-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Digestive Disorders
How to Treat Crohn’s Disease With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Abdominal pain that flares up, persistent diarrhea and stomach pain, bloody stool? These can be signs of Crohn’s Disease, an autoimmune disorder that affects the gastrointestinal tract. Along with ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease is a type of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help reduce the inflammation that causes IBD symptoms.
About 3 million people in the U.S. are living with Crohn’s disease; it can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. Crohn’s symptoms sometimes begin to show up in childhood or during the teenage years, but most people are diagnosed with Crohn’s in early adulthood. As it does tend to run in families, it is believed that Crohn’s is caused partially by genetic makeup, but even if you have a close family member who has Crohn’s that doesn’t necessarily mean you will get it.
Crohn’s disease is a type of autoimmune disease. In autoimmune disorders, the body’s immune system, which is designed to fight potentially dangerous pathogens, mistakenly attacks normal cells or tissues. In the case of Crohn’s disease, inflammation is caused by the body’s immune system launching an attack against bacteria that are normally present in the gastrointestinal tract to help with digestion. As with other autoimmune diseases (Lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), fibromyalgia, Type 1 diabetes, Graves’ disease, hyperthyroidism, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, etc.), the causes are not fully understood by medical science.
Symptoms of Crohn’s disease are similar to ulcerative colitis symptoms; both are related to chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The difference is the specific location. Ulcerative colitis only affects the colon, or the large intestine. Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth, all the way through the stomach, small intestine and large intestine, to the anal area.
IBDs create inflammation that causes pain, cramping, and compromises the healthy functioning of portions of the GI tract. Over time, Crohn’s can cause so much damage to the tissues of the intestines and other organs that surgeries are required to repair it.
Treatment of Crohn’s aims not only to reduce symptoms of nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, but to prevent this kind of damage. Conventional medicine for Crohn’s can help control the disease to some extent. TCM methods, used as an alternative or adjunct to pharmacological treatment for Crohn’s, can relieve symptoms and help to restore healthy digestion and bowel function.
Acupuncture and other TCM treatments such as moxibustion have been shown to help patients with Crohn’s disease by reducing inflammation, allowing for the repair and healing of damaged tissues in the GI tract, and reducing IBD symptoms like nausea and joint pain.
Top 5 Types of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s Disease is classified according to where in the GI tract inflammation is causing pain and problems.
-
Ileocolitis – affects the area where the small intestine connects to the large intestine, causing diarrhea and pain in the lower right abdomen.
-
Ileitis – affects just the lower part of the small intestine, causing diarrhea and abdominal cramps, weight loss, and possibly fistulas developing between sections of the intestine.
-
Gastroduodenal – affects the connection of the stomach to the small intestine, causing more upper GI symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
-
Jejunoileitis – affects the upper part of the small intestine, causing cramping and diarrhea
-
Granulomatous Colitis – Crohn’s that affects the colon area, causing diarrhea, rectal bleeding, bloody stool, and possible anal fistula or fissure. Skin rashes and joint pain are also more commonly seen with this type of Crohn’s disease.
Top 10 Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease

As with other autoimmune disorders, Crohn’s disease causes flares that come and go. You may have periods of time when everything seems fine, then some stress or change in your environment can trigger a flare up of IBD symptoms. Each person will have their own experience of Crohn’s symptoms:
- Diarrhea, explosive diarrhea, urgent need to go
- Stomach pain, lower abdominal pain, epigastric pain, stomach ache
- Stomach cramps, abdominal cramps, cramping
- Rectal bleeding, bleeding from anus, bloody stool
- Constipation, feeling like you can’t go or you still have to go even after you’ve gone
- Fatigue, tired all the time, chronic fatigue, low energy
- Poor appetite, not hungry
- Mouth sores, cold sores around mouth
- Red eyes, watery eyes, blurred vision, dry eyes, eye pain, sensitivity to light
- Swollen joints, joint pain, joint inflammation, colitic arthritis
When it shows up early in life, Crohn’s disease can affect a child’s growth and development. In adults, Crohn’s can cause weight loss and anemia. The chronic inflammation of the GI tract and persistent diarrhea associated with Crohn’s can impede the normal absorption of nutrients from food. Fevers, anemia, vitamin deficiencies, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances can all become concerns for someone with Crohn’s.
Other potentially related problems can include: kidney stones or other kidney problems, urinary problems, and inflammation of the bile ducts (pericholangitis).
More serious complications of Crohn’s involve tissue damage in the gastrointestinal tract, creating open sores or ulcers. An anal fissure is when there are tears in the rectal tissue, causing bleeding from the anus. A fistula develops when tissue breaks down between sections of the intestine, or between the intestine and the bladder, or the rectal area and the vagina. A stricture occurs when a section of the intestine becomes so inflamed that the passage becomes narrowed or blocked by scar tissue. Many people with Crohn’s disease end up having surgery to help remove these blockages, also called stenosis, due to bowel stricture, or to repair fistulas that have developed in the intestines.
Diagnosis and Medical Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
Again, as with many autoimmune diseases, it can be difficult to get a clear diagnosis for Crohn’s or IBD. Many people will suffer with stomach pain and diarrhea for a long time without realizing that something deeper is going on, and there is no simple, single test to show that you have Crohn’s. If blood tests and stool tests indicate that there is no other type of infection causing the symptoms, then colonoscopy and/or endoscopy, ultrasound or CT imaging can be used so that doctors can see where the inflammation is and where the ulcerative pain is centered.
