-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Can Acupuncture Help Bad Breath?
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

October 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Chinese Medicine
How to Treat Irregular Heartbeat With Acupuncture and TCM

Does if feel like your heart “skips a beat,” or your heart is “fluttering?” Maybe you feel your heart beat is fast or slow, compared to your normal heart rate. Lots of things can cause your resting heart rate to be uneven. Acupuncture and TCM can be beneficial as both an adjunct or alternative to drug therapy for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and other types of arrhythmia that cause heart palpitations or a fast heart rate.
The pulse rate is controlled by electrical impulses that originate in the sinus node, which is located in the right atrium, or upper chamber, of the heart. The feeling that your heart rhythm is off, or different from your normal pulse rate is called Arrhythmia. The average resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. A fast heart rate–more than 100 beats per minute–is called tachycardia. A slow heart rate–less than 60 beats per minute– is called bradycardia.
It is natural to have a slightly high heart rate during or just after exercise, or or a slow heart rate during sleep or times of relaxation, as when meditating. In some cases, a rapid heartbeat is related to anxiety or panic attacks. Sometimes a rapid or irregular heart rate may be related to caffeine consumption or a side effect of some medication. Other times, it may be a sign of heart disease or other chronic condition that needs to be addressed. Other symptoms related to irregular heartbeat include: shortness of breath, chest pain, sweating, and dizziness.
The heart is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are called the atria, into which blood is received, and the two bottom chambers, the ventricles, from which blood is pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body. Medical science classifies deviations from a normal resting heart rate both according to their rapidity and the chamber of the heart that seems to be problematic.
There are different medications available to help restore the regular rhythm of the heart, as well as therapies that deliver electrical impulses to the heart through a catheter, and devices, such as pacemakers or defibrillators.
In many cases, arrhythmia is not a serious problem. But in other cases, it can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and other life-threatening conditions. It is advisable to consult a medical professional if you are having an irregular heartbeat often enough to be concerned.
Acupuncture and TCM offer a natural way to help restore heart function and a good resting heart rate without the unwanted side effects of medications or invasive procedures.
Top 10 Types of Irregular Heartbeat

There are many different terms that describe deviations from a regular, healthy heart rate. Some irregular heartbeat issues are due to congenital conditions, while others may occur due to trauma, disease, or aging.
- Atrial flutter – an accelerated heart rate that occurs in an organized and rhythmic way due to rapid electric impulses in the atria.
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib or AF) – a rapid heart rate, also caused by increased electrical impulses in the atria that happen in a chaotic, arrhythmic way. Fibrillation refers to the rapid and irregular movement of muscles. In the case of AFib, the upper chambers of the heart quiver quickly. This condition is associated with stroke. AFib with RVR (rapid ventricular response) is a condition that occurs when patients are critically ill, often in the ICU, when the atrial fibrillation causes the ventricles to beat faster.
- Ventricular fibrillation – rapid impulses in the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart) cause ineffective pumping of blood out to the body.
- Supraventricular tachycardia – this refers to types of arrhythmia that originate in the atria (above the ventricles) and cause brief episodes of accelerated heart rate.
- Ventricular tachycardia – a fast but regular heart rate that does not allow the ventricles to fill with as much blood as usual.
- Sick sinus syndrome – more common among older people, this is when the sinus node is malfunctioning and may sometimes cause a fast heart rate, and other times, a slow heart rate.
- Long QT Syndrome – a heart disorder found in people with a particular genetic mutation that causes rapid heartbeat and fainting spells.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome – some people are born with an extra electrical pathway that can cause extra or irregular signalling to occur.
- Conduction Block – a block of the electrical pathways that sometimes results in a slower heart rate.
- Premature ventricular contractions – this is when an extra heartbeat beat originates from the ventricles, rather than the atria. It can feel like a “skipped” beat, or your heart pounding or jumping in your chest, but it is actually a kind of extra beat. This can happen occasionally due to drug stimulants like caffeine or nicotine, or other medications like decongestants or antihistamines. It can also be due to heart disease creating scarring in the ventricles or in the structural parts of the heart that hold the pathways for electrical impulses.
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of blood clots and strokes because blood is not being effectively pushed from the atria into the ventricles, so blood pools or collects in the atria.
What Causes Irregular Heartbeat?
In general, most types of arrhythmia are caused by some disorder of the electrical conduction system that controls the beating of the heart valves, or weakness of the heart itself, which is known as cardiomyopathy.
Causes of tachycardia include:
- Not enough blood nourishing the muscles of the heart.
- Dilation or one or more valves of the heart, meaning that the muscle tissue becomes thinner and the chamber becomes enlarged.
- Thickening of the walls of the heart chamber makes them stiff; this is known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Scar tissue makes the heart tissue more rigid (restrictive cardiomyopathy or dysplasia). This can happen due to inflammation, high levels of iron or protein in the tissues, sometimes as a side effect of cancer treatments (radiation and/or chemotherapy). Arrhythmic right ventricular dysplasia may be an inherited condition.
Causes of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter include:
- High blood pressure
- damage to the heart from a heart attack or heart surgery
- Coronary artery disease
- Congenital heart defects
- Hyperthyroidism
- Lung disease, infections, or pneumonia
- Sleep apnea, snoring
- Smoking or overuse of other chemical stimulants
Chronic conditions like diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, kidney problems, alcoholism, Parkinson’s disease, or a family history of heart problems increase a person’s risk for developing an arrhythmia.
Treatment for Irregular Heartbeat
There are several different types of medications to treat irregular heartbeat. Tachycardia may be treated with antiarrhythmic drugs, which work by suppressing or depressing the electrical impulses that are misfiring or transmitting signals too quickly. Beta blockers slow down the heart rate and reduce blood pressure by reducing the production of adrenaline. AFib treatment often involves anticoagulants or blood thinners, which prevent the formation of blood clots. In some cases, these medications can work to help people maintain a steady heart rate and prevent serious events like strokes. The downside is that they must be taken daily on an ongoing basis, and in some cases, they can actually cause the heartbeat to become even more erratic.
Medical procedures that are designed to help irregular heartbeat include: electrical cardioversion, in which an electric shock is used to help “reset” the heart rate, and ablation, in which the tissues that contain the electric impulse pathways are intentionally scarred in order to reduce their output. Implantable devices such as defibrillators or pacemaker monitor the heart rate and deliver small “shocks” to alter the rhythm of the heartbeat. For some people, these methods work to keep the heart functioning. In some cases, though, the surgery to implant the device causes complications or damage to critical tissues around the heart or lungs.
Can Acupuncture Help Irregular Heartbeat?

