-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Can Acupuncture Help Bad Breath?
- How to Treat Atopy with Acupuncture and TCM
- Plantar Fasciosis Treatment With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Protect Yourself When Air Quality Is Poor
- How to Treat Spinal Headache With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Sarcoidosis With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Flu With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2025 Year of the Snake
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

July 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Pain
Plantar Fasciosis Treatment With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Foot arch pain? Ache in the bottom of the foot or heel? This condition has commonly been known as plantar fasciitis, but now more practitioners are calling it “plantar fasciosis.” Acupuncture treatment can help relieve arch and foot pain and get you walking comfortably again.
What Is Plantar Fasciosis?
The plantar fascia ligament connects the heel bone to the toes, spanning the whole bottom of the foot. It absorbs shock every time your foot touches the ground, as you walk.
When this band of connective tissue starts to cause you pain, it’s usually due to overuse, overstretching, or wearing shoes that don’t give you enough support and cushioning.
This condition, which is the most common cause of heel pain and pain in the bottom of the foot, has been called “plantar fasciitis” for some time, because it was believed to be caused by inflammation in the connective tissue. The suffix “-itis” means “inflammation,” as in “tendinitis,” “pancreatitis,” and many other health conditions that are related to inflamed tissues.
If the bottom of the foot shows signs of swelling, warmth, and redness, then it is probably related to inflammation.
However, many cases of plantar fascia pain are not caused by inflammation. Sometimes, arch pain is due to a degenerative condition, in which the tissues are breaking down. Microtears in the connective tissues, or cell death, because of lack of blood flow, are often the real problems causing the pain.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciosis
Arch and foot pain when you first get up in the morning is one of the most common signs of plantar fasciitis or plantar fasciosis. This pain can be sharp and stabbing, or more of a dull ache.
Often, walking or exercise makes the foot feel better for a while, but then, after you sit down and rest, and then get back up, the pain flares up again.
The signs that you may have damage in your plantar fascia include:
- Pain in the heel of your foot
- Sore foot arch or foot arch tenderness
- Stiffness in the foot
- Tight Achilles tendon
- Swelling around the heel
Why Does the Bottom of My Foot Hurt?
Lots of activities can cause damage to the sensitive connective tissue in the bottom of your foot. Some of the causes of plantar fasciosis include:
- Standing for long periods of time
- Working out, dancing, or just walking on a hard surface (like a concrete floor or sidewalk)
- Exercising without stretching or warming up your feet and leg muscles
- Wearing shoes with little support, like sandals or flat sneakers
- Walking around barefoot a lot (even at home)
You might be more susceptible if your arches are very high, or if your feet don’t have much of an arch at all. You may also be at higher risk for foot pain if you are carrying a lot of extra weight.
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis can also contribute to the development of plantar fasciosis.
Plantar Fasciosis Treatment
Typically, a doctor does not even need to perform any special diagnostic testing to conclude that a person is experiencing plantar fasciitis, or “heel spur syndrome.”
A treatment protocol typically includes some stretching exercises, the use of orthotics, OTC pain medications, and possibly corticosteroid injections.
Rest and patience, and a gradual increase of physical activity are usually recommended.
Acupuncture treatment can help by relieving pain and helping to promote healing in the damaged tissues.
Can Acupuncture Help Plantar Fasciosis/Plantar Fasciitis?
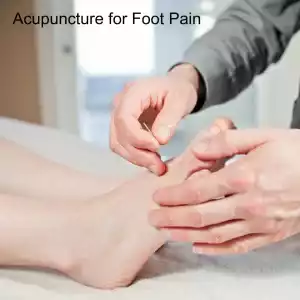
TCM takes a holistic approach to treating pain conditions and sports injuries. From the TCM perspective, trauma to the plantar fascia area can lead to stagnation and deficiency in the flow of Qi and blood.
Acupuncture, Tuina massage, and gua sha are all TCM modalities that can help improve blood flow and promote healing.
