-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Digestion
How to Treat Splenomegaly (Enlarged Spleen) With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
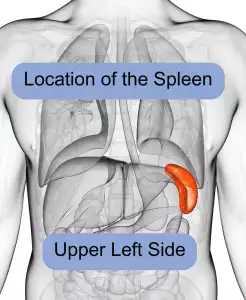
Left side abdominal pain that is tender to the touch? Feeling full after eating a small amount? Signs of anemia, bleeding easily? These may be enlarged spleen symptoms. Acupuncture and TCM can help with splenomegaly, along with spleen function and swollen spleen symptoms.
Splenomegaly is the medical term for an enlarged spleen. In conventional medical wisdom, the spleen is an organ that stores and filters blood, regulating the amounts of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that are in circulation.
The spleen removes waste products and damaged blood cells from the bloodstream. It also produces antibodies (white blood cells) that fight germs and infection.
The spleen is located inside the left side of the ribcage, just above the stomach. Usually, the spleen is about the size of your fist—on average, about 12 centimeters long.
People often will not be aware of an enlarged spleen, but in some cases, there will be noticeable signs, such as pain in upper left abdomen and feeling “full.”
Spleen function is considered very important for overall health and happiness in TCM. Acupuncture treatment and Chinese herbs can provide an adjunct or alternative treatment for enlarged spleen.
Enlarged Spleen Symptoms
The most common swollen spleen symptoms include:
- Left upper quadrant pain, pain behind left ribs, left abdominal pain (upper abdomen), left side abdominal pain
- Pain that radiates to the left shoulder
- Feeling full even when you haven’t eaten
- Feeling full after eating only a small amount
- Anemia, low red blood cell count
- Bruise easily
- Bleeding easily
- Fatigue
- Catch colds frequently or suffer from other infections often
If you experience tenderness or serious left abdominal pain and feel dizzy, and/or have a rapid heartbeat, it is important to seek care immediately. These could be signs of ruptured spleen, which can lead to internal bleeding that could be life-threatening.
Enlarged Spleen Causes

There are several different conditions that can cause the spleen to become enlarged. What causes a big spleen, or should we say, bigger spleen?
Some of the health issues that can cause splenomegaly include:
- Liver cirrhosis, or other liver disease
- Viral hepatitis, Mononucleosis, or other viral infections
- Different types of hemolytic anemia
- Blood cancers, including: polycythemia vera and other myeloproliferative neoplasms, Leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease
- Blood clot near the spleen or liver
- Autoimmune disorders, including Lupus or Sarcoidosis, or rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Malaria, or other parasitic infections
- Bacterial infections
- Gaucher disease or Niemann-Pick disease
Medical Treatment for Enlarged Spleen
The treatment of splenomegaly in Western medicine primarily depends on addressing the underlying cause of the condition.
When an enlarged spleen is caused by infections like viral hepatitis or mononucleosis, the focus is typically on treating the infection itself. Antiviral medications may be prescribed to manage viral hepatitis, while mononucleosis, caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, usually requires supportive care. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be recommended to alleviate symptoms. In some cases, particularly when there’s a risk of the spleen rupturing, patients may be advised to avoid contact sports or strenuous activities.
For blood disorders that cause an enlarged spleen, treatment typically involves managing the specific blood condition. For example, in hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be produced, treatments may include blood transfusions, corticosteroids to suppress the immune system, or medications like rituximab.
In conditions like polycythemia vera, where there’s an overproduction of red blood cells, treatment might involve phlebotomy (removing blood from the body) to reduce blood volume, or medications like hydroxyurea to suppress the bone marrow’s production of blood cells.
When liver disease such as cirrhosis is the cause of splenomegaly, the treatment approach focuses on managing the liver condition. Cirrhosis management may include lifestyle modifications such as reducing alcohol intake, using medications to control liver damage, and managing complications like portal hypertension. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be considered. Controlling the liver condition can help reduce spleen enlargement.
In cases where the spleen enlargement is due to cancers like leukemia or lymphoma, treatment usually involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted drug therapies to address the cancer. The goal is to reduce the size of the spleen by shrinking the cancerous cells that are contributing to its enlargement. In certain situations where the spleen is significantly enlarged and causing symptoms, or if it’s not responding to other treatments, splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen) might be recommended.
Autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can also cause splenomegaly. Treatment for these conditions often involves immunosuppressive medications such as corticosteroids, methotrexate, or biologic agents that target specific parts of the immune system. By controlling the underlying autoimmune disorder, the symptoms associated with spleen enlargement can often be managed effectively.
When does an enlarged spleen need to be removed?
In some cases, if the spleen is severely enlarged or if it’s causing significant symptoms or complications (such as a high risk of rupture), a splenectomy may be considered. This surgical procedure involves removing the spleen entirely. While splenectomy can relieve symptoms and prevent complications, it also has long-term implications, as the spleen plays an important role in the immune system. Patients who undergo splenectomy may require vaccinations and prophylactic antibiotics to reduce the risk of infections.
Unless the spleen is ruptured, in most cases, a splenectomy is not necessary. Trying a holistic approach with TCM and acupuncture may be able to help relieve symptoms and improve spleen function.
Can Acupuncture Help Enlarged Spleen?
Traditional Chinese Medicine takes a different few of key organs and organ systems than we are used to in modern medicine.
In TCM, the spleen is considered vital to the digestion of food, working in harmony with the stomach. The spleen is also partially responsible for the transport of blood and water throughout the body, delivering nutrition to the muscles.
The spleen is also vital to the proper excretion of waste. When there is a buildup of excessive fluids or “dampness” in the body, it is often due to a deficiency of the spleen.
Fatigue and a sense of fullness after eating are considered signs of spleen deficiency, which can affect whether or not other organs are getting the nutrition they need.
Problems with the spleen may also be related to the liver and/or the stomach, so the acupuncture practitioner will carefully look at all of a patient’s presenting symptoms to determine the appropriate diagnostic pattern and course of treatment.
In TCM, organs are related to certain emotions, and the spleen is connected to anxiety. Thus, worrying, overthinking, and other manifestations of anxiety are believed to negatively impact the spleen.
TCM treatment to help strengthen spleen function may focus on clearing stagnation and dampness, and improving circulation of blood and Qi. Your acupuncture provider can develop a course of treatment with acupuncture and herbs to address the underlying causes of an enlarged spleen, while also helping to relieve any symptoms of splenomegaly.
Acupuncture for Enlarged Spleen Near Me in West Los Angeles
If you are experiencing enlarged spleen symptoms, acupuncture and TCM offer holistic approaches that can support spleen function and address the root causes of various health issues. At Art of Wellness, our experienced practitioners can help tailor a treatment plan to your unique needs. Contact us today to learn more about how TCM can benefit your health and well-being.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat SIBO With Acupuncture and TCM
by Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea? These can be SIBO symptoms. SIBO, or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, can cause bloated stomach, abdominal cramps and pain. Acupuncture and TCM can offer alternative SIBO treatment and bloating relief.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition in which an abnormal increase in the population of bacteria occurs in the small intestine.
Unlike the large intestine, which is rich in bacterial flora essential for digestion and immune function, the small intestine typically contains relatively few bacteria. When these bacteria proliferate excessively in the small intestine, they can disrupt normal digestion and nutrient absorption, leading to a variety of uncomfortable and sometimes debilitating symptoms.
Problems with gut motility also contribute to SIBO symptoms. Peristalsis is the process by which the smooth muscle tissues in the intestine move food matter through the gastrointestinal tract. When peristalsis isn’t happening the way it should, this is known as dysmotility. This can lead to stagnation of food matter in the intestine, which allows for an overgrowth of bacteria to build up. This in turn can causes hydrogen and methane gas to be produced by the fermentation of carbohydrates that are stagnant in the small intestine. This excess gas causes painful bloating and distension of the abdomen.
SIBO can cause a range of digestive symptoms, such as bloated stomach, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, and malabsorption of nutrients from food, which can result in unwanted weight loss and nutritional deficiencies. Vitamin B12 deficiency is particularly common among people suffering from SIBO.
Other symptoms, seemingly unrelated to the gastrointestinal system, can include: fatigue, headache, low fever, and rosacea.
SIBO is often associated with other health issues, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, and diabetes.