In conventional medicine, and indeed, in Western culture, the heart is seen as one of the most important, if not the most important, organ in the body. Not only does it supply the whole body with oxygenated blood, but it also is associated with our deepest emotions. TCM also views the heart as a central organ that governs the blood and vessels, and also the mind and spirit.
The traditional diagnostic methods employed by TCM practitioners can tell us a lot about the health of the heart. The feeling of the pulse gives us detailed information about the strength, quality, and speed of the heart rate. According to TCM theory, the heart “opens” out into the face, and so observing the pallor or color of the face, the brightness of the eyes, and the appearance, especially, of the tongue, also gives the acupuncturist vital information about the heart.
TCM providers classify different causes of irregular heartbeat by looking at the whole concert of presenting symptoms:
- Heart Qi deficiency or Blood deficiency: may happen after a long illness or loss of blood and be marked by heart palpitations, dizziness, memory problems, and/or insomnia. The pulse will be weak, and the tongue pale pink.
- Kidney yin deficiency with Heart Fire: chronic illness can deplete the kidneys so that they can no longer manage the balance of fluids and heat, so heat rises and disturbs the Heart. With this presentation, a person may be experiencing strong feelings of fear or anger, depression, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and stomach problems.
Depending on the type of arrhythmia, the acupuncturist will choose acupuncture points and herbs to clear heat and dampness, nourish the blood, and calm and strengthen the heart. Specific herbal formulae work to activate and maintain blood flow, removing stasis, while also helping to protect the spleen and stomach.
A controlled study that compared patients with arrhythmias and tachycardias who were treated with medication (Lopressor) versus patients treated with both the medication and acupuncture and Chinese herbal formulations. The patients who received integrative care showed statistically very significant improvement over the patients using medication only.
A systematic review of randomized trials that compared acupuncture treatment versus typical medication treatment found that both types of treatment were equally effective for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, that acupuncture in addition to medication was effective for ventricular premature beat, and that acupuncture was beneficial over no treatment at all for sinus tachycardia.
Acupuncture Near Me for Irregular Heartbeat
Unfortunately, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death among Americans. Over five million people in the U.S. experience atrial fibrillation, or heart flutter. The conventional methods of treating heart problems such as AFib and other types of arrhythmia can work, but they require people to become completely dependent upon medications or devices. These methods of treatment are also very expensive. Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative or adjunct approach that can help improve heart function and restore a healthy heart rate without side effects.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Hemorrhoids With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Bleeding and discomfort when you go to the bathroom? Burning or itching around the anus? Hemorrhoid pain is caused by swollen blood vessels around the rectum. Acupuncture and TCM reduce inflammation and can bring swift hemorrhoid relief.
Sometimes called “piles,” (from the Latin “pila,” meaning “balls”), hemorrhoids often do resemble little balls or clusters of grapes. The word “hemorrhoid” actually refers to the specific formation of blood vessels and cushioning tissues that surround the anus. Colloquially, though, the term is usually used to describe the condition of inflammation and irritation that can occur in this area.
Hemorrhoids are very common; probably more than half the population experiences them at some point in their life. However, the discomfort of talking to a doctor about hemorrhoids can be almost as miserable as the physical discomfort of having them, so many people avoid getting hemorrhoid help.
How do you know if you have a hemorrhoid? Sometimes people have a lot of itching, burning and discomfort after a bowel movement, or throughout the day. Sometimes there is no pain, but you may see a little bit of blood in the toilet bowl, or when you wipe with toilet paper. When you touch the area, you may feel a lump, or swollen tissue.
Hemorrhoids are generally classified into two categories based on their location: internal hemorrhoid and external hemorrhoid. Internal hemorrhoids form inside the anus and lower rectum and can cause bleeding, usually without pain. In some cases, though, the swollen veins can protrude out from the anal sphincter during or after a bowel movement and then need to be pushed back in. This is called a “prolapsed internal hemorrhoid.” The situation can become more serious if the internal hemorrhoid can’t be pushed back in, or if a blood clot develops in the vessel (thrombosis); then, it becomes painful to go to the bathroom, or even sit. In some cases, a prolapsed hemorrhoid becomes “strangulated,” meaning the blood supply is cut off, which can cause severe pain. Hemorrhoids become prolapsed because the connective tissues in the area weaken due to intense pressure, usually due to straining during a bowel movement, or because of the extra weight of pregnancy or obesity.
External hemorrhoids develop outside the anus, under the skin. These are the kind of hemorrhoids that tend to cause itching and a little bit of bright red bleeding. Again, they are aggravating, but not too serious unless a blood clot forms; then, it is called a “thrombosed external hemorrhoid.” This type of hemorrhoid can turn blue or purple in color and become acutely painful. In some cases, surgery will be performed to drain blood from the clot, or remove the hemorrhoid.
Most of the time, people suffer quietly with hemorrhoids, waiting for them to go away on their own. Only when they cause severe pain and bleeding are medical treatments considered. However, TCM and acupuncture offer a way to deal with hemorrhoids so that they heal more quickly and reduce the chance to return.
Top 10 Hemorrhoid Causes

