-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Can Acupuncture Help Bad Breath?
- How to Treat Atopy with Acupuncture and TCM
- Plantar Fasciosis Treatment With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Protect Yourself When Air Quality Is Poor
- How to Treat Spinal Headache With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Sarcoidosis With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Flu With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2025 Year of the Snake
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

July 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
fatigue
How to Treat PTSD With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac, Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a type of mental illness that develops after a person has gone through a traumatic life event. PTSD flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and sleep disorders are a few of the most common signs of PTSD. Acupuncture and TCM are widely accepted as a highly effective way to treat complex PTSD and other stress disorders, as well as anxiety, depression, panic attacks, and insomnia.
PTSD is mostly commonly associated with veterans of the military, as many soldiers who have served in combat experience trauma related to war violence. A significant amount of scientific research and psychiatric study has been devoted to finding out about PTSD and what treatments for PTSD are effective. Relative to other conditions, there have been quite a few studies showing that acupuncture can be helpful for PTSD. The U.S. Navy has even started an acupuncture training program in San Diego, after a Pentagon study showed that TCM is beneficial for veterans.
PTSD is not only a problem for military veterans, though. PTSD can result from all kinds of traumatic life events, including things like: accidents, natural disasters, surgeries, assaults, attacks, abandonment, or the death of a loved one. More than 8 million Americans are currently living with post traumatic stress. People of all ages can experience PTSD. PTSD can result from experiencing something traumatic directly, or being a witness to such an event. People whose jobs involve exposure to violence or disturbing situations, such as first responders, social workers, or police officers, can also have PTSD because of things they have seen. A person can be deeply traumatised by something they didn’t see happen firsthand, but that they heard happened to someone close to them.
The body’s response to extreme stress is one of its ways of protecting us. Stressful situations cause the “fight-or-flight” response and chemicals like adrenaline to be released. When this happens repeatedly, or to an extreme degree, because a person is literally in fear for their life, there can be long-lasting physical and emotional effects. Normal, everyday stress we hope to release from the body through exercise, meditation, laughter, and other stress-reducing activities. But when a person has endured abuse or life-threatening danger, they may not be able to release the stress from their bodies so easily.
TCM theory offers a way to help people deal with mental health issues like PTSD because it creates a context in which emotional and mental symptoms interact with physical symptoms. TCM addresses the way that trauma and negative emotions are stored in the body, sometimes causing overwhelming emotional and physical symptoms. Acupuncture and herbs are holistic treatments for PTSD that can be used as an adjunct to therapy and medications to help relieve stress, sleep problems, mood disorders, negative emotions, and problems with cognitive function.
Top 10 Signs of PTSD

Many people don’t realize that they are experiencing post traumatic stress. PTSD can overlap with several other types of mental health problems, and the symptoms of PTSD can often seem similar to those of other anxiety disorders or symptoms of depression. What PTSD feels like can be highly individual to each person and what caused their initial trauma.
The most commonly recognized symptoms of PTSD include:
- Flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, reliving traumatic events, can’t stop thinking about what happened
- Nightmares, recurrent, vivid, disturbing dreams
- Avoidance of triggering places, activities, or people
- Memory loss, amnesia, unable to remember periods of time related to the traumatic event
- Negative perception of self, negative perception of the world, blaming self or others
- Isolation, unable to connect with other people, relationship problems
- Feelings of anger, irritability
- Hypervigilance, always aware of perceived threat, can’t relax, exaggerated startle response, always on guard, panic attacks
- Difficulty concentrating, inability to focus on the present
- Insomnia, can’t sleep
PTSD often coexists with other mental health issues like anxiety, panic attacks, and depression. Chronic fatigue syndrome (also knowns as ME/CFS)has been associated with PTSD. Fibromyalgia, a syndrome that can cause generalized muscle pain, sleep problems, fatigue, and other problems can be related to PTSD. Sometimes fibro manifests after a traumatic event.
Types of PTSD

The term “stress disorder” refers to a combination of physical and emotional symptoms that are the body’s and mind’s stress responses to some type of trauma.
Different types of stress disorders include:
- Normal stress response – even common everyday work stress and relationship stress can cause widespread health problems. Serious issues like a relationship breakup, or job loss can lead to negative emotions and physical problems due to stress. People of all ages can experience debilitating symptoms of stress like: stomachaches, headaches, trouble concentrating, rapid heartbeat or trouble sleeping. If stress is allowed to build up over time, it can seriously damage health. Past illnesses or viral infections, like Epstein Barr and mononucleosis can also be a factor.
- Acute stress disorders – acute post traumatic stress is the immediate aftereffect of some sort of traumatic event or life-or-death situation. If the short-term (30 days or less) acute signs of trauma are left unaddressed, they can turn into PTSD.
- Uncomplicated PTSD – this refers to PTSD symptoms related to a specific traumatic event, such as a car accident, being the victim of a crime or assault, or surviving a natural disaster and its aftermath. This type of PTSD causes symptoms like: flashbacks, nightmares, avoiding a particular area, thing, or person, and strong feelings of anger, blame, and fear that impact your relationships and sleep patterns.
- Complex PTSD – complex trauma is the result of multiple, repeated traumatic episodes, like suffering abuse as a child, being in an abusive relationship, domestic violence, or repeated sexual abuse. Complex PTSD could also happen to people living in wartime conditions or who are part of a targeted community under brutal conditions. PTSD attacks can be brought on by complex PTSD triggers that remind you of the traumatic events, such as: a particular place or smell, a time of year or date, a physical pain or sensation in a particular part of the body, or reading a story or seeing a movie or TV show that brings up the memory.
- Comorbid PTSD – this refers to PTSD that coexists with other serious issues such as substance abuse, addiction, and/or depression. Comorbid PTSD is very common, because many people suffer from more than one of these mental health conditions at the same time.
In general, complex PTSD and comorbid PTSD are considered more difficult to treat and more likely to affect people throughout their lives than uncomplicated PTSD.
PTSD Treatment
Treatment for PTSD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy/cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychiatric medications for PTSD such as antidepressants (SSRIs like Zoloft, Prozac, or Paxil) and anti-anxiety medications (like Xanax, Ativan, Valium, or Klonopin). Long-term use of anti-anxiety medications is generally not recommended, as patients can become dependent on them, leading to abuse of the drugs. SSRIs can be helpful for symptoms of depression, but they can also have negative side effects, like sexual dysfunction (ED), weight gain, nausea, dizziness, and making sleep problems worse.