Acupuncture and TCM can work as an adjunct or alternative treatment for SIBO symptoms.
This can lead to hydrogen and methane gas being produced by the fermentation of carbohydrates that are stagnant in the small intestine. This excess gas can cause painful bloating and a distended abdomen.
What Causes SIBO?

A wide variety of different issues can play a role in the development of SIBO. Many conditions may cause problems with the secretion of gastric acids, with motility of the small intestine, gut immune function, and structural issues related to surgeries, injuries, or other abnormalities of the intestine.
Conditions that may contribute to SIBO include:
- Gastroparesis due to diabetes, or connective tissue disorders, viral infection, or ischemia
- Cirrhosis
- Chronic renal failure
- Scleroderma
- Crohn’s disease
- Celiac disease
- Recurrent rounds of antibiotics
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- GI tract surgeries that create structural abnormalities
- Immune deficiencies of T-cell or antibody responses
What’s the Difference Between IBS and SIBO?
Symptoms of SIBO are very similar to IBS symptoms, and it is possible for a person to have both IBS and SIBO at the same time. The difference between SIBO and irritable bowel syndrome is that IBS is a functional syndrome stemming from issues in the large intestine, whereas SIBO occurs in the small intestine.
One review of studies showed that the incidence of SIBO among patients with IBS is much higher than among people who don’t have IBS symptoms. The exact link between IBS and SIBO has not yet been clarified by medical science.
Medical Treatment for SIBO
In Western medicine, the treatment of SIBO typically involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at reducing the bacterial overgrowth, addressing the underlying causes, and managing symptoms.
Along with trying to find and address any underlying conditions that may be causing or contributing to SIBO, the mainstays of conventional treatment include antibiotics and medications to help improve gut motility.
The primary treatment for SIBO is the use of antibiotics to reduce the bacterial load in the small intestine. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include rifaximin, metronidazole, and ciprofloxacin. These antibiotics are chosen for their ability to target the small intestine bacteria while minimizing disruption to the rest of the gut microbiota.
Unfortunately, while antibiotics may help reduce bacteria, but they can also come with unwanted side effects. Rifaximin can cause bladder pain, urinary frequency, difficulty urinating, and cloudy urine. It can also contribute to feelings of anxiety, dizziness, headaches, fast breathing, fast heartbeat, and problems sleeping.
Antibiotics do not necessarily ease symptoms like gas and bloating, and can cause constipation and black, tarry stool.
Prokinetics are medications that help improve gut motility, ensuring that food and bacteria move efficiently through the digestive tract, which can help prevent bacterial stasis and overgrowth. Common prokinetics include erythromycin in low doses, prucalopride, and metoclopramide.
Dietary modifications will usually be recommended to help manage SIBO. Patients are often advised to follow specific diets such as the low FODMAP diet, which reduces the intake of fermentable carbohydrates that can feed bacterial overgrowth. Other dietary approaches may include the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) or an elemental diet, which involves consuming easily digestible, nutrient-rich formulas.
It can be difficult for people to follow a SIBO diet, and many physicians are not able to spend the time with patients that is required to properly support these behavioral changes. Without dietary support, the antibiotics and prokinetics may not do enough to get rid of SIBO.
Successful treatment of SIBO often requires addressing any underlying conditions that contribute to bacterial overgrowth. This could involve treating gastrointestinal motility disorders, managing chronic pancreatitis, or addressing structural abnormalities such as strictures or diverticula.
By understanding the underlying causes and employing a comprehensive treatment strategy, conventional medicine aims to alleviate symptoms and reduce the recurrence of SIBO. However, due to the chronic nature of the condition and the complexity of the gut microbiome, many patients seek complementary treatments such as acupuncture and herbal medicine to support their overall gut health and enhance the effectiveness of their treatment plan.
Can Acupuncture Help SIBO?

Chinese herbal medicine has its own way of helping to relieve SIBO, improve motility and digestion, and soothe uncomfortable stomach pain and bloating.
TCM theory views stagnation of Qi and blood as being one of the primary pathogenic forces in the body that causes pain and disease. In the case of SIBO, weakness or stagnation of organ systems, such as the stomach, liver, and spleen, is often part of the diagnostic pattern.