Pain sensations stem from injury and damage to bodily tissues, but the pain signals themselves are controlled by the central nervous system and brain activity. Acupuncture has been shown to have effects that can calm down this signalling, which can alter how a person experiences feelings of pain.
Medical science is still conducting research to understand how it is that acupuncture treatment works effectively to reduce and relieve pain.
The action and “excitability” of neurons in the hypothalamus are related to pain sensations. It has been suggested that acupuncture treatment may help to change the excitability of the neurons, thus changing the perception of pain.
It has also been suggested that pain in the plantar fascia is related to the activation of trigger points in the muscles of the foot. Electro-acupuncture can help “deactivate” these trigger points to relieve pain.
Acupuncture needling may affect nerve endings in the local area that release vasoactive neuropeptides, which play a key role in blood flow to an area and the release of hormones. It may also reduce electrical activity, or the “twitch” response in muscle tissues.
Acupuncture can also increase the levels of endorphins, serotonin, and noradrenaline released by the body’s own pain relief system, and help to decrease the number of pain signals that are being sent through the central nervous system.
One study compared patients who were given exercises to help with their plantar fasciopathy versus patients who did the exercises and were given acupuncture treatment. The exercise-only group experienced an overall 21% reduction of their pain scores, while the acupuncture group reported a greater than 50% reduction in pain right after the treatments.
How to Help Plantar Fasciosis Pain
Here are a few important tip for how to help heal and prevent foot pain from coming back.
- Wear shoes with a wide toe box and flat heels (not high heels). Be sure to replace your shoes as needed; the cushioning foam in shoes breaks down, even if you haven’t been wearing them often.
- Wearing toe spacers that help create more space around your toes can help by reducing the constriction of blood vessels and getting more blood flow to your whole foot.
- A warm foot bath every night before bedtime, especially with Chinese herbs or Epsom salt, is very helpful for circulation, which is essential for healing damaged connective tissue.
- Warm up properly before your workout, and vary your workouts, so that you are not just engaging in the same repetitive actions every time you exercise.
- Avoid running and walking on concrete surfaces, and avoid exercising outdoors when it is damp, rainy, and cold.
Acupuncture Near Me for Plantar Fasciosis in West Los Angeles
Plantar fasciosis pain can get in the way of your daily exercise routine and make walking painful for months, if you don’t take proper care of it. The right combination of gentle exercise, acupuncture treatment, herbs and nutrition can help you get back to walking normally without pain more quickly. If you are feeling that pain in the bottom of your foot every morning when you get out of bed, please consider coming and seeing Dr. Tan or Dr. Cai to help relieve heel pain.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Wrist Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac. Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Wrist pain when you bend it? Is it hard to open jars or doors? Popping sound in wrist? Pain at the base of the thumb? Wrist or fingers swollen? Wrist pain can be caused by a variety of joint issues, including tendinitis of wrist, or De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Acupuncture and TCM can help treat the root cause of wrist pain.
The wrist is a complex joint composed of several small bones, tendons, ligaments, muscles, and nerves. In medical terminology, the thumb side of the wrist is the radial wrist (wrist pain on thumb side, radial thumb pain, or inner wrist pain), while the little finger side is the ulnar wrist (wrist pain on pinky side, ulnar wrist pain, or outer wrist pain).
Injuries, such as a wrist fracture, are a particularly common cause of acute wrist pain, as people will often try to catch themselves with an outstretched hand when falling, which can easily lead to wrist injury. Wrist fractures can result in wrist pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to move the wrist normally.
Fractures may also damage nearby ligaments, nerves, and tendons, which can complicate healing and prolong discomfort. Proper alignment and stabilization are essential for healing, and if not treated correctly, a fracture can lead to chronic pain and arthritis in the wrist.
Acupuncture treatment can certainly be helpful for reducing inflammation, relieving acute pain, and helping to speed the healing of a wrist fracture.