Medicine like Imodium is commonly used to help reduce the severity of diarrhea. Immunosuppressant medications, immunomodulators, or monoclonal antibodies may be prescribed to help block the immune responses causing the inflammation. Corticosteroids are often used to help reduce inflammation. These medications, used in combination, can help to reduce symptoms of Crohn’s. However, these drugs can have serious side effects. Biologics can increase the risk of serious respiratory infections and may increase the risk of certain cancers. Corticosteroids can contribute to bone loss (osteoporosis) and cause swelling in other parts of the body. Immunosuppressants can stress the liver and pancreas.
Can Acupuncture Help Crohn’s Disease?

TCM treatments have been proven to be effective for helping to reduce inflammation and relieve pain for many types of conditions, including autoimmune disorders that can be difficult to treat with conventional medicine. TCM works well to help bring relief to people with autoimmune diseases because acupuncture and herbs work upon both the physiological and emotional aspects of the illness. Crohn’s flare ups can be triggered by stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues or strong emotions. Acupuncture can help to relieve stress and worry, so that they are less likely to feed into physical symptoms.
Acupuncture and moxibustion can help improve symptoms of diarrhea, stomach cramps, and epigastric pain. Through using these safe healing modalities, acupuncture practitioners are able to help people with bloated stomach, IBS symptoms, and nausea. Acupuncture treatment can also positively affect the vagus nerve in the brain, which plays an important role both in the functioning of the immune system and the parasympathetic nervous system that controls the action of the entire GI tract. Acupuncture can also positively impact the microbial bacteria that reside in the intestines, bringing them closer to normal levels.
A trial study that compared Crohn’s patients treated with acupuncture and moxibustion for 12 weeks with patients who received “sham acupuncture.” The patients who had real treatment showed significant improvement of symptoms over those in the control group.
A study to discover how electro-acupuncture treatment affects the brain-gut connection in patients with Crohn’s showed that acupuncture and moxibustion had a positive impact on activity in the hippocampus and vagus nerve areas of the brain.
Another study that looked at the chemical composition of intestinal mucosa found that acupuncture treatment helped improve the health of the lining of the intestines and reduced inflammation.
Acupuncture Near Me for Crohn’s Disease in Santa Monica, CA
Living with Crohn’s symptoms can be seriously debilitating. Chronic diarrhea and stomach pain can feel like they’re taking over your whole life. It is possible to manage Crohn’s disease symptoms without negative side effects. If you or someone you know is suffering with an IBD, or possibly an autoimmune disorder, or more than one autoimmune disease, it is worth trying TCM methods to see if they work for you.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Parkinson’s Disease With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Hand tremor or shaky hands, stiffness in limbs, trouble walking, or problems with balance? These may be signs of Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Parkinsons is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects the brain cells that produce dopamine. Integrative care with acupuncture treatment may help relieve symptoms of Parkinson’s disease better than conventional treatments alone.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that causes damage and dysfunction in brain cells, so that communications between the brain and the body don’t work the way they usually do. Sometimes a range of symptoms similar to those experienced by people with Parkinson’s occurs due to small strokes that affect the blood supply to the brain. This condition is called vascular parkinsonism.
More than ten million people are currently living with Parkinson’s disease worldwide. The chances of having PD increase with age, and men are more likely to have Parkinson’s than women. Early onset Parkinson’s can occur in people under 50. While it is often considered a movement disorder that causes hand tremors and other problems with mobility, Parkinson’s disease can cause less obvious symptoms, too.
Parkinson’s disease causes both “motor” and “non-motor symptoms;” the motor symptoms include physical problems like trembling hands or hand shaking, stiffness in the arms and legs, and trouble with balance when walking. The non-motor symptoms may include cognitive problems with memory, foggy-headedness, and trouble sleeping. It might even seem like a person’s personality and social behavior change, because they have trouble speaking and making their usual facial expressions.
Neurological diseases like Parkinson’s can slow the production of chemicals usually produced by the nervous system, including both dopamine and norepinephrine, a chemical that constricts blood vessels to raise blood pressure. It may be this lack of norepinephrine that causes some of the symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as low blood pressure, digestive problems, and fatigue.
Parkinson’s is a progressive disease, which means that people with PD go through stages as the condition affects more and more brain cells. In the early stages, the motor symptoms are mild and may only occur on one side of the body. In the later stages, a person may not be able to perform basic daily activities like getting dressed, eating, or walking without assistance.
What causes Parkinson’s disease? Medical science does not currently have an answer for why the brain cells become damaged or die in people with Parkinson’s. Scientists have observed that patients with Parkinson’s often have unusual clumps of a protein (alpha-synuclein) in their brain cells; these are called “lewy bodies” (lewy body parkinsons). These may be causing mutations in the cells that impair their ability to produce dopamine and other neurochemicals. Genetics, aging, and toxins in the environment or diet may all play a role in the development of Parkinson’s.
Conventional treatment for Parkinson’s involves finding a combination of medications that may help to reduce tremors and stiffness, and the myriad other symptoms a person with PD may experience. TCM offers an effective and safe adjunctive Parkinson’s treatment. Acupuncture treatment is widely accepted as a way to help relieve pain and nausea related to all types of diseases. TCM treatment can also have a positive effect on neurochemical activity, increase dopamine levels, help improve motor function and gait, and relieve fatigue.
Top 10 Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease

The early signs of Parkinson’s are generally related to movements of the body, like feeling stiff when getting up or mild hand tremors. People may not realize that other symptoms, like low blood pressure and dizziness, are also related to early stage Parkinson’s. The most common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include:
- Tremor – a small, involuntary shaking movement occurs most often in the hands, but can also be in a finger or thumb, or the chin. Sometimes called static tremor or resting tremor.