Diet, herbs, and supplements may all play an important role, in addition to acupuncture treatment for SIBO. Digestive enzymes and/or probiotics may be helpful in some cases. It may be necessary to eliminate some foods for a time to help control excessive fermentation and bacterial proliferation that is causing the gas and bloating.
There are foods and herbs that can work as natural prokinetics, to help improve gut motility and aid in proper absorption of nutrients. Ginger, turmeric, and peppermint oil are a few easy-to-find products that can help with digestion. There are also classic Chinese herbal preparations that can work even better than pharmaceutical prokinetics to help relieve constipation and indigestion.
A review of trials in China using Modified Runchang-Tang (MRCT) showed that in a sampling of over 2000 patients, this herbal formula worked better than conventional laxatives for relieving constipation.
Another review found that Modified Chaihu Shugan powder (MCSP) worked better than chemical prokinetics to help resolve symptoms of dyspepsia, or indigestion.
In addition to specific Chinese herb formulas that can help relieve digestive issues and work to get rid of unhealthy bacteria, there are other well-known common herbs that can also be helpful:
- Black cumin
- Garlic
- Cloves
- Cinnamon
- Thyme
- All-spice
- Bay leaves
- Mustard
- Rosemary
Acupuncture practitioners have generally received much more specialized training in nutrition than conventional doctors. Your acupuncturist will be able to make dietary recommendations that are specific to your symptoms and condition.
Acupuncture for SIBO Near Me in Los Angeles
Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in West Los Angeles/Santa Monica have over 30 years of experience helping people with all types of gastrointestinal disorders. You do not have to suffer with gas pain and bloating, constipation or persistent diarrhea. Try Chinese medicine as an alternative or adjunct treatment for SIBO and IBS.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Nausea With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Feeling nauseous, nauseated, queasy? Feel like vomiting or throwing up? Nausea can be brought on by many different health conditions. Acupuncture and TCM can provide nausea help in many situations, whatever the cause of nausea.
Nausea is that feeling that you have to vomit, or throw up. It’s an uneasy feeling that is often referred to as being “sick to your stomach.” Feeling nauseous may or may not precede actually vomiting.
Nausea is a symptom, not a disease in and of itself. There are many different kinds of health issues that can make you feel nauseated, or cause you to vomit.
Symptoms of Nausea
A queasy stomach is often accompanied by other symptoms. Nausea can often include or coincide with:
- Feeling like you are going to vomit
- Stomach ache, pain in belly
- No appetite, stomach turns at the thought or sight of food
- Sweating, clammy skin
- Salivating, swallowing a lot
- Uneasy feeling in the back of your throat
- Contractions of the respiratory or abdominal muscles
- Retching
- Dizziness
- Headache
Sometimes people feel nauseous after eating, or have a headache and nausea, or dizziness and nausea.
Some of the most common causes of nausea are a stomach flu, or gastrointestinal virus, morning sickness during pregnancy, and motion sickness.
There are many reasons why a person may feel nauseated, related to various health conditions.
Acupuncture and TCM provide a very effective way to help relieve nausea caused by all kinds of health issues.
Why Do I Feel Nauseous?

We all know what it is like to feel car sick or have a 24-hour stomach bug that makes us feel queasy and vomit. But sometimes we have recurrent nausea and do not know why.
The cause of nausea can sometimes be hard to pinpoint, if nausea comes and goes, or becomes a chronic, ongoing problem.
Top 10 Causes of Nausea
The medical conditions that most commonly cause nausea include:
- GERD – Acid reflux can cause excess salivation and regurgitation of food
- IBS – irritable bowel syndrome can lead to changing symptoms of nausea, gas, diarrhea, and constipation
- IBD – inflammatory bowel disease like ulcerative colitis can cause nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea
- Hepatitis – HBV or Hepatitis C can cause loss of appetite, nausea, and abdominal pain
- Migraines – nausea and vomiting can be part of a migraine headache
- Meniere’s disease – inner ear problem that can cause dizziness, vertigo, and nausea
- Anxiety – anxious feelings, depression, and other mental health issues like claustrophobia or PTSD can cause nausea
- Pregnancy – morning sickness
- Diverticulitis – inflamed sacs in the intestine can cause gas, bloating, and nausea
- Guillain-Barre syndrome – autoimmune disease affecting the neurological system can cause nausea in addition to muscle weakness and fatigue
- HIV/AIDS – people experiencing the acute phase of HIV often feel nauseated and fatigued
Being constipated can cause nausea.