Other, more chronic conditions can also cause wrist pain.
Top 5 Causes of Wrist Pain

Certain chronic health conditions that build up slowly over time can ultimately lead to wrist pain and dysfunction. Some of these include:
- Arthritis of the Wrist – Osteoarthritis of the wrist and rheumatoid arthritis can both be causes of wrist pain. Osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear on the cartilage of the wrist joint. This condition usually develops slowly over time, especially in individuals who have experienced previous injuries or repetitive stress on the wrist. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the wrist joints, leading to pain, warmth, and eventual joint damage. Both types of arthritis can severely limit the range of motion and strength in the wrist, making even simple activities painful.
- Repetitive Stress Injury (RSI) – Repetitive stress injuries in the wrist are caused by continuous or repetitive movements, such as typing, gripping, or lifting, which can strain the tendons and ligaments in the wrist. Over time, this repetitive strain can lead to inflammation, pain, and decreased mobility. Carpal tunnel syndrome and tendonitis (discussed further below) are common forms of repetitive strain injury that cause wrist pain. RSI often requires rest and modification of activities to allow the wrist to heal, as continuous stress can worsen the condition and lead to long-term issues.
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis – De Quervain’s tenosynovitis (also known as Quervain disease or styloid tenosynovitis) affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed, leading to pain and tenderness, particularly during movements that involve gripping or pinching. This condition is often the result of repetitive thumb movements, such as those used in typing or texting. De Quervain’s disease tenosynovitis can cause sharp pain on the radial (thumb) side of the wrist, and people may find it difficult to grasp or hold objects.
- Tendonitis (or Tendinitis) of the Wrist – Tendonitis of the wrist refers to inflammation of the tendons that cross the wrist joint. It is commonly caused by repetitive motion, excessive strain, or sudden injury. Tendonitis can affect various tendons depending on the type of movement that led to the condition. Pain and swelling are typical symptoms, and the affected area may feel warm to the touch. Wrist tendonitis is often seen in athletes and individuals who perform repetitive tasks with their hands and can result in decreased wrist function and grip strength.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – Carpal tunnel syndrome is a type of neuropathy, or nerve pain, caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. This compression leads to pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is often associated with repetitive wrist movements and can be exacerbated by activities that involve gripping or bending the wrist. If left untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to permanent nerve damage and reduced hand function.
Other possible causes of wrist pain could include: bursitis (small, fluid-filled sacs that form between bones), ganglion cysts (fluid-filled cysts that form near joints), or Kienbock’s disease (in which the lunate bone of the wrist begins to break down).
Treatment for Wrist Pain
When a patient presents with wrist pain, diagnosis usually begins with a physical examination to identify the specific cause of pain. The doctor will assess the patient’s range of motion, grip strength, and any areas of tenderness or swelling in the wrist. Imaging via X-rays, MRI or ultrasound may be used to confirm a diagnosis, especially if a fracture, ligament tear, or nerve compression is suspected.
For nerve-related issues like carpal tunnel syndrome, a nerve conduction study (NCS) or electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to assess the functionality of the median nerve. This can help differentiate between arthritis, repetitive strain injuries, or specific tendon and nerve issues.
Conventional treatments for wrist pain depend on the specific diagnosis. In cases of arthritis, anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, or physical therapy are commonly recommended to manage pain and improve joint mobility.
For fractures, immobilization with a cast or splint is typically required, and surgery may be necessary for more severe breaks. Repetitive stress injuries like tendonitis or De Quervain’s tenosynovitis often respond to rest, ergonomic modifications, and anti-inflammatory treatments.
Physical therapy exercises to strengthen and stretch the affected muscles and tendons can be helpful. In cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, wrist splints are often used to keep the wrist in a neutral position, particularly at night, and corticosteroid injections may be administered, aimed to reduce inflammation.
If these methods do not relieve symptoms, surgical intervention, such as carpal tunnel release, might be recommended to decompress the median nerve.