- Trouble moving or walking – limbs may feel stiff or rigid, there may be hip pain or shoulder pain. Most noticeably, the arms may not swing naturally when a person walks, or a person may shuffle, feeling it is hard to lift their feet off the floor. Movements that have been automatic for one’s whole life become challenging.
- Dizziness – fainting or feeling dizzy when you get up from sitting or lying down. This happens due to a sudden drop in blood pressure called orthostatic hypotension. A general feeling of weakness, feeling lightheaded, foggy headed, headache, blurred vision, and difficulty thinking or concentrating, and memory problems.
- Change in handwriting – this symptom is called micrographia, and it refers to a noticeable difference in a person’s writing, as they make smaller letters and the words are crowded closer together.
- Loss of smell, loss of taste, loss of appetite – many people with Parkinson’s develop an inability to smell in the early stage of the disease, known as olfactory loss. This can also affect a person’s ability to taste foods, which can lead to loss of appetite. Some medical theories suggest that Parkinson’s may begin in the olfactory region of the brain.
- Disturbed sleep, sleep disorder – sleep problems might simply be trouble falling asleep or trouble staying asleep, but they may also involve a lot of movement, or “tossing and turning,” or even talking in your sleep, crying out or yelling due to vivid dreams. Restless leg syndrome, when the limbs jerk, or leg cramps, may also be caused by Parkinson’s.
- Constipation, nausea, or trouble swallowing – cell damage in the gut may actually be one of the first symptoms of Parkinson’s, causing gastrointestinal problems due to slower movements of the smooth muscles of the digestive tract. Feeling nauseous or having a bloated stomach happens when the contents of the stomach empty too slowly into the intestine.
- Changes in the voice – people may notice that your voice sounds hoarse, weaker or more quiet than usual. This can be due to both motor and non-motor problems of PD, related to difficulty swallowing, sore throat due to heartburn, sensation of choking or food stuck in throat. It is also related to cognitive difficulties that make it harder to think of words, causing slow speech, or in other cases, talking too fast to be understood. Sometimes it may seem that a person with Parkinson’s doesn’t feel like talking much.
- Changes in facial expression – called “facial masking,” some people with Parkinson’s will find people asking them if they are upset because the expression on their face looks very serious, sad or angry, or they appear to be staring. This happens because of decreased motor function of the muscles of the face.
- Changes in posture – people with Parkinson’s may begin to hunch over while sitting, with shoulders hunched forward, or assuming a “stooped” posture while standing or walking. Again, this is due to a lack of communication between the brain and the muscles. This hunched posture can affect deep breathing, and increase the risk of falls.
Parkinson’s symptoms are complex, and vary widely from person to person. People with Parkinson’s are often subject to feelings of depression and anxiety, as well. Treatment for Parkinson’s symptoms requires a multipronged approach that addresses each individual patient’s physical, emotional, and mental health.
Medical Parkinson’s Treatment
When treating Parkinson’s, doctors will often try various combinations of drug therapy, some of which aim to replace dopamine, to help relieve tremors and other motor symptoms of PD. Levodopa/Carbidopa (or Sinemet) is a combination medication that creates a controlled release of dopamine. This can help to alleviate some symptoms, but the symptoms return when the medication is not in the bloodstream. Unfortunately, this medication can cause side effects like nausea and vomiting, and people will often need to take larger doses to get the same effect as the disease progresses. Long-term use sometimes causes dyskinesia, or involuntary movements of the limbs. Doctors may then prescribe another medication, such as Amantadine or Gocovri, to help mitigate these effects, or to help stave off motor symptoms during “off” times when the dopamine-replacing drugs wear off.
Patients with Parkinson’s will often be given other medications to help with problems like constipation, high blood pressure, sleep problems, pain, and depression. TCM and acupuncture offer a holistic way to treat many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s at the same time, without so many drugs and their potential side effects.
How Can Acupuncture Help Parkinson’s?

Part of TCM theory involves the concept of Ben and Biao, or “Root and Branch.” We observe that the expression of illness in the body is like the system of roots and branches of a tree. The branches show us the outward symptoms, while the root of the disease is hidden deeper under the surface, where we can’t see it. In order to treat the symptoms of any illness, we study the branches to find out where the problem originates, then we go to the root of the problem to solve it. We do this with a combination of acupuncture, herbs, and other modalities like moxibustion, cupping, and tuina massage. These TCM treatments allow us to address problems in the organ systems of the body, where lie the roots of illness, while at the same time, helping to relieve the pains and uncomfortable symptoms occurring in the branches.
Parkinson’s disease is considered by TCM philosophy to occur due to deficiencies in the root, which cause excess in the branches. Deficiency of the kidney, liver, spleen, blood and Qi (root problems) contribute to heat, phlegm, stasis, and wind in the limbs (branches). Tremors in the hands, and changes in facial expressions and movements are caused by Wind and Phlegm. According to TCM, Wind causes problems, often in the upper body, that come and go, such as stiffness, spasms, facial tics, and shaking of the limbs–like the wind shaking the branches of a tree. Wind can also cause symptoms like ringing in the ears (tinnitus), sudden headaches, and hives. Phlegm, which blocks the energy channels of the body, disrupts the smooth flow of blood and Qi to the limbs, creating a sense of stiffness, heaviness in the limbs, resistance to moving or speaking, staring, heavy feeling in the chest, and lack of coordination.
Acupuncture treatment for Parkinson’s disease, then, focuses on clearing heat, wind, and phlegm, strengthening and nourishing the blood, and getting the Qi moving smoothly again.
When we use acupuncture and herbs to help Parkinson’s, we see changes occurring in the neurochemical activity of the brain.