What causes hemorrhoids? The tissues and blood vessels around the anal area can become weak, irritated, and inflamed. The upright posture of our human bodies naturally puts pressure on the elimination organs. Many women get hemorrhoids during pregnancy and/or birth because of intense pressure on the perineal area.The major reasons for hemorrhoids include:
- Pregnancy
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Straining while on the toilet
- Sitting too long on the toilet without progress
- Lack of dietary fiber
- Obesity
- Family history of hemorrhoids
- Aging
Overall, focusing on eating a diet that includes plenty of fiber, drinking enough water, maintaining good bathroom habits (going when you feel the urge and not waiting) and a healthy weight will go a long way towards preventing hemorrhoids. But what can you do when you already have hemorrhoids?
Treatment for Hemorrhoids

Often, people will just deal with hemorrhoid itching and pain on their own by using over-the-counter products like creams that contain phenylephrine, which constricts blood vessels (Preparation H), or disposable wipes impregnated with witch hazel and other soothing ingredients (Tucks medicated pads). These treatments may help reduce pain and swelling temporarily, but they do not get rid of hemorrhoids at their root.
When people do talk to their doctor about hemorrhoids, they may be prescribed something stronger, like a steroid cream, or hydrocortisone rectal suppositories.
If the situation persists or becomes more severe, there are several types of outpatient procedure to treat hemorrhoids, including rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, infrared photocoagulation, and electrocoagulation. All of these procedures cut off blood supply to the hemorrhoid, so that it will form scar tissue and fall off. Hemorrhoid stapling and hemorrhoidectomy are outpatient procedures in which the hemorrhoids are surgically removed, and/or prolapsed tissues are affixed back inside the anus. While these surgeries may be helpful in some cases, recovery can be painful, and there can be problems with the way things work afterwards, potentially leading to more surgery later on.
When hemorrhoids are severe, it is a good idea to consult your doctor, as there are more serious conditions that may produce similar symptoms of pain, itching, or bleeding, including anal fissure (torn tissue or open sore in the anus due to trauma or Crohn’s disease complications), anal abcess (infected cavity in the anus) or anal fistula (an opening from the anal or rectal area that drains pus and/or fecal matter). Sometimes skin tags develop around the area where a hemorrhoid has healed. These can be irritating and difficult to keep clean, so they may need to be surgically removed.
For the treatment of hemorrhoids, TCM methods can provide relief from symptoms and help to reduce the inflammation that caused them.
Can Acupuncture Help Hemorrhoids?
According to TCM philosophy, hemorrhoids can often be related to a build-up of heat and/or dampness in the lower abdominal area; it’s the heat and dampness that cause the blood vessels to swell. You might be concerned by the idea that acupuncture treatment for hemorrhoids would involve needles being placed in a highly sensitive, private area. Let us reassure you this is not the case. The Du Mai meridian, also known as the “Sea of Yang,” is the channel which runs from the rectum area up along the spine to the top of head and then down to the mouth, controlling Yang energy throughout the body. We use points along this meridian, on the top of the head, and in other parts of the body to draw excess heat and dampness away from the area where the hemorrhoids are.
Other presentations of hemorrhoids include:
Top 5 Types of Hemorrhoids Presentation in TCM
- Spleen Qi Deficiency – This is when people tend to have poor digestion, bloating, gas, and diarrhea, going to the bathroom very often; the hemorrhoids feel swollen, but not as red. We use moxibustion to work on stomach point 36 meridian point, CV points 6 and 4, and spleen 6 in the middle of the abdomen to help digestion.
- Spleen Qi Sinking- This presentation tends to happen to people who are thinner, not only having hemorrhoids, but all the organs tend to be lower than usual; may also have prolapsed bladder or uterus, and poor digestion. Moxibustion applied to the middle of the top of the head will head the Qi rise up. For both types, doing Kegel type exercises regularly can help to strengthen the rectal area, also the uterus and bladder. Do three sets, increasing a bit every time: for example squeeze 30 times, release, do again 35, rest, next 40, then rest. Do this exercise every morning and evening.
- Blood Stasis – This type is more and more common because of our modern lifestyle, due to sitting a lot for work, which causes blood circulation to be compromised. In Chinese, we have a proverb: “for 10 people who sit too long, 9 will have hemorrhoids.” These manifest more as red, swollen, maybe bleeding. Kegels will also be helpful here, too.
- Lower Jiao Fire/Heat – This is when the lower part of the body has too much fire. For this type of hemorrhoids, people tend to have more bleeding, especially triggered by having alcohol, spicy food, crunchy food. These are the kind that may feel very sore with a burning sensation and tend to bleed, especially when wiping.
- Intestinal Dryness – especially here in California, where we have hot, dry weather, without a good habit of drinking water, people can tend to constipation, even going only once or twice a week. These types of hemorrhoids are due to dry, uncomfortable bowel movements, and may have itching and bleeding. Adding more water (warm is better) and more moisturizing foods (sesame oil and lots of ripe bananas, flax seeds, chia, sweet potato/yam, prunes) will be helpful.
Kegel type exercise is helpful for all of these types, to strengthen the sphincter muscle and bring more circulation to the area. Add more movement overall. At bedtime, leg lifts, bicycle movements in the air, upside down, are a good way to exercise without putting pressure on the lower body.
Ideally, when there is good digestion, between 5:00 – 7:00 a.m. is when people should naturally want to go, quickly, without too much need to push. Sitting on the toilet for too long creates the pressure that leads to hemorrhoids.

