By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

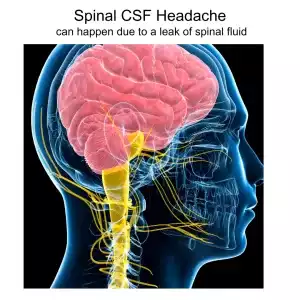
Bad headache that feels worse when you sit up and better when you lie down? Severe headache that lasts for days or weeks? This might be a spinal headache, also known as a post-dural headache or low CSF pressure headache. Acupuncture treatment and TCM remedies can help relieve the intense pain of a spinal headache.
What Is a Spinal Headache?
A spinal headache is a type of headache that can occur after medical procedures like a spinal tap (lumbar puncture) or an epidural block, often used during labor and delivery. These headaches are caused by a leak of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which leads to changes in pressure around the brain and spinal cord.
CSF surrounds the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning and support, while also aiding in waste removal from the brain. If the fluid pressure drops—usually due to a tear in the protective meninges—the brain can sag downward when the individual is upright, leading to pain and other symptoms.
During a spinal tap or similar procedure, a needle is inserted into the fluid-filled space around the spinal cord. Occasionally, this puncture can cause spinal fluid to leak out.
When too much fluid escapes, it disrupts the pressure that cushions the brain and spinal cord, potentially leading to a spinal headache. This fluid leakage can cause stretching of the tissues around the brain and nerves that support it, sometimes resulting in the severe pain of a post-dural headache.
What Causes Low CSF Headache?
Common causes of CSF leaks include:
- Having a spinal tap procedure (lumbar punctures).
- Epidural during labor and delivery.
- Injuries to the meninges (the protective covering of the brain and spinal cord).
Spinal headaches affect 10% to 40% of people who undergo lumbar punctures or epidural anesthesia. The symptoms, such as severe, positional headaches, often resolve on their own, but they can last for days or even weeks in some cases.
Spinal Headache Symptoms

The most common symptom of a post-dural headache is positional pain. The headache is worse when you are standing or sitting upright and subsides when you are lying flat.
Typically absent when you wake up in the morning, symptoms often develop shortly after getting out of bed.
Other symptoms of low CSF headache include:
- Headache pain: Dull, throbbing, and worsened by sitting or standing; improved by lying down.
- Dizziness
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Hearing loss
- Blurred or double vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Nausea
- Stiff neck
Treatment for Spinal Headache
While many spinal headaches resolve on their own within a few days to two weeks, persistent cases may require treatment.
In Western medicine, spinal headaches are typically managed with simple measures such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers.
Fluids may be administered intravenously, to help restore CSF pressure.
Drinking caffeinated beverages, like coffee or tea, may be recommended, because caffeine constricts blood vessels and increases cerebrospinal fluid production.
Medications like gabapentin (used to treat nerve pain), hydrocortisone, or theophylline (which may help build more CSF may be prescribed if other remedies are ineffective.
When symptoms persist, more invasive treatments may be needed, such as an epidural blood patch. This procedure involves injecting a small amount of your own blood near the puncture site to seal the leak, offering rapid relief near the site of the leak to seal it. Another option is a glue injection: using X-ray guidance, doctors can seal leaks with medical glue.
In rare cases, surgery might be recommended.
While these methods are effective, they don’t address the underlying imbalances or promote the body’s self-healing capabilities in the way that acupuncture and TCM can.
Can Acupuncture Help Spinal Headache?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, spinal headaches are not viewed as isolated conditions but as manifestations of deeper imbalances within the body.
TCM practitioners consider spinal headaches a type of head pain related to disruptions in the flow of Qi (energy) and Blood in the body.
Several TCM patterns may contribute to spinal headaches:
- Qi and Blood Deficiency: Weakness from CSF loss can lead to a deficiency of Qi and Blood, resulting in fatigue, dizziness, and headaches.
- Kidney Deficiency: The Kidney is closely related to the spine and brain in TCM. A deficiency in Kidney energy can cause spinal fluid imbalances.
- Liver Qi Stagnation: Stress and emotional strain may block the free flow of Qi, intensifying headache pain.
- Phlegm Obstruction: Excess fluids or “Phlegm” in TCM can block energy pathways, leading to dizziness, nausea, and heaviness in the head.

One clinical trial looked at 60 patients in three groups: one group received conventional care with pharmaceuticals for spinal headache, one group received acupuncture treatment, and one group received sham acupuncture (placebo).
The results for the patients who received acupuncture were similar to those who had been given medication and those who had been given acupuncture, while the placebo group had lower scores. This trial concluded that acupuncture was a good alternative to drugs for spinal headache pain.
Another case study followed 6 patients who were suffering from post-dural headaches after having given birth. All of them agreed to receive acupuncture treatment. Four of the patients got immediate relief after starting treatment. Two patients reported having some temporary relief, but then went on to have blood patch procedures.
Acupuncture Near Me for Spinal Headache
Even though a post-dural headache will usually go away on its own within days or weeks, it can seriously compromise a person’s well-being in the meantime. If you or a loved one is experiencing a low CSF headache, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West L.A.. Doctors Tan and Cai have over three decades of experience helping patients find relief from severe headaches due to all kinds of causes.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.