Bacterial meningitis, swelling of the brain that can happen due to a bacterial or viral infection, can cause nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder that affects digestion, can often cause nausea, bloating, and abdominal pain.
People often feel nauseated or vomit when experiencing a gallbladder attack or when passing a kidney stone.
Hormonal changes during PMS, the menstrual period, ovulation, and pregnancy can cause nausea.

Nausea and vomiting can often be side effects of medications that are used to treat some conditions. Opioid painkillers, in particular, can cause dizziness and nausea.
Stomach ulcers, or peptic ulcers, can cause nausea, as can gastroparesis.
Antibiotics can cause nausea and diarrhea. Even NSAIDs like Ibuprofen and and Motrin can cause nausea or stomach upset. Some blood pressure medications can also cause queasiness.
Feeling nauseous is a common side effect of chemotherapy for cancer treatment.
TCM has acupuncture protocols and herbal formulas to help alleviate the nausea associated with all of the conditions listed above.
Nausea Medicine
Most people probably have OTC preparations to relieve nausea and stomach upset in their medicine cabinet, such as Pepto-Bismol, or Dramamine to prevent motion sickness.
If you seek medical care for recurrent or chronic nausea, you may be prescribed antiemetics (such as promethazine), which block the receptors in the brain that trigger nausea sensation.
Drugs known as prokinetic agents work by affecting the lower esophageal sphincter and moving food more quickly through the digestive system. Erythromycin and domperidone are examples.
Certain antihistamines, like Benadryl, are also sometimes prescribed to help reduce nausea, as they block certain chemical responses and reduce stomach acids that can cause nausea.
More recently, cannabinoids may be used medicinally to help quell nausea. These may be prescribed as a synthetic form of TCH.
While these medications may help to relieve nausea in some cases, they do generally come with side effects, like drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, or vision problems.
Acupuncture is widely considered to be an effective modality to treat nausea, without any side effects.
Can Acupuncture Help Nausea?
One of the foundational principles of TCM theory is that an acupuncturist may use the “same treatment for different diseases.”
This means that while a condition, such as nausea, may be caused by any one of several different internal or external factors, the treatment may be the same. It also refers to the concept that many different types of conditions can be caused by a disharmony in a particular organ system.
Therefore, using acupuncture and herbs to bring balance to a particular organ system can help relieve many disorders that would be considered separate and distinct from one another in modern conventional medicine.
There are several key acupuncture points that will have a positive effect on the reduction of nausea, and no matter what is the cause of nausea, they will work in many cases to alleviate nausea in the short term. The point known as P6, in particular, is a classic point for quickly quelling queasiness.
Beyond that, a TCM practitioner will look carefully at other symptoms to find the root cause, which may be related to a deficiency of stomach or spleen Qi. These are the organs primarily responsible for the processing of food. If there is too much heat or phlegm in the stomach or spleen, there will be indigestion.
Emotional factors can also affect the stomach Qi. Worry, repetitive thoughts and rumination are associated with stomach problems in TCM. Acupuncture can also help to relieve the physical and emotional symptoms of anxiety.
The liver also plays a role in digestion, by producing bile. So when any one of these organs is stagnant or not functioning smoothly, it can cause indigestion and the reversal of stomach Qi – causing the energy to move upwards rather than downwards.
One study of patients suffering from mild to moderate nausea and dyspepsia who had not responded to conventional medications showed that symptoms were greatly reduced after just three acupuncture sessions.
Acupuncture can help relieve nausea caused by morning sickness and other conditions because it affects the release of endorphins and ACTH, a pituitary hormone that inhibits the vomiting trigger response.
A research study that looked at thousands of cases found the acupuncture was effective at reducing nausea due to morning sickness, as well as postoperative nausea and chemotherapy induced nausea.
Chinese herbs can also be used to help balance the organ Qi and to relieve stomach upset. Your acupuncturist will create a formula that addresses both nausea symptoms and the deeper issues that are the cause of nausea.