Exposure therapy is a specific type of therapy that helps people learn coping skills by working with the distressing memories or exploring possibly frightening situations in a safe environment with a therapist. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) helps patients learn to adapt to the stress tied to the past trauma by thinking about it while looking at a movement pattern or listening to a repetitive sound. This treatment has been shown to help PTSD patients heal emotional trauma more quickly than talk therapy or CBT alone.
The conventional treatments for PTSD can help some patients, to different degrees, but many people with complex trauma do not want to go through this type of treatment. Talk therapy, trauma-based CBT, and exposure therapy may be terribly intimidating to people who are suffering with PTSD, and patients may be more afraid of entering into these kinds of therapy than continuing on with their current symptoms.
The TCM modality of acupuncture can have a positive effect on neurotransmitters, the brain chemicals that influence cognitive thought patterns and moods, without the potential negative side effects or dependency that can result from medications. Acupuncture can be a helpful alternative or complementary treatment to other types of therapy for PTSD.
Can Acupuncture Help PTSD?
In historical records of TCM, we do not see a word or description of a condition that is directly synonymous with PTSD. However, in TCM, we view emotional states as being related to the function, or dysfunction, of specific organ systems. The symptoms of PTSD can correlate with these relationships between the organs, the mental state, and physical manifestation of symptoms:
- Lung – Grief – Wheezing, trouble breathing, sweating, fatigue
- Spleen – Worry – Nausea, gastric problems, loss of appetite
- Liver – Anger – Headaches, muscle pain, dizziness
- Heart – Anxiety – Palpitations, insomnia
- Kidney – Fear – Urinary frequency, night sweats, memory problems
A TCM provider will look carefully at how each individual describes their physical symptoms and emotional state, and will choose acupuncture points for PTSD and herbs to help strengthen the organ systems that need nourishment.
In regards specifically to military veterans with PTSD, many survivors are wary of seeking medical or psychological treatment for complex trauma. The majority of soldiers who have served in the Middle East in recent years have been diagnosed with PTSD, but less than half of those veterans are receiving medical treatment for PTSD. Many people, in general, are reluctant to seek care, either because they don’t trust that it will work, or their complicated feelings of shame, guilt, grief, and anger are too overwhelming to share with others.
Acupuncture can be particularly helpful for some people suffering from PTSD because it does not necessarily have to involve talking about the original trauma or abuse. Some patients may avoid psychotherapy for this very reason, as they are not ready, and may never be ready, to go over these details with another person. An acupuncturist can help relieve symptoms of anxiety and depression by focusing on the person’s emotional and physical needs and tailoring the treatment to fit their symptoms and lifestyles.
A clinical study done by the Long Beach V.A. randomly divided patients into “real acupuncture” and “sham acupuncture” groups, and the patients received treatments twice per week over the course of 12 weeks. The veterans who received real acupuncture showed significant physiological improvement, with less startle reactions, as measured by skin sensors, than the sham group.
A Rand review found that acupuncture helped improve symptoms of depression, anxiety, and sleep problems in PTSD patients.
Acupuncture Near Me for PTSD in Los Angeles
It can be a long and challenging process to overcome complex PTSD, but with the right combination of PTSD treatment, it is possible to reduce or even eliminate symptoms. With a TCM approach and acupuncture treatment, we can help reduce anxiety and depression, address feelings of anger and grief in a clinically meaningful way, and help to promote better sleep. If you or a loved one is dealing with unresolved trauma and needs help, you may find that acupuncture is a low-risk and supportive way to treat PTSD.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Parkinson’s Disease With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Hand tremor or shaky hands, stiffness in limbs, trouble walking, or problems with balance? These may be signs of Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Parkinsons is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects the brain cells that produce dopamine. Integrative care with acupuncture treatment may help relieve symptoms of Parkinson’s disease better than conventional treatments alone.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that causes damage and dysfunction in brain cells, so that communications between the brain and the body don’t work the way they usually do. Sometimes a range of symptoms similar to those experienced by people with Parkinson’s occurs due to small strokes that affect the blood supply to the brain. This condition is called vascular parkinsonism.
More than ten million people are currently living with Parkinson’s disease worldwide. The chances of having PD increase with age, and men are more likely to have Parkinson’s than women. Early onset Parkinson’s can occur in people under 50. While it is often considered a movement disorder that causes hand tremors and other problems with mobility, Parkinson’s disease can cause less obvious symptoms, too.
Parkinson’s disease causes both “motor” and “non-motor symptoms;” the motor symptoms include physical problems like trembling hands or hand shaking, stiffness in the arms and legs, and trouble with balance when walking. The non-motor symptoms may include cognitive problems with memory, foggy-headedness, and trouble sleeping. It might even seem like a person’s personality and social behavior change, because they have trouble speaking and making their usual facial expressions.
Neurological diseases like Parkinson’s can slow the production of chemicals usually produced by the nervous system, including both dopamine and norepinephrine, a chemical that constricts blood vessels to raise blood pressure. It may be this lack of norepinephrine that causes some of the symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as low blood pressure, digestive problems, and fatigue.
Parkinson’s is a progressive disease, which means that people with PD go through stages as the condition affects more and more brain cells. In the early stages, the motor symptoms are mild and may only occur on one side of the body. In the later stages, a person may not be able to perform basic daily activities like getting dressed, eating, or walking without assistance.
What causes Parkinson’s disease? Medical science does not currently have an answer for why the brain cells become damaged or die in people with Parkinson’s. Scientists have observed that patients with Parkinson’s often have unusual clumps of a protein (alpha-synuclein) in their brain cells; these are called “lewy bodies” (lewy body parkinsons). These may be causing mutations in the cells that impair their ability to produce dopamine and other neurochemicals. Genetics, aging, and toxins in the environment or diet may all play a role in the development of Parkinson’s.
Conventional treatment for Parkinson’s involves finding a combination of medications that may help to reduce tremors and stiffness, and the myriad other symptoms a person with PD may experience. TCM offers an effective and safe adjunctive Parkinson’s treatment. Acupuncture treatment is widely accepted as a way to help relieve pain and nausea related to all types of diseases. TCM treatment can also have a positive effect on neurochemical activity, increase dopamine levels, help improve motor function and gait, and relieve fatigue.
Top 10 Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease

The early signs of Parkinson’s are generally related to movements of the body, like feeling stiff when getting up or mild hand tremors. People may not realize that other symptoms, like low blood pressure and dizziness, are also related to early stage Parkinson’s. The most common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
- Tremor – a small, involuntary shaking movement occurs most often in the hands, but can also be in a finger or thumb, or the chin. Sometimes called static tremor or resting tremor.
- Trouble moving or walking – limbs may feel stiff or rigid, there may be hip pain or shoulder pain. Most noticeably, the arms may not swing naturally when a person walks, or a person may shuffle, feeling it is hard to lift their feet off the floor. Movements that have been automatic for one’s whole life become challenging.
- Dizziness – fainting or feeling dizzy when you get up from sitting or lying down. This happens due to a sudden drop in blood pressure called orthostatic hypotension. A general feeling of weakness, feeling lightheaded, foggy headed, headache, blurred vision, and difficulty thinking or concentrating, and memory problems.
- Change in handwriting – this symptom is called micrographia, and it refers to a noticeable difference in a person’s writing, as they make smaller letters and the words are crowded closer together.
- Loss of smell, loss of taste, loss of appetite – many people with Parkinson’s develop an inability to smell in the early stage of the disease, known as olfactory loss. This can also affect a person’s ability to taste foods, which can lead to loss of appetite. Some medical theories suggest that Parkinson’s may begin in the olfactory region of the brain.
- Disturbed sleep, sleep disorder – sleep problems might simply be trouble falling asleep or trouble staying asleep, but they may also involve a lot of movement, or “tossing and turning,” or even talking in your sleep, crying out or yelling due to vivid dreams. Restless leg syndrome, when the limbs jerk, or leg cramps, may also be caused by Parkinson’s.
- Constipation, nausea, or trouble swallowing – cell damage in the gut may actually be one of the first symptoms of Parkinson’s, causing gastrointestinal problems due to slower movements of the smooth muscles of the digestive tract. Feeling nauseous or having a bloated stomach happens when the contents of the stomach empty too slowly into the intestine.
- Changes in the voice – people may notice that your voice sounds hoarse, weaker or more quiet than usual. This can be due to both motor and non-motor problems of PD, related to difficulty swallowing, sore throat due to heartburn, sensation of choking or food stuck in throat. It is also related to cognitive difficulties that make it harder to think of words, causing slow speech, or in other cases, talking too fast to be understood. Sometimes it may seem that a person with Parkinson’s doesn’t feel like talking much.
- Changes in facial expression – called “facial masking,” some people with Parkinson’s will find people asking them if they are upset because the expression on their face looks very serious, sad or angry, or they appear to be staring. This happens because of decreased motor function of the muscles of the face.
- Changes in posture – people with Parkinson’s may begin to hunch over while sitting, with shoulders hunched forward, or assuming a “stooped” posture while standing or walking. Again, this is due to a lack of communication between the brain and the muscles. This hunched posture can affect deep breathing, and increase the risk of falls.
Parkinson’s symptoms are complex, and vary widely from person to person. People with Parkinson’s are often subject to feelings of depression and anxiety, as well. Treatment for Parkinson’s symptoms requires a multipronged approach that addresses each individual patient’s physical, emotional, and mental health.
Medical Parkinson’s Treatment
When treating Parkinson’s, doctors will often try various combinations of drug therapy, some of which aim to replace dopamine, to help relieve tremors and other motor symptoms of PD. Levodopa/Carbidopa (or Sinemet) is a combination medication that creates a controlled release of dopamine. This can help to alleviate some symptoms, but the symptoms return when the medication is not in the bloodstream. Unfortunately, this medication can cause side effects like nausea and vomiting, and people will often need to take larger doses to get the same effect as the disease progresses. Long-term use sometimes causes dyskinesia, or involuntary movements of the limbs. Doctors may then prescribe another medication, such as Amantadine or Gocovri, to help mitigate these effects, or to help stave off motor symptoms during “off” times when the dopamine-replacing drugs wear off.
Patients with Parkinson’s will often be given other medications to help with problems like constipation, high blood pressure, sleep problems, pain, and depression. TCM and acupuncture offer a holistic way to treat many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s at the same time, without so many drugs and their potential side effects.
How Can Acupuncture Help Parkinson’s?