Moxibustion treatment–the burning of the herb mugwort near an area–can be very effective for reducing pain quickly. Chinese herbal formulations, used both internally and externally, can help relieve inflammation and pain. An herbal tea formula may include herbs to help strengthen the energy of the spleen, and to lubricate the digestive tract.
We also recommend sitz baths as a home remedy for hemorrhoids: short, 15-minute baths in warm water, to help soothe the area and keep it clean. Your acupuncturist may give you an herbal bath sachet to use to help reduce inflammation and soother the tissues.
One study of acupuncture treatment for internal hemorrhoids showed that, after 24 days, 86% of patients were “cured,” while another 8% showed significant improvement.
Your acupuncture practitioner will also talk with you about changes you can make in your diet and bathroom habits that will help you get things moving more easily.
Acupuncture Near Me for Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are not only irritating; they are a sign that you may need to pay more attention to what you’re eating, and that you need to give yourself a little more time for relaxation, in and out of the bathroom. A combination of acupuncture, herbs, and other TCM treatment for hemorrhoids can help get the pain and swelling behind you.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How To Treat Dizziness With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Feeling light-headed and dizzy? Maybe you feel like your head is spinning, or that the world is spinning around you? Headache, nausea, dizziness, and vertigo are symptoms that can be caused by a variety of health problems. Acupuncture and TCM offer vertigo treatment that can help relieve that sense of dizziness and nausea, or feeling light-headed and tired all the time.
Feeling dizzy is one the most common reasons that people go in for a doctor’s visit, or even visit the emergency room. Dizziness is a fairly general term that can mean anything from feeling light-headed, woozy, faint, off-balance, or unsteady to feeling nauseated or like you’re about to pass out.
Vertigo is a specific type of dizziness that refers to a sensation of spinning, as if the room around you is moving. You might feel like you’re leaning to one side, or about to fall over. It can make you feel sick to your stomach, similar to motion sickness. In popular culture, the word “vertigo” is sometimes used to mean a “fear of heights,” but that is actually called “acrophobia.” The sensation of vertigo can be triggered by looking down from above, or looking up at something very tall, but this is not the cause of most episodes of vertigo.

Vertigo causes include migraines and problems with the inner ear. The inner ear and eyes both relay information to the brain about a person’s spatial relation to the environment, so when the functioning of the eyes or ears is disrupted, it can cause a sense of imbalance, and even nausea. Migraine headaches, particularly a specific type called a vestibular migraine, can cause pressure in the head and dizziness and nausea.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is one type of vertigo that causes short-term bouts of sudden dizziness. Benign positional vertigo is caused by the shifting of calcium crystals (canaliths) in the inner ear. This can happen due to a head injury or simply aging.
Other inner ear problems that can cause signs of vertigo include Meniere’s disease and Labyrinthitis. Meniere’s disease is a chronic disorder related to abnormal amounts of fluid (endolymph) collecting in the inner ear. The exact cause of Meniere’s is unknown, but it develops more frequently later in life. Meniere’s disease causes attacks of vertigo that can last from a few hours up to 24 hours. Like migraines with an aura, there is often a period of time during which a set of “warning symptoms” begin to occur, such as: a feeling of uneasiness, being off-balance, headache and dizziness, queasiness, hearing loss or ringing in the ears, or extra sensitivity to sound. Once an attack of vertigo hits, it can be quite severe, causing intense pressure in the ear, blurred vision, vomiting or diarrhea, cold sweats, rapid heart rate, and feelings of fear and panic. There is currently no cure for Meniere’s.
Labyrinthitis refers to inflammation of the small parts of the inner ear, or around the nerves of the inner ear that can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, such as: a flu, measles, herpes, hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, chicken pox, or childhood ear infections. Symptoms of labyrinthitis can include: dizziness, nausea, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and difficulty concentrating.
Lightheadedness is a similar sensation to dizziness in some ways, but is usually caused by a sudden change in blood pressure or the flow of blood to the head. You have probably experienced feeling light headed and dizzy when you get up too fast from sitting or lying down. Other causes of lightheadedness include: allergies, anxiety, anemia, hyperventilating, arrhythmia, or heavy bleeding (as during menstruation).
Dizzy spells happen to everyone once in a while. But recurrent headache and dizziness should be addressed. Acupuncture and TCM have been used to help dizziness for thousands of years and offer natural solutions to the underlying causes of vertigo.
Top 10 Causes of Dizziness