Ginger is also one of the most effective natural remedies for nausea. A few slices of fresh ginger, with the skin still on, steeped in hot water as a tea can help relieve nausea in many situations.
Acupuncture Near Me for Nausea in Los Angeles
TCM offers nausea help for people of all ages, with all types of health issues. Drs. Tan and Cai at Art of Wellness in West Los Angeles have 35 years of experience helping people with all types of gastrointestinal disorders, hormonal conditions, and autoimmune conditions. Our expertise in reproductive health allows them to help women who experience morning sickness or nausea during ovulation or menstrual issues. We also have extensive experience helping cancer patients who are undergoing chemotherapy feel more comfortable and deal with side effects of cancer treatment.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Gallbladder Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Pain on right side abdomen? Sudden, sharp right abdomen pain? This could be a sign of a gallstone or gallbladder issue. Gallbladder attacks can cause severe gallbladder pain. Acupuncture and TCM can provide an alternative or adjunct treatment for gallstones symptoms.
The gallbladder is a small organ located on the right side of your abdomen, under the liver. The liver produces bile, a liquid that helps break down fats into fatty acids. The gallbladder stores bile and releases it into the small intestine as needed, to help with digestion.
When the bile that your body produces has too much cholesterol or bilirubin in it, or when bile is not draining out of the gallbladder properly, it can become too concentrated and begin to harden into a solid.
Gallbladder pain usually occurs because a person has gallstones, which are just what they sound like: little stones that develop inside the gallbladder and are made up mostly of cholesterol. The medical term for gallstones is “cholilithiasis.”
Many people have gallstones and are not aware of it. It is possible to have gallstones with no symptoms at all.
Top 5 Gallstone Symptoms
People who have gallbladder disease or gallstones are likely to experience a condition known as “biliary colic.” This means that they have an intolerance for fatty foods and may experience dyspepsia, nausea, and/or bloating when they eat something that disagrees with them.
Severe, sharp right side stomach pain is the most common sign of a gallbladder attack, which is when a gallstone becomes lodged in one of the small tubes or ducts that lead to and from the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Gallbladder symptoms may include:
- Pain in lower right abdomen
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Yellow skin and/or yellow eyes, jaundice
- Fever and/or chills
- Brown pee, brown urine, light-colored poop
Sometimes gallbladder pain can refer to the right shoulder, or between the shoulderblades.
Gallbladder pain can also happen due to inflammation of the gallbladder. This condition is known as cholecystitis and occurs when a gallstone blocks the duct that leads out of the bladder, causing bile and bacteria to build up and become infected.
Stones can sometimes become lodged in the common bile duct, which not only causes pain, but can lead to pancreatitis. Gallstones are the primary cause of acute pancreatitis, in which the pancreas becomes irritated and inflamed due to a backup of bile and/or digestive enzymes.
The pain of a gallbladder attack is unignorable. If it doesn’t go away within a few hours, most people choose to go to the emergency room for urgent care.
Gallstones may pass on their own, or drugs are sometimes used to help dissolve the gallstones. These drugs can be expensive, and sometimes cause problems like atherosclerosis, or fatty buildup in the arteries.
When gallstone pain comes and goes, and the gallstones are present but not causing the blockage of a duct, usually pain management and patience are the only treatment.
If gallbladder issues keep coming up, the typical medical treatment is gallbladder surgery.
Acupuncture can offer an alternative treatment to help relieve gallbladder pain. TCM is considered an effective treatment for biliary colic due to gallbladder disease.
Gallbladder Removal

It is very common for people presenting with acute pancreatitis or a gallbladder attack to have a cholecystectomy, or gallbladder removal. Over 300,000 cholecystectomies are performed in the U.S. each year.
While this gallbladder surgery is usually done laparoscopically and is minimally invasive, there are disadvantages to living without a gallbladder.
Some people have what is known as postcholecystectomy syndrome, in which they continue to experience pain on right side abdomen, heartburn, nausea, indigestion, and vomiting, even though their gallbladder is gone.
Some research studies have suggested that gallbladder removal may not be necessary or desirable for everyone. It may be worth considering alternative or adjunct gallbladder pain treatment with TCM and acupuncture.