While typical treatment usually involves pain medication, rest, and possibly physical therapy, acupuncture treatment can be an excellent adjunct or alternative treatment to relieve wrist pain.
Can Acupuncture Help Wrist Pain?

Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) can offer natural pain relief for injuries and chronic pain conditions, by reducing pain and inflammation, improving circulation, and supporting the body’s healing process.
According to TCM theory, the health of the internal organ systems is related to the rest of the body parts. For example, the spleen is responsible for transforming Qi and blood. If the spleen is weak, it can cause blockages in blood flow that create stasis, stiffness and pain in the limbs and joints. The liver governs the tendons of the body. When the liver is not functioning well, often due to emotional stress, than there may be pain and dysfunction in the tendons and joints.
Therefore, an acupuncturist does not only treat the painful area, but also looks at the deeper root cause and addresses them with acupuncture treatment, Chinese herbs, and other therapeutic modalities, to help relieve pain and inflammation and bring about healing.
A systematic review of trials showed that acupuncture treatment led to significant pain reduction for patients treated for rheumatoid arthritis affecting the wrist. It also concluded that acupuncture brought about pain relief and functional improvement for patients with tenosynovitis and carpal tunnel syndrome.
One study separated patients with carpal tunnel syndrome into two groups: one group received pain medication for wrist pain and the other group had 12 acupuncture treatments. Comparatively, the acupuncture group had greater reduction in pain, tingling, and numbness and greater functional improvement.
Studies of MRI results after acupuncture have suggested that acupuncture for carpal tunnel syndrome actually has a positive impact on nerve function in the wrist and changes the way the brain and nerves are signaling pain.
A trial involving patients treated for De Quervain’s disease tenosynovitis with five acupuncture sessions over the course of two weeks showed improvement in pain and grip strength, and the results were still maintained at a ten week follow up visit.
The combination of acupuncture and moxibustion can be particularly helpful for treating Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
Overall, the evidence shows that acupuncture and other TCM modalities can be a relatively low cost, non-invasive way of helping to treat wrist pain, without surgery or the unwanted side effects of pain medications or steroid injections.
Acupuncture Near Me for Wrist Pain in Los Angeles
Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in West L.A. have over 35 years of experience helping people recover from sports injuries, repetitive stress injuries, and orthopedic pain conditions of all kinds. Acupuncture treatment for wrist pain can be used in addition to your medical protocol to help speed recovery and bring about pain relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Cervical Radiculopathy With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Neck pain? Stiff neck? These could be signs of cervical radiculopathy caused by a pinched nerve in neck. Acupuncture and TCM can provide neck pain relief and address the underlying causes of cervical radiculopathy.
Cervical radiculopathy occurs when a nerve in the neck becomes compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal cord. This is often referred to as a “pinched nerve.” This condition can lead to neck pain, weakness, and other symptoms not only in the neck but radiating into the arms and hands as well.
Cervical radiculopathy can be caused by several different factors, most of which involve some form of nerve compression in the neck.
One of the most common causes is a herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc in neck, or bulging disc in neck. This happens when the gel-like center of a spinal disc pushes out through a crack in the tougher exterior, putting pressure on a nearby nerve root. This can happen due to injury or degeneration over time.
Cervical spondylosis, also known as neck arthritis or cervical osteoarthritis, is a common age-related condition that affects the joints and discs in your neck. As the discs and cartilage between the cervical vertebrae wear down, this can cause neck pain and stiffness.
Degenerative disc disease and osteoarthritis are also common causes of a pinched nerve in neck. As we age, the spinal discs lose water content and shrink, leading to decreased cushioning between the vertebrae. This can cause the bones to rub against each other and lead to the formation of bone spurs, which can press on nerves and cause radiculopathy.
Another potential cause is spinal stenosis, which is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine. Lumbar spinal stenosis can result from a variety of factors, including thickened ligaments or overgrown bones, and leads to pinching or compression of the nerve roots as they exit the spinal column.