Feeling light headed and dizzy, or having headache, nausea, dizziness, can occur as symptoms of a variety of imbalances. Reasons for dizziness may include:
- Inner ear imbalance, or labyrinthitis
- Meniere’s disease
- Sleep apnea, snoring
- Migraine – vestibular migraine
- Dehydration – alcohol, diuretics
- Sinus issues
- Ear infection
- Low Blood Sugar – diabetes, hypoglycemia
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Prescription Medication side effects
Dizzy spells that occur first thing in the morning are common for some people. This can be simply due to the change in pressure in the ear when you get out of bed. Waking up dizzy due to sleep apnea occurs because this condition obstructs your breathing during the night, and you may have lower oxygen levels when you wake up. Being dehydrated is another common cause of dizziness, which is exacerbated by drinking alcohol before bed. In general, drinking too much caffeine, too much alcohol, and not enough water, or taking diuretics can all lead to dizzy spells. Low blood sugar, whether due to diabetes, or simply not eating regularly enough, can also be a cause of light-headedness. Hepatitis, HBV, or HCV can also cause dizziness.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) causes dizziness when moving from a seated or position or lying down to standing up.
Cervical vertigo, or cervicogenic dizziness, is another type of vertigo caused by the positioning of the neck or cervical spine; in this case, the feelings of imbalance and spinning may be accompanied by neck pain. This type of vertigo may happen, for instance, after a whiplash injury.
Treatment for Vertigo
The medical treatment for dizziness and vertigo depends wholly on the underlying causes for the symptoms. If a bacterial infection in the ear is confirmed, then antibiotics may be used. In cases of BPPV, a canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is a non-invasive technique that can help the crystals within the inner ear move back into their proper place. Migraine-related vertigo may be treated with the medications typically prescribed for migraines. Anti-nausea drugs like Dramamine may be suggested. Patients suffering from cervical vertigo may be referred to physical therapy to help improve the positioning and strength of their neck/cervical spine.
Can Acupuncture Help Dizziness?

One of the central concepts of TCM is that of the root and the branches. The branches are the visible, outward signs or symptoms of a problem, while the root refers to what is going on deeper in the organ systems of the body. In the cases of dizziness and vertigo, there is deficiency in the root and excess in the branches.
Pathogenic factors involved in dizziness and vertigo are phlegm, wind, fire, and deficient Qi. When there is weakness in organs like the spleen, stomach, kidney, or heart, pathogens like wind, heat, and phlegm can take hold. The San Jiao, also known as the “triple burner,” is another important concept in TCM; one of its primary functions is to control the movements of fluids in the body so that they don’t collect and build up inappropriately. In case of vertigo, phlegm and heat develop to the point of causing stagnation and malfunctioning of the Jiao, pushing phlegm upwards in the body. An acupuncture practitioner will carefully listen and observe to discover which organ systems are out of balance, and work to strengthen those areas. For example, dizziness combined with emotional disturbances like anger and depression is a sign of too much wind or heat in the Liver. Weakness in the heart or spleen may follow a long illness or period of stress and anxiety. Too much phlegm, heat, and dampness in the stomach and spleen can result from an improper diet and too much stress.
Acupuncture and herbs to tonify these organs and clear heat and phlegm will take care of the root of the dizziness. Meanwhile, specific acupuncture points can have an almost immediate effect at relieving immediate discomfort, facilitating a natural vertigo cure.
A study conducted at a hospital in Taiwan used acupuncture to treat patients with dizziness and vertigo. The findings conclusively showed immediate improvement in symptoms.
A study of 60 patients who were admitted to an emergency room suffering from vertigo from a variety of causes, including Meniere’s and BPPV, showed that acupuncture treatment provided immediate relief of symptoms and is therefore a good alternative for dizziness due to various causes.
Top 5 Tips to Get Rid of Dizziness
Depending on the cause of the vertigo, there are different ways to manage with TCM techniques, including vertigo exercises, acupressure for dizziness, moxibustion, and foods to avoid.
Major 4 types of Vertigo/Dizziness presentation:
- Hypertension type – When a person has high blood pressure, too much liver yang, and is overheated, it can cause dizziness. For this, we use acupressure Liver points 2 and 3 on the toes.
- Qi and Blood deficiency – if a person shows signs of anemia, or has heavy periods, hemoglobin is low, or if a person has chronic conditions, or has suffered a major injury, or recently given birth, experienced major blood loss. For this we want to ensure a good diet with plenty of soups and easy to digest foods. Moxa on the back can help to strengthen the body’s Qi and produce enough blood. Qi Gong exercise of squeezing the earlobes and outer ear up and down is helpful.
- Kidney essence deficiency – this could be due to some constitutional weakness, or due to old age, or someone who tends to have chronic illness, diarrhea. The kidney essence can’t support rising essence to the head. For this, acupressure for Kidney 1 – on the bottom of the foot.
- Phlegm stagnation – when the middle jiao is not working due to stagnation of phlegm creating blockage so Qi cannot ascend. This happens when people are overweight, or have poor digestion, diarrhea. Avoid dairy and fried foods, which encourage phlegm. Moxibustion treatment to the back is helpful, and applying pressure to Stomach-36 acupressure point can help the middle jiao open up.
- Neck Pain – if a neck problem is causing a blockage, due to a neck disease or bulging disc, unhealthy cervical disks, compression, tension, and muscle spasms can block upwards energy. Exercises to encourage the health of the neck discs, loosen up the muscles and allow flow of Qi and blood up to the head. Your acupuncture practitioner will recommend neck exercises to help with this.
Acupuncture Near Me for Dizziness
Vertigo and dizziness may not be life-threatening symptoms, but they can have a big impact on your daily life. Frequently being blindsided by unexpected dizziness, spinning sensations, nausea, and headaches is unsettling and debilitating. Medications can be helpful in some cases, but they can also cause unwanted side effects. Getting to the root cause of vertigo with acupuncture and TCM will help get rid of dizzy spells so they don’t keep coming back.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat TMJ With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
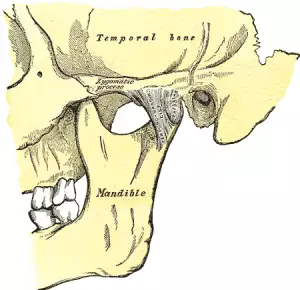
What is TMJ? “TMJ” is an acronym for “temporomandibular joint,” which is the double joint structure that attaches the lower jaw to the skull. “TMJ” is also used as a general term to refer to disorders of the jaw joint. Popping or clicking of the jaw joints, tension or pain in the jaw, grinding teeth, headaches, neck pain, and shoulder pain can all be signs of a TMJ disorder, or TMD. Acupuncture and TCM offer relief from TMJ jaw pain and inflammation.
The jaw joint is totally unique among joints in the human body in a few ways. It is really two joints that must always work together; you cannot choose to just move one side of your jaw. Also, the temporomandibular joint has two ways in which it moves; it “hinges,” and then, it “slides.”
Hinge joints, like the knees and elbows, allow flexion and extension on one plane, while remaining stabilized by a complex group of muscles, ligaments, and other connective tissues. Most of these joints are made of bones that are “molded” to fit and move together. Gliding joints, also called plane joints, like those in the ankles, wrists, and vertebrae, have flat sides that slide alongside each other when they move. The jaw joint combines both of these actions. Essentially the movement of the jaw is a kind of dislocation by design. Small discs of cartilage help to cushion the areas where the jawbone interacts with the sides of the skull in front of the ears.
It can be difficult to determine the exact causes of “TMD,” or temporomandibular disorders that cause pain and dysfunction. Injury to the jaw, dislocation of the jaw, inflammation of tissues, arthritis, and bruxism (clenching or grinding the teeth and jaw) can all potentially lead to jaw pain or clicking in the jaw. Erosion or damage to the cartilage sometimes causes TMD, impacting the usually smooth motion of the opening and closing of the jaw. Structural issues like missing teeth or an uneven bite can cause jaw problems. Dental and orthodontic work that requires the patient to hold the mouth open for long periods of time can sometimes lead to TMJ pain. Habitual movements like teeth grinding, biting on things like pencils, nail biting, or leaning your chin on your hand can also contribute to TMJ pain. Chronic pain syndromes like fibromyalgia can also cause jaw pain.
Most cases of TMJ disorders resolve themselves over time, usually within a few to several months. Resting the jaw and eating soft foods is usually recommended. Medical treatment usually involves medications to reduce inflammation and relieve pain while waiting for the jaw joint to gradually regain its normal function. Only in rare cases is surgery necessary to get rid of jaw pain.
TMJ, or myofascial pain in the muscles around the jaws, is experienced by a third or more of all adults at some point in their lives. TCM modalities like acupuncture can help alleviate the pain and impeded mobility of the jaw joint caused by TMJ disorders.
Top 10 Symptoms of TMJ