Part of TCM theory involves the concept of Ben and Biao, or “Root and Branch.” We observe that the expression of illness in the body is like the system of roots and branches of a tree. The branches show us the outward symptoms, while the root of the disease is hidden deeper under the surface, where we can’t see it. In order to treat the symptoms of any illness, we study the branches to find out where the problem originates, then we go to the root of the problem to solve it. We do this with a combination of acupuncture, herbs, and other modalities like moxibustion, cupping, and tuina massage. These TCM treatments allow us to address problems in the organ systems of the body, where lie the roots of illness, while at the same time, helping to relieve the pains and uncomfortable symptoms occurring in the branches.
Parkinson’s disease is considered by TCM philosophy to occur due to deficiencies in the root, which cause excess in the branches. Deficiency of the kidney, liver, spleen, blood and Qi (root problems) contribute to heat, phlegm, stasis, and wind in the limbs (branches). Tremors in the hands, and changes in facial expressions and movements are caused by Wind and Phlegm. According to TCM, Wind causes problems, often in the upper body, that come and go, such as stiffness, spasms, facial tics, and shaking of the limbs–like the wind shaking the branches of a tree. Wind can also cause symptoms like ringing in the ears (tinnitus), sudden headaches, and hives. Phlegm, which blocks the energy channels of the body, disrupts the smooth flow of blood and Qi to the limbs, creating a sense of stiffness, heaviness in the limbs, resistance to moving or speaking, staring, heavy feeling in the chest, and lack of coordination.
Acupuncture treatment for Parkinson’s disease, then, focuses on clearing heat, wind, and phlegm, strengthening and nourishing the blood, and getting the Qi moving smoothly again.
When we use acupuncture and herbs to help Parkinson’s, we see changes occurring in the neurochemical activity of the brain.
One study looked at the changes in neural response in the brain immediately after acupuncture treatment. This study concluded that after 8 weeks of treatment, patients with Parkinson’s showed significant improvement in brain function.
Another clinical study showed that acupuncture helped to increase levels of Tyrosine hydroxylase, a brain chemical involved in the production of dopamine.
TCM herbal formulas have also been clinically demonstrated to help relieve Parkinson’s symptoms like speech problems, tremors, and gait disturbances.
Research has shown that using TCM herbs to treat Parkinson’s is a safe and effective adjunctive therapy to conventional medical treatment.
Acupuncture Near Me for Parkinson’s Disease Santa Monica Westside

The goal of treatment for Parkinson’s is to slow down the progression of the disease and do what we can to maintain mobility and cognitive function. The sooner we begin treating Parkinson’s disease with acupuncture and TCM methods, the better chance we have to limit the effects of the disease and help patients stay active. If you or someone you love has Parkinson’s, consider adding a TCM doctor to your health care team. Integrative treatment for Parkinson’s with acupuncture and herbs can help treat Parkinson’s naturally.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat HIV/AIDS With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac.,Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