One study looked at the changes in neural response in the brain immediately after acupuncture treatment. This study concluded that after 8 weeks of treatment, patients with Parkinson’s showed significant improvement in brain function.
Another clinical study showed that acupuncture helped to increase levels of Tyrosine hydroxylase, a brain chemical involved in the production of dopamine.
TCM herbal formulas have also been clinically demonstrated to help relieve Parkinson’s symptoms like speech problems, tremors, and gait disturbances.
Research has shown that using TCM herbs to treat Parkinson’s is a safe and effective adjunctive therapy to conventional medical treatment.
Acupuncture Near Me for Parkinson’s Disease Santa Monica Westside

The goal of treatment for Parkinson’s is to slow down the progression of the disease and do what we can to maintain mobility and cognitive function. The sooner we begin treating Parkinson’s disease with acupuncture and TCM methods, the better chance we have to limit the effects of the disease and help patients stay active. If you or someone you love has Parkinson’s, consider adding a TCM doctor to your health care team. Integrative treatment for Parkinson’s with acupuncture and herbs can help treat Parkinson’s naturally.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Bloated Stomach With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac,. Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Do you feel constantly gassy or have a bloated stomach after eating? Digestive problems like gastritis or colitis can cause abdominal bloat. Stress and hormonal imbalances can also contribute to inflammation and bloated stomach pain. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help improve digestion and relieve abdominal bloating.
Abdominal bloating occurs when gas builds up in the gastrointestinal tract, filling the stomach and/or intestines with air. This can cause the belly area to get swollen and distended. Bloating can cause an inflated belly, sharp pain in the abdomen, belching and flatulence, nausea, or a sudden strong urge to go to the bathroom. Bloating can be related to fluid retention; this is sometimes called “water bloat.”
Problems with digestion that lead to a feeling of heaviness, “like a rock” in your belly after eating, are common. People who have been diagnosed with some type of functional gastro-intestinal disorder (FGID)–like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or dyspepsia (indigestion)–are extremely likely to experience abdominal pain and bloating after eating, while up to 30% of all people report having bloating at least some of the time. Inflammation in the walls of the stomach (gastritis) or intestine (ulcerative colitis) can also cause bloating.
Women often feel bloated before or during their menstrual period, and female reproductive disorders like endometriosis, fibroids (leiomyoma of the uterus), and PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome) can cause abdominal pain and bloating.
FGIDs can be very hard to manage; it may be difficult to get a clear diagnosis or effective medical treatment. Problems like constipation, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain and bloating are highly subjective, and people are often made to feel like it’s normal to have these issues, or that all they need to do is avoid certain foods.
Feelings of anxiety and depression are common among people who suffer from moderate to severe bloating on a regular basis. This can become a vicious cycle, as the pain and swelling of the abdomen causes anxiety, and the physiological effects of the emotional stress trigger the bloating to happen again and again. Sometimes people dread eating meals because they are so afraid of the painful and embarrassing bloated stomach.
Digestive upsets are complex to treat because there can be many factors contributing to the discomfort. So many different conditions can cause bloating, it can be hard to get a clear handle on the true cause. This is a case when TCM methods of diagnosis offer many advantages, because a TCM practitioner will be able to study the whole picture presented by a patient and pinpoint what underlying conditions are causing gas and distension. Acupuncture and herbs can help resolve abdominal bloating and other symptoms at their root source.
Top 10 Abdominal Bloating Causes

Why might someone feel bloated and gassy all the time? Many different types of gastrointestinal disorders can contribute to a bloated belly and excess gas, as can hormonal and emotional changes. What causes abdominal bloating can be one issue or a combination of factors:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Inflammatory bowel disease, Ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s Disease
- Gastritis, stomach ulcers, inflammation of the stomach
- Food intolerance, gluten intolerance, celiac disease
- PMS, menstruation
- Stress, anxiety, depression
- Pregnancy
- Constipation
- Liver disease
- Abdominal adhesions, or scar tissue from surgeries
Eating behaviors like eating too quickly, swallowing air while eating, or eating fiber-rich foods that cause gas like beans, can lead to bloating. Drinking a lot of carbonated beverages can lead to excess gas in the GI tract. Smoking can also be a factor. Some medications can cause bloating as a side effect, including antibiotics, oral birth control pills, opioid pain medications, medicines to relieve constipation, and even some supplements, like iron pills.
Cancers of the abdominal organs, such as ovarian cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer, or pancreatic cancer, can also cause bloating in the belly. Gallstones or gallbladder disease, gastroparesis, kidney problems, and liver problems can all cause stomach pain and bloating.
Medical Treatment for Abdominal Bloating
Many people do not seek medical help for bloating, trying to manage it on their own with over the counter medications that promise relief from gas pain and acid reflux. Antacids only help with the kind of bloating that is caused by food, though; they don’t help with bloating related to FGIDs, hormones, or emotional stress. When a person does ask their primary care doctor or even a gastroenterologist for help with bloating, they may find that the treatment options are very limited. Doctors will usually reassure patients that gas and bloating, while uncomfortable, are not actually dangerous. Then, they will often advise that patients go on a strict elimination diet, cutting out wheat, dairy, and most vegetables and legumes. Sometimes doctors will prescribe antibiotics to alter the balance of gut bacteria. Antidepressants are sometimes prescribed to help with bloating. Conventional medical science still has a ways to go to fully understand the underlying causes of digestive problems like bloating.
Because bloating is not viewed as a disorder in and of itself, not much serious research has been done to show what types of treatments work best to get rid of bloating. TCM treatment has been shown in a randomized controlled trial, a peer-reviewed study, and a hospital-based investigation to help in relieving stomach pain due to chronic gastritis.