Pain around the jaw joints that comes and goes is the most common complaint of people with TMJ disorders. However, problems with the jaw can contribute to pain and tension in other parts of the head and shoulders, too. The most common signs of TMJ include:
- Pain in cheeks, tension in the jaw
- Jaw clicking, popping of jaw bones
- Limited movement of jaw, can’t open jaw normally
- Clenching of jaw, grinding teeth at night
- Tooth pain, pain in the back teeth
- Ear pain, ringing in the ears, tinnitus
- Headaches, migraines, pain behind eye, sensitive to light
- Stiffness in shoulders or neck, pain in neck, shoulder pain
- Numbness or tingling in arms, hands, or fingers
- Dizziness, vertigo
The combination of hard bony structures, muscles, and cartilage that are all involved in TMD causes TMJ pain that is hard to pinpoint because it may move around, and come and go. Most people describe the sensation as a dull ache. Some people don’t experience pain, but still have trouble with jaw clicking or opening and closing the jaw.
What Is the Treatment for TMJ?

A doctor or dentist may check for signs of TMJ by observing and manually examining the movement of the jaw joint. Dental X-rays may be used to help determine the cause of jaw pain. CT scan or MRI may be recommended to get a more detailed look at the bones and cartilage.
The primary recommendations for jaw pain and clicking is to rest the jaw as much as possible and eat only soft foods. Physical therapy (PT) can help strengthen the muscles of the face and encourage people to change habitual behaviors that might be contributing to TMJ. Wearing a splint or bite plate keeps the mouth and jaw in place and prevents grinding teeth in the night. This combination of PT and splinting is called stomatognathic treatment. If pain is serious enough to require further medical treatment, doctors will usually prescribe either pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants, or some combination of these. Surgery is only used in rare cases when the jaw has become “locked,” or TMJ inflammation and pain has become chronic.
Acupuncture and TCM treatment offer a way to reduce inflammation and pain related to TMJ disorders without risky surgical procedures or the adverse side effects sometimes caused by corticosteroids and other medications.
Acupuncture Treatment for TMJ
Acupuncture can work to reduce inflammation and pain from many different conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders like TMD. Acupuncture is effective at reducing sensations of pain, both by reducing inflammation in areas from which the pain is originating and by stimulating the release of endorphins and other neurotransmitters that help boost feelings of well-being. Acupuncture treatment can also help the muscles involved with jaw function to relax, alleviating the “clicking” or “popping” associated with TMJ disorders.
In TCM theory, TMJ is often related to what we call different types of “obstruction” syndrome. Stress and trauma, both physical and emotional, can cause Qi stagnation and/or blood stagnation. Pathogenic forces like cold, heat, wind, and damp can cause painful obstruction, or blockages of energy and blood in certain areas of the body. People suffering from TMJ do not necessarily only have dental pain or myofascial pain, a clicking jaw, or limited movement. They may also be experiencing a variety of other symptoms that are actually related. A TCM practitioner will look at the whole picture of what each patient is feeling, and treat accordingly.