What does it mean to be HIV positive? HIV is a viral infection that harms the immune system over time and, if untreated, can eventually lead to AIDS, a syndrome that causes people to become weaker and get serious infections easily. There is no cure for HIV/AIDS, but there are various therapies that can slow the progression of HIV. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help to improve immune function and relieve symptoms related to the side effects of other HIV/AIDS drug therapies.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an infection that affects the immune system by destroying the white blood cells (CD4 and T-cells) that are such an important part of the body’s immune response, causing people with HIV to be much more prone to all kinds of infections. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is the late stage of HIV, in which the CD4 cells have reached a critical low point and other infections are taking hold in the body.
Over a million people in the U.S. are currently living with HIV. Many more people may have HIV and not know it. People can have HIV for several years without feeling any symptoms, while the illness is in its early stages.
HIV is a progressive illness, which affects the functioning of the immune system over a long period of time.
4 Stages of HIV Infection:
- Infection – when a person contracts the HIV virus, it spreads quickly in the body, often causing flu-like symptoms: fever, headache, rash, sore throat. If you have these types of symptoms, and you think you may have had contact with an infected person or a needle recently, it is very important to go get tested for HIV. Early testing allows people to get treatment as soon as possible, and to know if they are contagious and can spread the virus to others.
- Asymptomatic – the HIV virus remains in the body, causing damage to cells and weakening the immune system, while the person may have no symptoms of HIV/AIDS. This latent stage of HIV can last for quite a long time, averaging 8-10 years. This is why many people do not realize they have HIV until they are tested.
- Symptomatic – Eventually, a person with HIV will begin to feel the effects: fatigue, mouth sores from oral candidiasis, diarrhea, and weight loss. Other infectious diseases can easily get into the body because of the weakened immune system; these are called opportunistic infections. Common co-infections associated with HIV include: tuberculosis (TB), cryptococcal meningitis, toxoplasmosis, hepatitis, and pneumonia.
- HIV progression to AIDS – In some cases, people with HIV who receive treatment to help boost their immunity are able to stave off progression into the AIDS stage of illness. However, if the CD4 cell count drops and other infections take hold, a person is considered to have progressed into the AIDS stage.
Being diagnosed with HIV can be emotionally devastating. Knowing you have a serious illness with no cure is naturally going to cause a lot of stress, feelings of anxiety, and even depression. With good health care, it is possible these days to live a long life with HIV. Putting together a team of caring health care professionals who can provide integrative care for HIV/AIDS will help you maintain the best physical and mental health possible. TCM provides holistic care for patients living with HIV or AIDS that works on all levels: keeping your mental outlook positive, helping you sleep better, boosting immune function, and relieving symptoms that are due to side effects of medical treatment, or caused by concurrent infections.
How Do You Get HIV/AIDS?
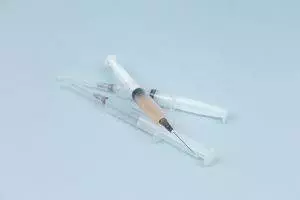
The HIV virus is carried through certain bodily fluids: blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breastmilk. In order for HIV to be transmitted from one person to another, one of these types of body fluids must have the infection present in it, and must get into the other person’s bloodstream through broken skin or mucous membrane.
HIV is not transmitted through saliva, sweat, urine, or feces, and is not carried in the air in droplets. You cannot get HIV through water or air, or by touching surfaces. The way that HIV is most often passed from person to person is through sexual contact. Other ways you can get HIV are by sharing needles while using drugs, getting a tattoo with a needle that wasn’t properly sanitized, or a blood transfusion. (As a reminder: we only use single-use, disposable, sterile needles for acupuncture treatment.) A woman could also pass HIV to her baby when breastfeeding. Using condoms during sex and only using sterilized needles are the primary ways to prevent HIV infection.
Top 10 Symptoms of HIV
Most people with HIV will go through a long phase of having no noticeable symptoms. Eventually, after the virus has spread slowly, people with HIV will begin to show symptoms such as:
- Fatigue, feeling tired all the time
- Fever, or feeling hot even if you don’t show a fever
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia, night sweats
- Weakness, dizziness
- Weight loss, wasting, loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Skin rash, or purple spots on skin, bruise easily
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen lymph glands
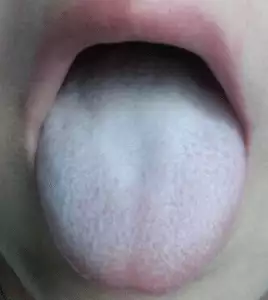
Oral candidiasis, also known as thrush or oral candida, is also common among people living with HIV because the suppressed immune system makes it easier for the fungal infection to take hold. Burning sensation or pain in the mouth cavity and redness with white patches are the signs of oral candidiasis. Long-term use of antifungal medication (Fluconazole) to control thrush can cause side effects and eventually cease to be effective as the body develops a resistance to it.
HIV can also lead to neurological problems, like peripheral neuropathy, in which the signals between the brain and the rest of the body are compromised, causing symptoms like: muscle twitching, loss of balance and coordination, tingling or burning sensations, or numbness.
Medical Treatment for HIV and AIDS
Advances have been made in medical treatment for HIV/AIDS. Different combinations of medications that block the replication of the virus can help to slow the progression of HIV in the body. This type of drug therapy for HIV used to be called HAART, short for “highly active antiretroviral therapy.” Now, it is usually referred to as ART or cART, which stands for “combination antiretroviral therapy.” This form of treatment for HIV can increase chances of survival and quality of life, but is not well-tolerated by all patients. Lifelong use of the medication is required, which, for some, makes HIV a manageable chronic illness. For other patients, the side effects of cART may not be tolerable. Side effects of HIV medications can involve gastric problems, headaches, fatigue, and peripheral neuropathy. Medications can cause liver dysfunction, damage to the liver, and bone marrow suppression, meaning fewer blood cells are being made by the bone marrow.
While a person is still in the asymptomatic phase of HIV, doctors may not begin using antiretroviral therapy because of concerns related to side effects and resistance. However, taking some steps to optimize immune function can potentially help stave off progression into symptomatic and AIDS stages. TCM herbs and acupuncture can be helpful during this phase to help strengthen the immune system and hopefully slow down the progression of disease.
Acupuncture and herbal treatment with TCM may also be used as an adjunct therapy during later phases in order to help people tolerate cART better by reducing nausea and other gastrointestinal effects of the medication and helping to improve appetite. For patients with HIV, TCM treatment is designed to help strengthen the body’s immune defenses in the hopes of preventing advancement to the AIDS stage of disease. For patients in the AIDS stage, TCM treatment focuses on helping to alleviate symptoms of opportunistic infections and to mitigate the side effects of other medications.
TCM for HIV/AIDS