Can Acupuncture Help Gallbladder Symptoms?
Chinese medicine has been used to treat gallstones for thousands of years, without surgery.
According to TCM theory, the gallbladder is the Yang organ that ideally works cooperatively and in harmony with the Yin liver. The gallbladder is an extraordinary organ in that it is part of the digestive system, but it never comes in direct contact with the food you eat. It stores and secretes bile to help break down fats.
In TCM, we consider the gallbladder to represent the part of our nature that makes decisions, takes action, and feels inspired. When the liver and the gallbladder are not functioning smoothly, we may feel frustrated, angry, and depressed. Repressing anger can exacerbate gallbladder problems, as can eating the wrong foods.

In TCM, the gallbladder is associated with spring, and the wood element. It is best nourished with lots of dark, leafy greens, herbs, roots, and green tea. Eating too many fatty, fried foods, and drinking too much alcohol can have a very negative effect on both the liver and gallbladder.
The stimulation of acupoints along the gallbladder meridian can help to regulate the sphincters of the gallbladder and its action, and help to promote the secretion of bile so that it does not remain stagnant inside the gallbladder.
Acupuncture can also have an analgesic effect that may even be superior to that of NSAIDs pain relief medications, without any of the side effects that may occur with regular use of these drugs.
Acupuncture can also be used to treat chronic cholecystitis, the chronic inflammation of the gallbladder due to infection. TCM treatment can help reduce inflammation and improve immune function so that infections can be more easily fought off.
Acupuncture and TCM can also be used as an adjunct treatment to help boost the efficacy of conventional medications. One study showed that patients who were given cefodizime for chronic cholecystitis and also received acupuncture had a 98% effective rate, as opposed to patients who received the medication only, who had only a 50% effective rate.
There are many Chinese herb preparations designed to help with gallstones. These formulas are based on TCM theories related to clearing the stagnation of Qi and blood in the liver and gallbladder, removing dampness and heat and treating yin deficiency.
These herbs have been shown to help discharge gallstones, control the metabolism of bilirubin, and help to prevent the formation of new stones in the future.
Acupuncture Near Me for Gallbladder Pain in West Los Angeles
Acupuncture and TCM can provide natural treatments for gallstones and many other problems related to the digestive system, such as diarrhea, constipation, Crohn’s disease, colitis, IBS, diverticulitis, and celiac disease. If you are experiencing abdominal pain and other digestive symptoms, consider consulting with a TCM practitioner. Acupuncture can help prevent conditions like gallstones from getting worse.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Diverticulitis With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Pain in lower left abdomen? Stomach pain or pain in lower abdomen? Nausea, vomiting? Constipation or diarrhea? These may be diverticulitis symptoms. Acupuncture and TCM offer a way to help relieve diverticulitis pain and restore normal bowel function.
Diverticulosis refers to the presence of small sacs or pouches of tissue inside the large intestine, most often the colon (colonic diverticulitis), which are called “diverticula.”
Diverticulitis refers to the condition that occurs when the sacs become inflamed and infected. Diverticulitis causes pain and other symptoms like bloating and pain in left abdomen that might feel better after you pass gas or have a bowel movement.
Diverticular disease is becoming more and more common and is particularly widespread amongst older people, with at least half of all people over the age of 60 showing signs of diverticulosis.
While medical science has not definitively determined why people develop diverticulosis, it is believed to be due to eating a diet that is low in fiber and high in fatty foods like red meat.
Sedentary lifestyle (lack of exercise), being overweight or obese, smoking cigarettes, and regular use of anti-inflammatory medications or OTC pain medications (NSAIDs) may also be factors in the development of diverticulosis.
Many people have diverticulosis but are unaware of it because they don’t have any symptoms. It is only when the diverticula become infected and inflamed that diverticulitis treatment becomes necessary.
Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative diverticulitis treatment that can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the colon.
Top 5 Diverticulitis Symptoms

Diverticulitis symptoms are believed to occur because something like a bit of undigested food or stool becomes trapped inside one of the diverticula, and then bacteria start to grow, causing an infection.
While a person can have diverticulosis for a long time without any signs, symptoms of diverticulitis may come on suddenly and be quite severe.