How Can Acupuncture Help With Bloating?
TCM offers a multidisciplinary approach to the digestive problems, hormone imbalances, and emotional upsets that can cause bloating. An experienced acupuncturist is able to use methods of diagnosis such as studying the appearance of the tongue, feeling the pulse, and asking lots of questions about how and when the symptoms occur to find the specific pattern of imbalance that is causing gastric distress.
Different presentations of digestive conditions that may cause abdominal bloating and pain include:
- Spleen/Stomach Deficiency – characterized by symptoms: chronic bloating, poor appetite, feel worse after eating, pallor, and fatigue. This type of bloating can be caused by antibiotics, too much raw or fermented food, eating disorders, a long period of illness, or chronic inflammatory disorders.
- Damp-Phlegm – symptoms include: distended stomach, nausea, acid reflux, diarrhea. This type of bloating can be caused by dietary habits that include excess sugar, alcohol, fatty or fried foods, and dairy products. Can also be related to damp environmental conditions.
- Liver Qi stagnation – common symptoms are: stomachaches, stomach gurgling, belching, and constipation. This type of bloating can be caused by stress, feelings of anxiety or anger, and irregular, emotional eating behaviors.
TCM treatment for abdominal bloating will use acupuncture and herbs to bring the stomach and liver back into harmonious function, clearing phlegm and improving digestion. Treatment will be individualized based on the underlying causes of the imbalance; if reproductive hormones are involved, then that factor will be taken into consideration when preparing the herbal formula. If mental health issues are a factor, specific points will be added to help relieve anxiety. Naturally, your acupuncturist will have some clear instructions on how to optimize your nutrition to reduce bloating.
Top 5 Tips for How to Stop Bloating

While bloating may be caused by all sorts of different factors, there is no doubt that making some changes to your eating habits will probably have an impact on how bloated you feel. What helps bloating may be different for each person’s constitution or lifestyle, so it will be very helpful to have an in-depth conversation with your acupuncture provider about what bloating diet is best for you.
- Chew your food thoroughly. Many people eat fast, and don’t pay much attention to chewing their food well before they swallow. Food is really meant to be broken down and mixed with saliva in the mouth before it moves down the esophagus and into the stomach. Skipping this important step by swallowing half-chewed food means that your stomach has to produce more acid and work much harder to digest the food before it moves deeper into your gastrointestinal tract. Eating too quickly can also easily lead to eating more than you need. It takes about 20 minutes for your brain to receive the message that the stomach is full. Chew slowly, and enjoy every bite; this will improve your digestion.
- Avoid icy cold drinks and foods. Cold liquids are shocking and unfriendly to your internal organs, both those of the digestive tract and the female reproductive organs. Constantly drinking ice-cold beverages irritates the smooth muscle tissues of the stomach, intestines, and uterus. Drink more warm liquids, which are soothing to these organs.
- Ginger tea – many of our herbal formulations include slices of fresh ginger to help soothe the stomach and GI tract. Ginger helps the body to produce more of the digestive enzymes that work to break down food, and relieves cramping in the belly. All you need to do is keep a knob of fresh ginger on hand, cut two or three slices and steep in hot water as you would a teabag. Sip anytime, but especially before meals, to help relieve gastritis pain and bloating.
- Choose foods in harmony with the season. Raw foods are appropriate in the summer, but in the winter, it’s better to eat cooked foods. Eating more bitter-tasting foods, like dark leafy greens, helps the liver and kidneys.
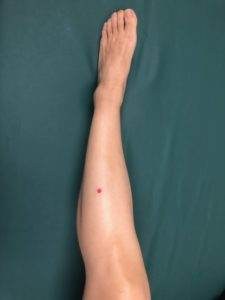
- Use acupressure to help relieve bloating and gassiness. Acupoints are located along the meridians and correspond to various organ systems. Applying gentle, steady, downward pressure to acupoint ST36 (Zu San Li), which is associated with the stomach, can help to relieve bloating, stomach pain, nausea, and feelings of stress. ST36 is located on the outer edge of the shin bone, about 4 finger widths beneath the kneecap.
Acupuncture Near Me for Abdominal Bloating
TCM offers a holistic approach to digestive problems of all kinds. Symptoms like abdominal bloating, stomach pain, and gassiness are usually signs that there is a deeper problem. If you haven’t been able to solve the problem of bloating with conventional medicine or dietary changes, you may be able to get help for digestive difficulties with acupuncture and herbs.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Manage IBS Diet With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? IBS is a chronic gastrointestinal problem that causes uncomfortable changes in the body’s elimination process. One day you’re constipated, then a day or two later, you may have diarrhea. Pains move around the whole abdominal area, and your belly feels full and tight with excess gas. IBS treatment typically involves taking medications and following a special IBS diet, but many people continue suffering with no IBS cure. In this article, we’ll talk about how to get rid of IBS naturally with acupuncture and TCM.
IBS is a common digestive problem that can cause a lot of pain and anxiety around your daily bathroom habits. IBS can cause stress and even depression, compromising your ability to live life without worrying about when you’re going to have to go to the bathroom. Conversely, stress and anxiety function as triggers for bouts of IBS, so the problem becomes cyclical.
This gastrointestinal problem is called Irritable Bowel Syndrome because people who suffer from this disorder seem to have a more sensitive intestinal tract that is highly reactive to IBS triggers. Sometimes this condition is referred to as “spastic colon.” People who have primarily loose stools as a result of this condition are said to have “IBS-D” (diarrhea-predominant IBS), while people who suffer more from sluggish bowels have “IBS-C” (constipation-predominant IBS).
