple dietary, exercise and lifestyle modifications.
- Avoid foods that can trigger migraines. The most common ones are processed or prepared foods with added nitrates or MSG. Dairy products, especially very salty or aged cheeses, and chocolate should be avoided if you are susceptible to migraine, as well as extremely cold drinks and desserts. Dried foods like fruits and beans, and pickled foods can also be problematic.
- Emphasize foods high in magnesium, especially nuts, seeds, and high quality eggs.
- Ginger is known to relieve nausea and vomiting, and may alleviate other effects of migraine. One study showed that ginger was just as effective as Sumatriptan for decreasing symptoms of migraine. We recommend simply slicing fresh ginger root and steeping it in hot water to drink as a tea.
- Try essential oils like lavender or peppermint. Rubbing a little bit into the temples can be soothing.
- Find a gentle practice that combines breathing, movement, and meditation. Yoga, particularly restorative yoga, has been shown to be helpful for headaches. This may be because it helps people relax more fully. It also encourages better symmetry between the right and left sides of the body and brain.
Best Acupuncture in Los Angeles for Migraine Help
Drs. Cai and Tan at Art of Wellness in Santa Monica have over thirty years of experience treating migraine and other types of headache with TCM, acupuncture, and herbal remedies. Headache help is just a phone call away. If you or someone you know has been suffering with severe headache or chronic migraines, please do not wait another day to call 310-451-5522 and get started with an acupuncture treatment program that will allow you to reclaim your life and experience headache relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.