For example, a person with Liver Qi stagnation may have:
- tension in the facial muscles
- neck pain
- feelings of anger or anxiety,
- ringing in the ear, tinnitus
- headaches
A person with a Wind/Cold Bi Syndrome presentation might feel:
- acute onset of pain
- pain moves around from one area to another
- aversion to wind and cold
- fever, chills
- ear ache, ringing in the ears
As a holistic form of medicine, TCM works not only to relieve jaw pain and swelling, but to get to the root of the problem.
A comparative study designed to evaluate TCM treatment for TMJ found that patients who received acupuncture treatment reported less pain and muscle tenderness than those that did not.
A clinical study that compared groups of patients who received acupuncture treatment for TMJ pain and limited motion to patients treated with decompression splints. Both groups experienced reduction in pain and increased mobility, and the researchers concluded that acupuncture can be considered beneficial as either an adjunct or alternative treatment.
In some cases, a stiff, painful jaw joint can be a secondary symptom of another, more systemic problem like rheumatoid arthritis or fibromyalgia. These conditions can also be addressed with acupuncture.
Acupuncture Near Me for TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders interfere with a person’s most basic activity: eating. While most cases of TMD improve within a matter of months with the proper rest, they can cause a lot of pain and frustration while a person is waiting to heal. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help relieve TMJ pain and restore normal jaw function, helping people get back to normal more quickly than rest alone. At Art of Wellness, we have over 30 years of experience helping patients with musculoskeletal disorders and pain of all kinds find relief and a return to their usual mobility.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Bloated Stomach With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac,. Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Do you feel constantly gassy or have a bloated stomach after eating? Digestive problems like gastritis or colitis can cause abdominal bloat. Stress and hormonal imbalances can also contribute to inflammation and bloated stomach pain. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help improve digestion and relieve abdominal bloating.
Abdominal bloating occurs when gas builds up in the gastrointestinal tract, filling the stomach and/or intestines with air. This can cause the belly area to get swollen and distended. Bloating can cause an inflated belly, sharp pain in the abdomen, belching and flatulence, nausea, or a sudden strong urge to go to the bathroom. Bloating can be related to fluid retention; this is sometimes called “water bloat.”
Problems with digestion that lead to a feeling of heaviness, “like a rock” in your belly after eating, are common. People who have been diagnosed with some type of functional gastro-intestinal disorder (FGID)–like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or dyspepsia (indigestion)–are extremely likely to experience abdominal pain and bloating after eating, while up to 30% of all people report having bloating at least some of the time. Inflammation in the walls of the stomach (gastritis) or intestine (ulcerative colitis) can also cause bloating.
Women often feel bloated before or during their menstrual period, and female reproductive disorders like endometriosis, fibroids (leiomyoma of the uterus), and PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome) can cause abdominal pain and bloating.
FGIDs can be very hard to manage; it may be difficult to get a clear diagnosis or effective medical treatment. Problems like constipation, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain and bloating are highly subjective, and people are often made to feel like it’s normal to have these issues, or that all they need to do is avoid certain foods.
Feelings of anxiety and depression are common among people who suffer from moderate to severe bloating on a regular basis. This can become a vicious cycle, as the pain and swelling of the abdomen causes anxiety, and the physiological effects of the emotional stress trigger the bloating to happen again and again. Sometimes people dread eating meals because they are so afraid of the painful and embarrassing bloated stomach.
Digestive upsets are complex to treat because there can be many factors contributing to the discomfort. So many different conditions can cause bloating, it can be hard to get a clear handle on the true cause. This is a case when TCM methods of diagnosis offer many advantages, because a TCM practitioner will be able to study the whole picture presented by a patient and pinpoint what underlying conditions are causing gas and distension. Acupuncture and herbs can help resolve abdominal bloating and other symptoms at their root source.
Top 10 Abdominal Bloating Causes