What is HIV from the TCM perspective? TCM puts a lot of emphasis on the prevention of disease by maintaining a balance of yin and yang energies in order to protect the body’s Vital Qi. It is Vital Qi that keeps invasive illnesses like viruses from getting into the body and taking hold there. There are no TCM historical records that point specifically to AIDS, but we do have centuries of practice treating various kinds of invasive viral infections. Modern TCM practitioners apply this knowledge when treating patients with HIV/AIDS.
Syndrome factors of HIV according to TCM:
- Qi deficiency
- Blood deficiency
- Yin deficiency
- Yang deficiency
- Phlegm
- Dampness
- Qi stagnation
- Essence deficiency
An invasion of heat causes the early symptoms of HIV infection: fever, itching (pruritis), and fatigue. Then, later on, as the virus moves deeper into the body, toxic heat causes problems with the organ systems of the stomach, spleen, kidneys, and liver that lead to the weight loss and poor appetite indicative of later stages of HIV and AIDS. Herbal formulations can help relieve the diarrhea that is often reported by patients with AIDS/HIV. Herbs that work to help strengthen the spleen can improve fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, diarrhea, and skin rash.
Strengthening deficient Qi is central to TCM treatment for HIV and can help to improve immune responses in the body. Chinese herbal formulations can aid in reducing the spread of the infection with results similar to those of cART medicines, while simultaneously having a positive effect on the immune system overall. Herbs do not come with the negative side effects associated with drug therapy for HIV/AIDS.
In addition to the other immune-related problems, people living with HIV/AIDS are also likely to have systemic inflammation. HIV can cause damage and inflammation in the gut, and cause blood clotting, making people more susceptible to cardiovascular problems and heart disease. Acupuncture has been shown to help reduce systemic inflammation in HIV patients. Some studies have suggested that herbs may help AIDS patients to live longer, and improve chances of long-term survival. Treatment of HIV with acupuncture and herbs can help to relieve symptoms and reduce the side effects of other treatments.
Acupuncture Near Me for HIV/AIDS in the Los Angeles Area
If you or someone you love is living with HIV, getting the best care possible as soon as possible is vital for improving the long-term outcome. Putting together a program of complementary health care for HIV/AIDS can help offer the best chances for survival, quality of life, and peace of mind.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Hepatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine–these are possible signs of Hepatitis infection, although many people infected with Hepatitis show no symptoms. For some people, a Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C infection goes away on its own, but in other cases, it can cause serious liver damage, leading to chronic liver disease. Acupuncture and TCM treatment, including Chinese herbs, offer a way to help improve liver function and reduce symptoms of Hepatitis.
There are several variants of the Hepatitis virus that can cause inflammation of the liver, leading to scarring (liver cirrhosis or liver fibrosis), and in some cases leading to chronic liver problems or liver cancer. Hepatitis B (HBV) and Hep C (HCV) are the types of infection that can lead to long-term illness and even liver failure. It is estimated that over 300 million people worldwide are living with the effects of HBV or HCV infections.
There is a vaccination that offers protection against Hepatitis B and Hepatitis A, but there is no vaccine for Hepatitis types C, D, and E. People who have contracted Hepatitis A or an acute form of HBV are usually told to rest and drink lots of fluids. Medical treatment for chronic Hepatitis that lasts for more than six months usually involves antiviral medications that help slow down the spread of the virus through the body. TCM treatment for Hepatitis with acupuncture and herbs works to improve the function of the liver and related organs (spleen, kidneys, gallbladder) and to strengthen the immune system so that the body can overcome the effects of the Hepatitis virus.
What Causes Hepatitis?
There are currently five different types of Hepatitis infection, referred to as: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C (HCV or Hep C), Hepatitis D, and Hepatitis E.
All of these viral infections affect the liver, causing inflammation and possibly scarring, known as cirrhosis of the liver or fibrosis of the liver.

Hepatitis A and E viruses are carried in contaminated water or food supplies. People might contract the Hep A or Hep E virus through eating something like raw shellfish that was in contaminated water, or eating food prepared by a worker who did not wash their hands properly. These variants of Hepatitis may cause an acute infection, but do not lead to chronic conditions.
HBV and HCV are spread through bodily fluids like blood and semen, and can therefore be spread through sexual contact, or the sharing of needles, or a woman may pass the infection to her baby during birth. Hepatitis is a common co-infection in people living with HIV/AIDS. People with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) can also be more prone to infections and liver problems. These more serious forms of Hepatitis can lead to chronic illness, including cancer of the liver, or liver failure, making it one of the primary reasons people end up having a liver transplant.
Autoimmune hepatitis, which has also been called plasma cell hepatitis or lupoid hepatitis, occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells.
Top 10 Symptoms of Hepatitis
Symptoms of a HBV or Hepatitis C infection often do not show up for a few weeks, a few months, or in some cases, years later. Some people, especially children, do not feel any symptoms of Hepatitis. The most common Hepatitis symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain, pain in right side
- Swelling in liver area, swollen belly (ascites – fluid buildup in the liver)
- Jaundice, yellow eyes, yellow skin
- Dark urine, pee is dark
- Light colored stools, poop is clay-colored
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Joint pain
Bleeding easily or bruising easily are also potentially signs of Hep C, as is a skin rash, or itchy skin (pruritus), little blisters, or itchy patches of skin like psoriasis. Some people have a sensation of their internal organs itching.
What Is the Treatment for Hepatitis?
If a person shows high levels of liver enzymes and still has the Hepatitis B virus in their body after six months or more, they will often be prescribed medications aimed to slow the spread of the virus and prevent further damage to the liver. There are several types of antiviral medications used to treat patients with long-term effects of Hepatitis, some of them are pills (adefovir, entecavir, lamivudine, telbivudine, tenofovir) that are taken daily for a year, or for several years. Some, known as Interferons, are given as an injection a few times a week over the course of several months or more. These medications can slow the virus in some patients, but for some people, they may not do much to protect the body from liver damage or stop the virus from spreading. These medications can cause serious side effects, including headaches, dizziness, fever, and severe depression. Acupuncture and TCM methods offer an alternative or adjunct support to help promote better liver function and boost the body’s defense against the Hepatitis virus.
What Acupuncture and TCM Can Do for Hepatitis