Many people never seek help from their medical providers for IBS treatment, perhaps because they think their discomfort is normal. The ever-changing nature of IBS means it’s hard to get a handle on what is actually happening. The pain in the gut seems to move around all the time, and bathroom habits can feel totally unpredictable. IBS can also lead to the bleeding and discomfort of hemorrhoids.
IBS Causes
According to conventional medicine, there is no one specific cause for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Having a more highly reactive intestinal tract may be due to many factors, some more clearly mechanical in nature, others more having to do with psychological factors. Inflammation in the gut, gastroenteritis, stressful or traumatic situations, heightened sensitivity to movements and sensations within the abdomen, and miscommunications of the autonomic nervous system between the digestive organs and brain may all play a role in IBS.
We usually think of serotonin as being a hormone in the brain that affects mood and the ability to fall asleep. But serotonin is a neurotransmitter that also plays a key role in the function of the gut, affecting how the intestines move and secrete gastric juices, as well as how we viscerally perceive these functions. Changes or abnormalities in serotonin release or uptake seem to be one of the issues related to IBS.
Top 5 IBS Triggers are:
- Stress
- Abnormal levels of serotonin in the digestive tract
- An infection or abnormal level of bacteria in the digestive tract
- Strong reactions to certain foods/Celiac disease
- Weak colon muscle action
IBS involves, on some level, problems with both the motor function of the bowel itself and the extent to which a person is physically aware of “stuff going on” in their intestines and colon. Inflammation from infections or hormone changes caused by the menstrual cycle can also directly affect bowel motility. Those same things can cause a person to be hypersensitive to every little movement of the intestines, making them feel like painful cramps.
IBS and Gut Health
The balance of gut bacteria, or “flora” in the intestines, has been more recently shown to play a vital role in overall health. Gut bacteria are instrumental in the proper functioning of the immune system and the assimilation of nutrients from our food. The balance of the gut flora can be disturbed by taking antibiotics or a gastric infection, such as norovirus or other flu-type illnesses. Medical science is still making strides in learning how the health of the gut is very closely connected with the brain. It is becoming clear that gut health is inextricably related to mental health.

We know that stress, both chronic and acute, can cause all kinds of health issues. The mind-body connection is particularly apparent when it comes to IBS triggers. Feelings of anxiety create a ripple effect through the middle of the body, affecting the whole digestive system, causing pain and volatile action. Fear, shame, and even feelings of panic about having to run to the bathroom keep the whole process in a repeating loop.
IBS treatment often involves antibiotics or probiotics, but this has not been shown to be effective long-term. Many times doctors will prescribe medicines for anxiety (like Valium or Atavan) or depression to help provide IBS relief. However, these pharmacological treatments do not really address the root causes of the syndrome, and they may cause negative side effects, and sometimes create a dependency on the medication.
Top 5 Signs of IBS
A syndrome is a collection of symptoms that often appear together for which there is no clear medical explanation. According to conventional medicine, irritable bowel syndrome is evident when a person has frequent abdominal discomfort, which could mean a “stomach ache” or cramping, and bouts of constipation or diarrhea, or sometimes both, in alternation. In other words, IBS is signified by changes in the frequency or consistency of bowel movements, accompanied by marked discomfort before having them.
Top 5 Symptoms of IBS are:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating and excess gas
- Constipation and/or diarrhea
- Mucus in the stool or other irregularities
- Nausea
IBS is more common among women than men. This may be due to fluctuations in hormones that affect the chemical balance and muscle action of the intestines. Women may experience more IBS symptoms in conjunction with their menstrual periods, or as a PMS symptom.
Conventional treatment for IBS typically involves the offering of various medications to deal with these symptoms. Anti-spasmodics may be used to help reduce cramping and contractions in the bowel, and anti-diarrheal medications such as Imodium may slow down the movements of the bowel, but these IBS medications do not help to restore true balance to the digestive system.
How to Treat IBS With Acupuncture
TCM and acupuncture work according to holistic principles, meaning that we are careful to look at the whole picture of what is going on with a person: emotionally, spiritually, physically, nutritionally, and energetically. According to TCM philosophy, the spleen is the organ responsible for processing our food and turning it into energy. IBS treatment with acupuncture is a matter of aligning the communications between the Shen (the mind) and the Spleen. Deficiency of the spleen is the primary TCM diagnosis for most patients with IBS symptoms. It is equally important to address problems of the Shen at the same time.
The most common TCM differentiations of IBS patterns are:
- Spleen Deficiency with Liver Qi stagnation: symptoms of this condition include diarrhea, mucus in the stool, abdominal pain, cramping, gassiness, bloating, irritability, and depression with lots of heavy sighing.
- Spleen Deficiency with Stomach deficiency: shows symptoms like watery stools, feeling of fullness and distension after eating, poor appetite, a pale complexion and fatigue.
- Spleen Deficiency with Kidney Deficiency: symptoms include diarrhea, especially in the morning, partially digested food in the stool, aches and pain in the abdomen, lower back, and knees, with a sense of coldness.
Moxibustion is a TCM treatment used in addition to acupuncture to treat IBS. One study showed that acupuncture treatment combined with moxibustion to get rid of IBS was extremely effective for reducing both the discomfort and frequency of bowel movements.
Another study that tested both herbal formulations and acupuncture treatment on patients with IBS showed that both methods were effective at reducing symptoms.
Acupuncture treatment will also focus on reducing stress, anxiety, and fatigue. Acupuncture has been shown to help restore the balance of serotonin levels, as well.