Why might someone feel bloated and gassy all the time? Many different types of gastrointestinal disorders can contribute to a bloated belly and excess gas, as can hormonal and emotional changes. What causes abdominal bloating can be one issue or a combination of factors:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Inflammatory bowel disease, Ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s Disease
- Gastritis, stomach ulcers, inflammation of the stomach
- Food intolerance, gluten intolerance, celiac disease
- PMS, menstruation
- Stress, anxiety, depression
- Pregnancy
- Constipation
- Liver disease
- Abdominal adhesions, or scar tissue from surgeries
Eating behaviors like eating too quickly, swallowing air while eating, or eating fiber-rich foods that cause gas like beans, can lead to bloating. Drinking a lot of carbonated beverages can lead to excess gas in the GI tract. Smoking can also be a factor. Some medications can cause bloating as a side effect, including antibiotics, oral birth control pills, opioid pain medications, medicines to relieve constipation, and even some supplements, like iron pills.
Cancers of the abdominal organs, such as ovarian cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer, or pancreatic cancer, can also cause bloating in the belly. Gallstones or gallbladder disease, gastroparesis, kidney problems, and liver problems can all cause stomach pain and bloating.
Medical Treatment for Abdominal Bloating
Many people do not seek medical help for bloating, trying to manage it on their own with over the counter medications that promise relief from gas pain and acid reflux. Antacids only help with the kind of bloating that is caused by food, though; they don’t help with bloating related to FGIDs, hormones, or emotional stress. When a person does ask their primary care doctor or even a gastroenterologist for help with bloating, they may find that the treatment options are very limited. Doctors will usually reassure patients that gas and bloating, while uncomfortable, are not actually dangerous. Then, they will often advise that patients go on a strict elimination diet, cutting out wheat, dairy, and most vegetables and legumes. Sometimes doctors will prescribe antibiotics to alter the balance of gut bacteria. Antidepressants are sometimes prescribed to help with bloating. Conventional medical science still has a ways to go to fully understand the underlying causes of digestive problems like bloating.
Because bloating is not viewed as a disorder in and of itself, not much serious research has been done to show what types of treatments work best to get rid of bloating. TCM treatment has been shown in a randomized controlled trial, a peer-reviewed study, and a hospital-based investigation to help in relieving stomach pain due to chronic gastritis.
How Can Acupuncture Help With Bloating?
TCM offers a multidisciplinary approach to the digestive problems, hormone imbalances, and emotional upsets that can cause bloating. An experienced acupuncturist is able to use methods of diagnosis such as studying the appearance of the tongue, feeling the pulse, and asking lots of questions about how and when the symptoms occur to find the specific pattern of imbalance that is causing gastric distress.
Different presentations of digestive conditions that may cause abdominal bloating and pain include:
- Spleen/Stomach Deficiency – characterized by symptoms: chronic bloating, poor appetite, feel worse after eating, pallor, and fatigue. This type of bloating can be caused by antibiotics, too much raw or fermented food, eating disorders, a long period of illness, or chronic inflammatory disorders.
- Damp-Phlegm – symptoms include: distended stomach, nausea, acid reflux, diarrhea. This type of bloating can be caused by dietary habits that include excess sugar, alcohol, fatty or fried foods, and dairy products. Can also be related to damp environmental conditions.
- Liver Qi stagnation – common symptoms are: stomachaches, stomach gurgling, belching, and constipation. This type of bloating can be caused by stress, feelings of anxiety or anger, and irregular, emotional eating behaviors.
TCM treatment for abdominal bloating will use acupuncture and herbs to bring the stomach and liver back into harmonious function, clearing phlegm and improving digestion. Treatment will be individualized based on the underlying causes of the imbalance; if reproductive hormones are involved, then that factor will be taken into consideration when preparing the herbal formula. If mental health issues are a factor, specific points will be added to help relieve anxiety. Naturally, your acupuncturist will have some clear instructions on how to optimize your nutrition to reduce bloating.
Top 5 Tips for How to Stop Bloating

While bloating may be caused by all sorts of different factors, there is no doubt that making some changes to your eating habits will probably have an impact on how bloated you feel. What helps bloating may be different for each person’s constitution or lifestyle, so it will be very helpful to have an in-depth conversation with your acupuncture provider about what bloating diet is best for you.
- Chew your food thoroughly. Many people eat fast, and don’t pay much attention to chewing their food well before they swallow. Food is really meant to be broken down and mixed with saliva in the mouth before it moves down the esophagus and into the stomach. Skipping this important step by swallowing half-chewed food means that your stomach has to produce more acid and work much harder to digest the food before it moves deeper into your gastrointestinal tract. Eating too quickly can also easily lead to eating more than you need. It takes about 20 minutes for your brain to receive the message that the stomach is full. Chew slowly, and enjoy every bite; this will improve your digestion.
- Avoid icy cold drinks and foods. Cold liquids are shocking and unfriendly to your internal organs, both those of the digestive tract and the female reproductive organs. Constantly drinking ice-cold beverages irritates the smooth muscle tissues of the stomach, intestines, and uterus. Drink more warm liquids, which are soothing to these organs.
- Ginger tea – many of our herbal formulations include slices of fresh ginger to help soothe the stomach and GI tract. Ginger helps the body to produce more of the digestive enzymes that work to break down food, and relieves cramping in the belly. All you need to do is keep a knob of fresh ginger on hand, cut two or three slices and steep in hot water as you would a teabag. Sip anytime, but especially before meals, to help relieve gastritis pain and bloating.
- Choose foods in harmony with the season. Raw foods are appropriate in the summer, but in the winter, it’s better to eat cooked foods. Eating more bitter-tasting foods, like dark leafy greens, helps the liver and kidneys.
- Use acupressure to help relieve bloating and gassiness. Acupoints are located along the meridians and correspond to various organ systems. Applying gentle, steady, downward pressure to acupoint ST36 (Zu San Li), which is associated with the stomach, can help to relieve bloating, stomach pain, nausea, and feelings of stress. ST36 is located on the outer edge of the shin bone, about 4 finger widths beneath the kneecap.
Acupuncture Near Me for Abdominal Bloating
TCM offers a holistic approach to digestive problems of all kinds. Symptoms like abdominal bloating, stomach pain, and gassiness are usually signs that there is a deeper problem. If you haven’t been able to solve the problem of bloating with conventional medicine or dietary changes, you may be able to get help for digestive difficulties with acupuncture and herbs.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.