Additionally, trauma or injury to the neck, such as from car accidents or sports injuries, can directly damage the vertebrae or discs and result in a pinched nerve.
In more rare cases, tumors or infections in the spine may also cause cervical radiculopathy by compressing nerve roots.
Top 5 Symptoms of Cervical Radiculopathy
Pain in the neck and shoulders and headache are the most common symptoms associated with cervical radiculopathy. Poor reflexes and muscle weakness can also occur with a pinched nerve in the neck.
- Neck and shoulder pain – sharp or burning pain that starts in the neck and may radiate down the shoulder, arm, and hand
- Neck Stiffness – difficulty turning or moving the neck, neck muscle pain, muscle spasm in neck
- Numbness or Tingling in the shoulder, arms, or hands due to nerve compression.
- Muscle weakness in the arms or hands, trouble gripping or lifting objects.
- Neck pain and headache, headache that starts with neck pain
Diagnosis and Treatment for Cervical Radiculopathy
Diagnosing cervical radiculopathy can be challenging because its symptoms—such as neck pain, numbness, or tingling radiating down the arm—can overlap with other conditions like muscle strain, carpal tunnel syndrome, or even heart problems.
The complexity of nerve pathways makes it difficult to pinpoint the exact location and cause of nerve compression based on symptoms alone. The pain can vary in intensity, and some patients may not experience obvious arm symptoms, leading to confusion in initial assessments.
Western medicine typically relies on a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic imaging to confirm cervical radiculopathy.
During the clinical evaluation, a doctor will perform a physical examination, testing the strength, reflexes, and range of motion in the neck and arms. A Spurling’s test, where the head is turned and pressure is applied to the top of the head, may be used to reproduce symptoms and help localize the nerve root affected.
To confirm the diagnosis, imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs are often used to visualize the spine and detect any structural issues, like herniated discs or bone spurs, that could be compressing the nerve roots. An electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction study may also be performed to assess how well the nerves are functioning and to rule out other conditions affecting nerve function.
Conventional treatments for cervical radiculopathy, or treating a pinched nerve, generally focus on reducing pain, managing inflammation, and restoring normal function.
NSAID medications like ibuprofen or naproxen are usually recommended to reduce pain and inflammation around the pinched nerve. Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation around the nerve root and offer temporary relief. Muscle relaxers may be prescribed to ease muscle spasms and reduce pressure on the pinched nerve.
Physical therapy exercises designed to improve neck mobility and strengthen supporting muscles, can potentially help relieve nerve compression. Using cervical traction devices to gently stretch the neck and reduce pressure on the affected nerve may be helpful in some cases.
In severe cases where non-surgical treatments don’t work, surgical options may be recommended to relieve pressure on the nerve by removing or repairing the affected disc or vertebra.
Acupuncture can be an effective modality for treating neck pain and stiffness due to cervical radiculopathy, without the unwanted side effects of taking pain medications and muscle relaxants.
Can Acupuncture Help Cervical Radiculopathy?

Acupuncture offers an alternative for patients suffering from neck pain who want to avoid surgery and the side effects of medication. Acupuncture treatment stimulates the body’s natural healing processes and alleviates pain by influencing the nervous system, reducing inflammation, and improving blood circulation to affected areas.
Acupuncture functions in multiple ways to help relieve nerve compression pain. It can help reduce swelling, or edema, that contribute to nerve compression. It also helps to relax muscle spasms. Acupuncture helps to increase blood flow to nerve roots.
Studies have shown that acupuncture can yield favorable outcomes, often comparable to conventional drug therapies. For instance, one randomized clinical trial found that acupuncture provided similar pain relief to drug therapy, making it a viable, safer alternative for pain management in cervical radiculopathy patients.
Additionally, some research has demonstrated the benefits of combining acupuncture with other conservative treatments, like cervical manipulations, to enhance therapeutic outcomes. In clinical trials, this combination has proven effective in reducing pain and improving mobility.