IBS Diet According to TCM
Chinese herbs, as always, are also integral to the successful treatment of IBS. In the TCM philosophy of healthcare, nutrition is considered to be just as important as acupuncture, moxibustion, herbal formulae, and other forms of therapeutic treatment. Herbs are a way to get nutrients into the body that are not necessarily present in the foods we commonly eat. TCM practitioners are trained extensively in the energetic and nutritional values of food and will spend time working with patients to modify eating habits and focus on a special IBS diet. Apart from reducing common problems like excessive coffee and alcohol intake, your acupuncturist will work with you to discover which foods act as IBS triggers for you and help you to make the most beneficial modifications to your IBS diet plan.
Top 5 Acupressure Points to Help IBS
Acupressure can be a very effective means how to treat IBS naturally yourself. Acupressure uses the same collection of points located along the meridians of the body as acupuncture to help eliminate blockages and encourage blood and Qi to move freely through the body. These points located along the spleen, bladder, stomach and “conception vessel” meridians can help provide IBS relief. The conception vessel meridian runs up the front and center of the torso, from the pubic area to the mouth. Also known as the “Sea of Yin,” this channel is instrumental in directing all the yin energy in the body. As it is very exposed, this energy center can feel vulnerable, and may be where we tighten up, hunch over, and try to hide and protect ourselves. Tension along this channel can be a major energetic factor in the cramping and spasming actions of IBS.
Try these top 5 acupressure point for IBS relief:
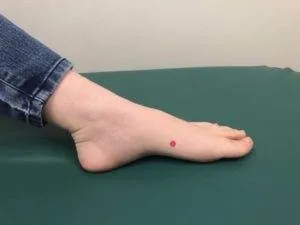
- CV6 – located two finger-widths beneath the navel, gently rubbing this point with circular motions helps to relieve belly pain, cramping,

Spleen 4 acupressure point and constipation.
- CV12 – located at the midpoint between the lower end of the sternum and the navel, rubbing this point in a circular motion can help relieve gas pain, bloating and acid reflux.
- SP4 – located on the inner edge of the foot, right above where the arch begins, stimulating this spleen point can help relieve gastric spasms and diarrhea.
- UB25 – these two points in the lower back, right beneath LV-4, can help relieve abdominal distension, constipation, and lower back pain.
- ST37 – also known as the “Upper Great Hollow,” these points are located along the outside edges of the shin bones, a few inches below the knees. Pressing firmly here can help relieve abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea.
Acupuncture Near Me for How to Solve IBS
If the IBS signs described here sound familiar because you or someone you know has been suffering from frequent abdominal discomfort and constipation or diarrhea, or both, it is important to seek help and advice from your healthcare providers. When conventional IBS treatment doesn’t seem to be helping, acupuncture and TCM may help you find IBS relief. Call us at Art of Wellness to get started with an IBS diet plan and course of acupuncture treatment.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Acid Reflux with Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Acid reflux, also known as heartburn, is the most common symptom of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), a chronic disease in which the contents of the stomach move upwards into the esophagus, irritating the lining of the food pipe and causing burning pain in the chest, among other symptoms.
It is estimated that at least 40% of adults experience heartburn symptoms at some point in their lives, while up to 20% experience heartburn at least weekly, making GERD one of the most commonly diagnosed digestive disorders in the US. If a person is experiencing GERD symptoms frequently, doctors will usually try to treat acid reflux with medications called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and lifestyle changes. However, in many cases, patients will continue to suffer with symptoms beyond chest pain and regurgitation, often in concert with other common digestive complaints like dyspepsia (indigestion), IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), and ulcers in the stomach, necessitating further investigation and treatment.
TCM and acupuncture offer an alternative course of action to deal with acid reflux and many other digestive disorders. Acupuncture treatment has been shown to be even more effective than medications for heartburn relief. Acupuncture and herbal natural remedies for heartburn provide long-term positive results for GERD symptoms by helping to resolve the digestive disorder at its origin.
Acid Reflux Symptoms
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is characterized mainly by the reverse flow of digestive fluids up into the esophagus. When this occurs regularly over time, it can damage the lining of the esophagus and cause other problems. The sensation of “heartburn” is the most commonly known symptom of acid reflux, but it is possible to have GERD and not experience this burning sensation. GERD can occur with other non-acidic digestive fluids and may not cause the type of pain caused by acidic stomach juices. GERD symptoms include:
- Burning in chest, worse after eating and when lying down
- Chest pain, even when you haven’t eaten
- Difficulty swallowing
- Regurgitation of food or sour-tasting liquid
- Excessive salivation
- Sensation of a having a lump in the throat
- Excess gas in stomach and bloating
- Intolerance of certain foods and beverages
- Bad breath, or a constant sour taste in the mouth
- Hoarse voice or laryngitis
- Constant need to clear the throat
- Chronic dry, sore throat
- Burning sensation in the mouth
- Inflammation of the gums and other dental problems
Acid reflux symptoms may appear at the same time as other symptoms like stomach pain, stomachache, and stomach cramps. These may be stomach ulcer symptoms, gastritis symptoms, or signs of dyspepsia, as it is common for two or more of these digestive issues to coexist.
Heartburn Causes

While there is no single clear cause of GERD, it is usually related to the functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle that separates the esophagus from the stomach. The LES, when it works correctly, allows chewed food matter to pass into the stomach, then closes to prevent matter from the stomach from flowing upwards. When this sphincter is relaxed or weakened, the contents of the stomach can breach this barrier. This can happen due to pregnancy or excess weight in the belly pushing upwards on these organs. Sometimes it may be due to a hiatal hernia, which can cause the upper part of the stomach and LES to push through the diaphragm muscle into the chest area.