Hepatitis infection is closely associated with the liver, as it is the liver that shows the most obvious damage as a result of infection, often resulting in cirrhosis or scarring of the liver. But according to TCM philosophy, the other internal organs work in concert with the liver, helping it to do the job of cleaning the blood and supplying it to the rest of the body. Patients with chronic Hepatitis B infection will demonstrate symptoms that help the acupuncture practitioner recognize a particular syndrome pattern, allowing them to use acupuncture points and Chinese herbs to work on deficiencies in the liver and other organs. In TCM theory, Hepatitis infection occurs due to pathogenic forces of toxic Heat and Dampness invading the body. The infection moves through different stages, and the TCM provider will tailor treatment with herbs, acupuncture, and moxibustion to the stage of infection and specific pattern of symptoms.
TCM differentiations of Hepatitis include:
- Liver Qi stagnation – causes symptoms like nausea, poor appetite, distension of the belly or bloated stomach
- Spleen and/or Kidney Yang deficiency – associated with poor appetite, loose stools, sallow complexion, weakness, loss of muscle
- Liver – Gallbladder Dampness and Heat – causes jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin), fever, nausea
- Liver – Kidney Yin Deficiency – indicated by headaches, dizziness, irregular periods, stiff joints, poor sleep, irritability, and ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Blood stasis – accumulation of blood in the liver contributes to fibrosis or cirrhosis, also causes pain in the lower rib area, menstrual problems, PMS, and depression.
A person may be more susceptible to getting Hepatitis because of some underlying deficiencies in their Qi, and/or the virus may cause those deficiencies to manifest. The main goal of acupuncture treatment for HBV or HCV, therefore, is to strengthen the liver, spleen, and kidneys, to clear any dampness or excess heat from these organs, and to increase the circulation of blood through the systems.
Traditional Chinese herb formulations have been shown in clinical trials to help improve liver function in patients with chronic Hepatitis B.
Herbs that help improve spleen function are believed to help rid the body of the virus and allow for healing of the liver.
Diet and nutrition are, naturally, also very important in helping to strengthen and detoxify the liver and other organs. Your TCM practitioner will go far beyond the usual advice (drink fluids, avoid alcohol), and will give you specific advice for a hepatitis diet plan.
Acupuncture Near Me for Hepatitis in West LA
Chronic Hepatitis B and Hep C infections can be difficult to treat. Using acupuncture and herbs as an adjunct to conventional antiviral therapy for HBV may help to prevent further damage to the liver and improve organ function so that patients can recover from a chronic viral infection more fully. At Art of Wellness, we have over 30 years of experience providing integrative care for those suffering from chronic illnesses of all kinds.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Stop Snoring With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Have you been told you’re snoring loudly? Do you feel tired even after 8 hours of sleep? Waking up with a dry mouth, feeling tired all the time, and having trouble staying asleep at night are all signs that you might have sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a sleeping disorder in which normal breathing is interrupted repeatedly. Acupuncture and TCM offer a natural way to treat obstructive sleep apnea, insomnia, fatigue, and other sleep-related problems.
Sleep Apnea (also known as sleep apnoea) is when a person does not breathe normally during sleep. When there is a pause in normal breathing during the night, the body is not getting enough oxygen, and the brain sends an urgent message to start breathing again. The person wakes, so briefly that they usually do not remember it, gasps for air and starts breathing again. Often people do not realize that they are snoring or making snorting or choking sounds while they sleep unless another person tells them it’s happening. Because of this, many cases of sleep apnea go undiagnosed, and people go on feeling fatigued all the time.
While people of any age or gender can experience sleep apnea, it is most common among older men. There are a few different kinds of sleep apnea; the most prevalent type is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), in which the throat and/or airway is physically obstructed by the positioning of the neck, jaw, and soft tissues of the throat, like the tongue and uvula. OSA is associated with being overweight or obese, because extra weight can affect the musculature of the upper respiratory system. Women who have already gone through menopause are more likely to develop sleep apnea because postmenopausal weight gain is more likely to occur in the upper body than it does prior to menopause. Sleep problems and obesity are related in many ways; getting less sleep or poor quality sleep can cause people to gain weight or have trouble losing weight. People with diabetes and/or metabolic syndrome are also at higher risk for obstructive sleep apnea.
Besides disturbing sleep and causing fatigue, apnea can lead to other serious health conditions, especially cardiovascular problems like high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and stroke. Sleep apnea can increase the heart rate and the production of stress hormones. Men with OSA are more likely to experience erectile dysfunction (ED). Lack of quality sleep can also have a negative impact on mental health, contributing to depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
The typical treatment for snoring involves the use of a sleep apnea machine, called a CPAP machine (continuous positive air pressure machine), which pushes air into the nose while you sleep, ensuring that the airway stays open and continuously active. This treatment can help people breathe easier throughout the night, but some people may find the machine noisy and uncomfortable.
TCM methods like acupuncture treatment for snoring and sleep apnea offer a way to address these problems at their source holistically, helping people to sleep well and breathe more freely.
Top 3 Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea causes loss of oxygen due to shallow breathing (hypopnea) and/or interrupted breathing while sleeping. Different types of sleep apnea are classified by their physiological causes:
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) – this is caused by the improper relaxation of the throat muscles while sleeping.
- Central sleep apnea (CSA) – is caused by disordered signalling from the brain to the organs that control breathing.
- Complex sleep apnea – (or treatment emergent sleep apnea) is a combination of both of the above.
Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis-Ekbom disease, is a condition wherein a person has an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, or sometimes arms or other parts of the body, accompanied by a sensation of itching, burning, crawling or throbbing. This usually happens when the person is lying in bed, trying to fall asleep. Restless leg syndrome can coexist with OSA, compounding the problem by making it difficult to get to sleep or stay asleep during the night.
Narcolepsy is a sleeping disorder in which overwhelming sleepiness during the daytime causes people to suddenly and uncontrollably fall asleep. Many people who suffer from narcolepsy also have sleep apnea. In this case, the sleep problem is not related to breathing so much as how the brain and body are moving through sleep cycles, like REM sleep. For people who have narcolepsy, treatment with a CPAP machine is often not very helpful.
Sleep apnea or snoring does not seem to be related to other abnormal sleeping behaviors (parasomnia), such as sleepwalking, night terrors, or sleep-related eating.
Top 10 Symptoms of Sleep Apnea

Many people snore and do not realize it. It is important to pay attention to the subtler sleep apnea symptoms. Signs of sleep apnea include:
- Loud snoring
- Interrupted breathing – moments during the night when the person’s breathing actually stops and then starts again
- Gasping for air while sleeping
- Waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat
- Headaches in the morning
- Insomnia, difficulty getting to sleep or staying asleep during the night
- Feeling very sleepy during the daytime (hypersomnia)
- Difficulty paying attention
- Feeling irritable
- Getting up often during the night to urinate (nocturia)
What Causes Snoring?