Acupuncture, used to complement other modalities, can be used as a valuable tool in the management of cervical radiculopathy, offering an effective, low-risk option to relieve pain and restore better mobility.
One case study of a patient with a C6/7 disc prolapse and radiculopathy showed that over a course of six acupuncture sessions administered within four weeks, significant improvements were observed in both pain and range of motion. Pain levels dropped from 8/10 to 2/10.
Acupuncture Near Me for Cervical Radiculopathy in West L.A.
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture and TCM in West Los Angeles, we have over 35 years of experience helping people find relief from all types of pain conditions related to nerve compression and neck pain, including herniated disks, spinal stenosis, cervical spondylosis, and cervical radiculopathy. Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai provide specialized care for each individual patient, including herbal remedies, therapeutic Chinese massage, and electroacupuncture to help relieve pain.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How To Treat Frozen Shoulder With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Can’t lift arm up? Front shoulder pain? Shoulders hurt when sleeping? Shoulder pain that doesn’t go away can be due to “frozen shoulder” and adhesive capsulitis. Acupuncture and TCM offer treatment for adhesive capsulitis frozen shoulder.
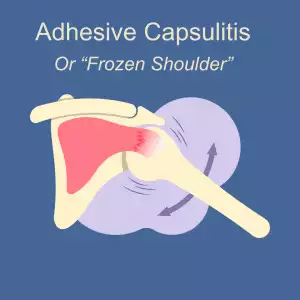
What Is Frozen Shoulder? Understanding Shoulder Pain and Adhesive Capsulitis
Frozen shoulder, medically known as adhesive capsulitis, is a painful condition that limits the range of motion in the shoulder. Over time, the shoulder joint can become stiff and difficult to move, leading to a significant loss of mobility.
Frozen shoulder typically progresses through three stages:
- Freezing – pain becomes gradually more intense, and range of motion decreases, sometimes until the arm is immobile – can last 6 weeks up to 9 months
- Frozen – pain may lessen, but the shoulder joint is still stiff and very difficult to move – can last 4-6 months
- Thawing – movement and strength is slowly regained – typically lasts anywhere between 6 months to 2 years
While frozen shoulder may be considered resolved when the pain has improved and basic functionality returns, many people continue to feel some stiffness and pain for many years.
What Causes Frozen Shoulder?
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint made up of three bones:
- The humerus (upper arm bone)
- The scapula (shoulder blade)
- The clavicle (collarbone)
The ball of the upper arm bone fits into a shallow socket in the shoulder blade, and this joint is surrounded by a thick capsule of connective tissue called the shoulder capsule. To help the shoulder move smoothly, synovial fluid lubricates the joint.
In cases of frozen shoulder, this capsule thickens and becomes stiff, with the development of adhesions or scar tissue, reducing the fluid in the joint. This usually leads to significant pain and often severely limited movement in the shoulder.
What Are the Risk Factors for Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder?
Frozen shoulder primarily affects adults, especially those between 40 and 60 years old, and it occurs more often in women than men. It is particularly common in women experiencing perimenopause and menopause, likely due to hormonal changes that can contribute to joint and connective tissue issues.
Certain medical conditions increase the likelihood of developing frozen shoulder. For example,
people with diabetes are at a higher risk for frozen shoulder, and they often experience more severe stiffness and longer recovery times.
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are associated with an increased risk of frozen shoulder.
Immobilization of the shoulder following surgery or injury can also trigger the onset of frozen shoulder, especially if movement is restricted for long periods.
Many people wake up with a sore shoulder from sleeping in a way that restricts movement. Shoulder discomfort or front shoulder pain can happen due to sleeping positions that put pressure on the sensitive shoulder joint.
Frozen shoulder can also cause discomfort on one side, leading to reports of sore right shoulder or ache in left shoulder depending on which shoulder is affected.