Heartburn can be triggered by eating spicy or acidic foods, by smoking or inhaling second-hand smoke, or the use of aspirin or ibuprofen, as well as some blood pressure medications. If abstaining from these triggers does not help, patients may be referred to a gastroenterologist for investigative testing to pinpoint the problem. Endoscopy of the upper GI tract can show whether there is a hiatal hernia, stomach ulcers, or damage to the esophagus.
Acid Reflux Treatment
Many people take over the counter antacids (like Tums, Rolaids, Maalox, or Mylanta) to try to get heartburn relief. These may help alleviate the burning sensation temporarily, but using antacids frequently can actually exacerbate the problem by creating more stomach acid. Histamine (H2) blockers (like Pepcid and Zantac) can help reduce production of acid, but they don’t work for everybody. PPIs (like Prevacid, Prilosec, and Nexium) work by blocking the production of stomach acids.
These GERD medications can help with healing stomach ulcers and reducing acid reflux, but there are downsides. These drugs are very expensive, and many people end up using them on a daily basis. PPIs also inhibit the output of certain enzymes, which creates a negative interaction with common heart disease medications. They can also reduce absorption of calcium in the digestive tract, which can lead to weaker bones and increased risk of fractures. PPIs can also affect kidney function and increase the levels of bacteria in the stomach; if this bacteria makes its way up into the chest area due to reflux, it can get into the lungs and cause higher risk of pneumonia and other respiratory infections.
Asthma and GERD are often considered to be related conditions, because acid reflux can irritate tissues that trigger asthma attacks, while asthma attacks can cause a weakness in the LES that triggers reflux. Asthma medications like theophylline can also cause heartburn attacks. People who suffer from both GERD and asthma need to manage both conditions in tandem.
Prescribed medications called prokinetics cause the stomach to empty more quickly, reducing the chances of reflux. However, they can also cause side effects like nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, anxiety and depression, as well as having contraindications with other prescriptions.
All of these medical treatments focus on the stomach acids that cause heartburn. Currently, there is no conventional treatment that helps to restore the normal functioning of the LES. Research has indicated that acupuncture treatment, in addition to helping regulate gastric secretions, may help to strengthen the motor function of the LES.
Acupuncture and Herbs for GERD
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a holistic system of medicine founded on over 3000 years of recorded research and practice. In TCM, all health problems are viewed as imbalances caused by blockages of Qi (life force energy) in the body. Disorders of the organ systems are often linked to emotional disturbances. According to TCM, acid reflux and other digestive problems are influenced by stress and anxiety. Long-term, ongoing feelings of worry, frustration, and anger impact the liver, spleen and stomach, increasing acidity and inflammation in these organ systems.
An “upset stomach” and feelings of tightness and pain in the chest are caused by Qi rising inappropriately, causing the backflow of acids. Acupuncture treatment for GERD focuses on calming anxiety, and restoring the downward flow of Qi, while toning the stomach and LES to improve their motor function.
TCM uses herbal formulations, developed over many centuries, to support the proper functioning of the internal organs on a deep nutritional level. Herbal remedies for acid reflux in TCM work to increase healthy mucus in the esophagus, soothing and healing damage from stomach acids.
An acupuncturist is also likely to ask questions about dietary habits, as certain foods are likely to be part of the problem. Working together with a qualified TCM practitioner to plan meaningful lifestyle changes, specific to each individual, will also help resolve heartburn, stomach pain, and indigestion.
TCM for Heartburn During Pregnancy
Many women experience acid reflux, which can happen at any time during pregnancy. This is due to hormone changes that can relax the LES so that it doesn’t close completely. In the later stages of pregnancy, the uterus pushes up on the digestive organs and diaphragm. According to TCM, stomach fire, indicated by a craving thirst for cold drinks, may need cooling. Stagnation in the digestive organ system can cause belching and bloating. Acupuncture treatments can be tailored to address these conditions, improving digestive flow and balancing hormones. Acupuncture can also help if baby is showing signs of colic or infant reflux.
Top 10 Tips for GERD Diet and Lifestyle

Creating and maintaining balance between Yin (cool) and Yang (warm) energies in the body and spirit is central to treating heartburn with TCM.
- High fiber diet – eat oatmeal and plenty of cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower and broccoli.
- Avoid citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits) and emphasize melon, bananas, apples and pears. Tomatoes and pineapple are also highly acidic and can cause problems, as can onions and garlic. Citric acid is also a common food additive and should be avoided.
- Eat several small meals per pay – eating larger amounts at one time increases the chance of the stomach becoming distended.
- Reduce fatty foods – high-fat foods stay in the stomach longer. Avoid fried foods, dairy ingredients and marbled meats.
- Avoid alcohol, especially red wine
- Avoid caffeinated drinks: coffee, tea and sodas can all trigger heartburn.
- Drink ginger or chamomile tea, which are both soothing to the stomach. Green tea can also positively stimulate the LES.
- Don’t lie down after you eat. Eat at least two hours before you intend to go to bed.
- Watch your workout positions: movements that affect your abdomen can cause reflux. Crunches, sit-ups, leg lifts, headstands, downward dog and other poses should be done carefully if at all. Never exercise on a full stomach.
- Sleep with your head elevated above your feet. A wedge-shaped foam lift will work much better than stacking pillows. Or, attach risers to the feet at the head of your bed.
Best Acupuncture Near Me for Heartburn Relief
Acupuncture treatment for heartburn is a safe and effective acid reflux remedy. If you or someone you know is suffering from GERD, acid reflux, gastroparesis, stomach pain, or symptoms of ulcer, we hope that you will not hesitate to find an acupuncturist in your area to schedule an initial consultation. We are practicing at Art of Wellness in Santa Monica, one of the top 20 acupuncture clinics in the greater Los Angeles area.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.