Sleep apnea is caused either by a physical obstruction of the throat and airways or by problems with brain signals to the breathing apparatus. Not everyone who has sleep apnea snores loudly. On the other hand, not everyone who snores necessarily has sleep apnea. Other reasons people snore may include:
- Congestion of the nose due to a cold or allergies
- In late pregnancy, the growing belly puts upward pressure on the respiratory system
- Sleeping pills, medications that work as relaxants, like Ativan or Valium
- Alcohol consumption
- Anatomy – large tongue or uvula, or swollen tonsils
People with sleep apnea are often advised to sleep on their side rather than on their back, as this helps prevent the obstruction, but it can be difficult for people to control their behavior while sleeping.
Treatment for Sleep Apnea

To firmly establish whether a person has sleep apnea, and what type, doctors will often evaluate the situation in a sleep study session. People will spend the night in a sleep center, where their heart and breathing functions are monitored (polysomnography).
CPAP machines are generally considered to be the best care available for sleep apnea. These devices can help stop snoring, allow a person to get more restful sleep, and cut the risks of serious issues like heart disease that are associated with sleep apnea. However, the machine does not actually do anything to improve the weak musculature that causes OSA or the disordered signalling that causes CSA. It is possible to swallow air while breathing with the CPAP machine, which can lead to gas and a bloated stomach. Some people may find the face mask, which must be strapped to the face, uncomfortable. The noise of the machine may be disturbing to the person using it, as well as to the person’s bed partner. It may be difficult for some patients to get used to using the machine, and if they are not using it regularly, they are not getting the health benefits.
There are also some oral appliances available, such as mandibular advancement devices (MAD), which are worn in the mouth to alter the placement of the jaw and tongue in order to keep the airway open during sleep. These can also be effective in terms of helping people breathe better while they sleep. Compared to CPAP, they are quiet, discreet, and cost-effective. Again, the main question is whether a person will be able to tolerate the device; some people may experience toothache or dental pain, TMJ jaw pain, dry mouth, or too much saliva.
Surgery for snoring and sleep apnea is usually only recommended if other methods of treatment have failed. Different procedures involve removing soft tissues (uvula, tonsils, adenoids), or changing the shape of the jaw bones. Small rods may be inserted into the upper palate to help keep the airway open. A device that monitors breathing and stimulates movement of the tongue may be implanted in the chest.
Sometimes people may use melatonin as a natural sleep aid. Melatonin may have a positive impact in terms of helping people fall asleep more easily. It also has strong antioxidant properties, which means it may help with the control of the breathing apparatus and the amount of oxidation a person is getting while sleeping. While it is generally considered safe as a health supplement, melatonin side effects can include problems with dizziness, headaches, and nausea, and it can also be contraindicated with other medications. Melatonin can affect blood coagulation, so it may be unsafe to take if a person is also taking blood thinners, for example.
Can Acupuncture Help Stop Snoring?
According to TCM theory, the spleen and stomach are responsible for transforming nutrients from food and fluids into Qi (life energy), which is then delivered to the heart and lungs. In the TCM view, sleep apnea is often a problem related to phlegm and Qi stagnation, as are many conditions related to fatigue or insomnia. If phlegm builds up and becomes stagnant in the spleen, the lungs cannot get the Qi they need. So, one possible differentiation for sleep apnea is Spleen Deficiency with Qi Stagnation. This condition of dampness and phlegm will often cause people to feel heavy and bloated.
In some cases, too much internal heat contributes to the problem. Snoring, combined with sweating, and waking up with a sore throat, is a sign that we need to clear heat and toxicity from the body.
Sleep disturbed by nightmares is associated with the gallbladder, while difficulty falling asleep is associated with the liver. An acupuncture practitioner will listen carefully to what specific symptoms of sleep apnea each individual patient is experiencing, and tailor the treatment accordingly.
A meta-analysis of over 200 randomized trials involving the use of acupuncture to treat sleep apnea concluded that acupuncture was more effective overall than CPAP treatment, in terms of improving breathing and oxygen levels.
Can Chinese herbs help snoring and sleep apnea? Specific herbs have been shown to help reduce inflammation and improve oxygen levels in patients with sleep apnea. Chinese herbal formulations can help stop snoring and reduce daytime fatigue.
Natural Remedies for Snoring

Acupressure can help snoring and sleep apnea. Since we are trying to clear heat and phlegm from the stomach, spleen, and large intestine, use acupressure points along the Stomach Meridian, which runs down the leg. On the front of the shin, apply pressure, kneading with your thumb, starting to the side of the shin bone a few inches below the knee, then moving down about 3 inches and doing the same thing. Knead each of the four points about 30 times as your move down the leg. If you are aware that one side of the nose is more blocked than the other while you are breathing during the night, practice the acupressure on the opposite leg. For example, if your left nostril is the one that is more stuffed up, do acupressure on the right leg.
Acupuncture Near Me for Snoring
As the population ages, and unfortunately, more people suffer from obesity and metabolic syndrome, sleep apnea is a growing health concern all over the world. Snoring can have a seriously negative impact on quality of life, health, and longevity. Conventional methods of treatment for sleep apnea can be effective, but many people find CPAP uncomfortable and inconvenient for long-term use. If you suspect you may have sleep apnea, or are worried because your partner snores loudly at night and seems to be gasping for air, do not wait to get help. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help relieve fatigue due to snoring and reduce the risk of more serious problems related to sleep apnea.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.