Treatment for Frozen Shoulder/Adhesive Capsulitis
A doctor will typically diagnose frozen shoulder after an examination to determine passive range of motion and active range of motion in your shoulder. They may choose to order X-rays to rule out other problems.
In most cases, using hot and cold therapy with compresses and icing may be recommended, as well as pain medications/anti-inflammatories like Ibuprofen. If pain continues to be severe, a physician may offer steroid injections (corticosteroids).
Patients may be referred for physical therapy or massage to help with stretching and improving range of motion.
If pain and immobility persists past a year, surgery may be recommended. A “capsular release” procedure involves making small incisions in the tissues of the shoulder capsule. Manipulation and massage, while a person is anesthetized, can also help loosen up the tissues to allow for more mobility.
Acupuncture treatment can help relieve pain and improve mobility for frozen shoulder treatment without negative side effects that can come from the ongoing use of OTC pain medication and cortisone shots/corticosteroids, so it may be considered as an adjunct or alternative treatment for adhesive capsulitis.
Can Acupuncture Help Frozen Shoulder?
The TCM Chinese term for “frozen shoulder” translates into English as “shoulder at the age of 50 years.” Clearly, people in their middle age have been experiencing this pain and limitation in the shoulder joint for centuries. TCM has developed ways of helping to improve this condition.

According to TCM theory, frozen shoulder may fall under the category of “Bi Syndromes.” “Bi” refers to an obstruction of some sort, and Bi Syndromes typically cause pain and stiffness in a part of the body, due to a blockage of the flow of Qi (life force energy).
In TCM, “wind,” “damp,” and “cold” are considered pathogenic forces that can settle in an area of the body and cause blood and Qi to stagnate. This can cause stiffness, lack of movements, tenderness, swelling, and pain in that area. Most types of arthritis, for example, are considered Bi Syndromes.
Conventional medicine tends to treat each person presenting with a condition with the same types of treatments and waits to see if they work. In TCM, there is an understanding that different people can have the same symptoms, and yet have different underlying problems that are causing pain and other symptoms.
Different people may experience pain and stiffness due to different factors. One person may have a stiff, sore shoulder due to an invasion of cold or damp, while another person may show signs of heat or wind. In other words, the very specific presentation of symptoms can help the acupuncture practitioner to determine the underlying causes of the condition and treat them accordingly, with acupuncture and herbal remedies.
The stimulation of specific acupoints can help bring more blood flow to the shoulder joint, so that more nourishment can help reduce inflammation. Electroacupuncture, in particular, can help activate the release of endorphins that reduce pain.
A review of 13 controlled studies of the usage of acupuncture treatment for frozen shoulder determined that it is a good modality for both reducing pain and restoring proper shoulder function.
A randomized, single blind controlled trial looked at 35 patients with frozen shoulder symptoms. Some of the patients were assigned to a group that would engage in physical therapy sessions twice per week, practice exercises at home daily, and not use any pain medications, except in “emergency” situations.
The other group also engaged in physical therapy and exercise, plus they also were given acupuncture treatment twice per week, with functional movement exercises being performed during the acupuncture session.
After six weeks of treatment, patients who had only had PT showed an average 39.8% improvement, while the PT plus acupuncture patients showed an average 76.4% improvement.
One recorded case study detailed that, after 24 acupuncture treatments, a patient regained full range of motion in their shoulder and reported that pain was entirely gone.
Acupuncture for Frozen Shoulder Near Me in West L.A. and Santa Monica
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West Los Angeles, we have over 35 years of experience helping patients find relief from joint pain of all kinds. Dr. Tan is a specialist in treating orthopedic pain. We successfully treat joint pain conditions like frozen shoulder, osteoarthritis of the knee, tennis elbow, bone spurs, bursitis/hip pain, gout, and more. If you are suffering from a lack of mobility and pain in shoulder, please consider visiting our acupuncture office in Los Angeles for a consultation.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.