The common signs of diverticulitis include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping, particularly pain in lower left abdomen—although in Asian countries, pain in lower right abdomen seems to be more prevalent. The pain may be constant, or it can come and go.
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Fever and/or chills
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding, bloody stool
Sometimes diverticulitis may cause a total lack of appetite and sudden weight loss, as a person just stops feeling like eating anything.
Diverticulitis can sometimes lead to more serious complications, like an abscess—which is when the infected area swells and fills with pus—or perforation of the bowel wall. These kinds of issues may require surgery.
Diverticulitis Treatment
Some other gastrointestinal disorders can present with symptoms that are similar to those of diverticulitis, such as: colitis or inflammatory bowel disease, IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), or bowel obstruction. Gynecological problems like endometriosis, an ovarian cyst, or an ectopic pregnancy could also cause severe pain in the lower left abdomen. A UTI could also cause acute abdominal pain.
Diagnosis of diverticulitis will usually begin with a doctor feeling the abdomen for signs of tenderness, then they will order tests (blood tests, urine tests, and/or stool tests) to check for infection. Once other problems have been ruled out, a CT scan may show the diverticula (infected sacs/pouches in the large intestine).
There is some debate about when to perform a colonoscopy in cases of diverticulitis, as the procedure can cause perforations of the intestinal lining to become worse. Usually, a colonoscopy is recommended several weeks after a person has recovered from an acute attack of diverticulitis.
Because diverticulitis is usually caused by an infection, the most common medical treatment is a course of antibiotics, along with rest and pain relievers, until the acute symptoms have abated. A liquid diet may be indicated until the situation improves, with the gradual reintroduction of solid foods.
Recommendations will usually include that a person quits smoking (if they smoke) and makes changes in their diet: especially eating less meat and fatty foods and increasing fiber intake. It used to be common for doctors to tell their patients not to eat foods like popcorn, seeds, or nuts, under the assumption that small, hard kernels might become trapped in the diverticula and cause irritation. However, more research has shown that eating these types of foods does not seem to cause flare-ups of diverticulitis.
If these treatments do not help to relieve diverticulitis pain, or if a complication like an abscess or perforation in the colon wall develops, surgery may be necessary. The most common surgery for diverticulitis is a colon resection, which involves removing the part(s) of the large intestine that have been damaged. Sometimes it is not possible to repair the colon completely, and in these cases, a person may have to have a colostomy.
Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative or adjunct treatment for diverticulitis that can help reduce inflammation in the bowel and relieve abdominal pain.
Can Acupuncture Help Diverticulitis?

An acupuncturist will make a TCM diagnosis based on where and what kind of abdominal pain and other diverticulitis symptoms a patient is experiencing. According to TCM theory, pain and problems with the digestive organs can be related both to stagnant Qi (life energy) or blood in that area, and the presence of a pathogenic force like dampness, heat, or cold.
The quality of diverticulitis pain and how it changes when you eat or move your bowels will provide clues as to what the root cause is.
In TCM, the spleen is considered to be responsible for turning nutrients into energy; when it is not functioning well, a person may have diarrhea. Strengthening the spleen is usually an important part of TCM treatment for diverticulitis and other digestive disorders.
Your acupuncture practitioner can help relieve symptoms like nausea, constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and stomach pain, while also helping to heal and strengthen the lining of the intestines and reducing inflammation. Boosting immune function will help prevent further infections.
It is generally necessary for a person with diverticulosis to make changes in their dietary habits. While increasing intake of fiber and fluids is important, there are probably even more specific foods that are triggering the dysfunction of the gastrointestinal system, creating excess heat or dampness in the internal organs. TCM nutrition views all foods as having properties that either cool or warm the body. So, your acupuncturist will be able to advise you on what food program will work best to balance your health.
In general, nourishing broths, soups, and well-cooked vegetables with lean proteins and whole grains with plenty of fiber are the best diet for people with diverticulitis. Avoid cold, raw foods, fatty foods, red meat, and dairy.
Acupuncture Near Me for Diverticulitis In West Los Angeles
Acupuncture and TCM provide an effective way to treat abdominal pain and gastrointestinal disorders of all kinds. At Art of Wellness, we have over 35 years of experience helping people find pain relief and improve their digestive health.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.