-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Can Acupuncture Help Bad Breath?
- How to Treat Atopy with Acupuncture and TCM
- Plantar Fasciosis Treatment With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Protect Yourself When Air Quality Is Poor
- How to Treat Spinal Headache With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Sarcoidosis With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Flu With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2025 Year of the Snake
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

July 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Herbal Medicine
How to Treat Pneumonia Symptoms With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.
Persistent cough with green or yellow mucus? Chest pain when you cough? High fever, sweating, trouble breathing? It’s important to know the signs of pneumonia, a serious lung infection that can be caused by bacterial infections or viruses like the flu, COVID-19, or even the common cold. You should seek medical help if you believe you have pneumonia; acupuncture and herbs can be considered as integrative care to help relieve symptoms of pneumonia.
The term pneumonia refers to an infection in the lungs that causes inflammation in the alveoli, or air sacs. These air sacs are clustered like fruits around the ends of the branches of the bronchial tubes that extend deep into the lungs. The alveoli inflate and deflate like tiny balloons. They are responsible for taking the oxygen from the air you inhale and depositing it into the bloodstream. When they become inflamed and filled with fluid due to infection, it is hard to breathe. If pneumonia infection is so severe that your body is not getting enough oxygen, then it can become quite dangerous.
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of infectious bacteria or viruses, and often develops after, or in the tail end, of some other type of illness. A pneumonia infection can range in seriousness from mild to very severe. Bacterial pneumonia requires treatment, especially for people who are considered high risk, or it can be potentially life-threatening. Acupuncture and TCM offer an effective adjunct to conventional pneumonia treatment, allowing people to recover more quickly and fully.
Early Signs of Pneumonia

In many cases, you start out having a cold, flu, or some other illness, and then it “turns into” pneumonia, as your lungs become inflamed and filled with pus or mucus. Symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Cough with green or yellow mucus
- High fever
- Sweating
- Trouble breathing, breathing fast
- Fatigue
- Fast heart beat
- Chest pain, especially when coughing
- Feeling confused or delirious
- Lips and/or nails turn blue
- Loss of appetite
Signs of pneumonia in children may be different that symptoms of pneumonia in adults. There may be coughing, wheezing and high fever, but there may also be vomiting and/or diarrhea, especially if the infection is in the lower part of the lungs. Children are at risk for becoming dehydrated under these circumstances.
Walking pneumonia symptoms are generally milder than other types of pneumonia, similar to symptoms of the common cold, like a low grade fever and hacking cough. A person may not feel so seriously ill that they can’t go about normal activities: hence the name “walking pneumonia.”
Pneumonia can affect just one one lung, or both. When both lungs are infected, it is called bilateral pneumonia, or double pneumonia. This does not necessarily mean the case is more severe.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Some types of pneumonia are caused by exposure to bacteria or viral particles in the air or on surfaces. Germs that cause colds and flu can lead to some people developing pneumonia, while other people could be exposed to those same germs and not get pneumonia. It really depends on a person’s constitutional health and immune system.
Other kinds, like fungal pneumonia or aspiration pneumonia, are not caught through contagion. They develop because of some substance, other than germs, getting into the lungs.
Some types of bacterial pneumonia would not be passed from person to person in normal day-to-day contact, but they may occur when a person is in a weakened state and/or an institutional setting. For example, klebsiella pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that normally lives in the intestines and doesn’t cause illness. However, in a hospital, it is possible to be exposed to this type of bacteria via a worker’s hands or contaminated equipment, such as a catheter or ventilator. If this bacteria then reaches the lungs, it can cause pneumonia symptoms.
Many people “catch” pneumonia when they are in a hospital or rehab setting. Sometimes, people develop pneumonia after being on a ventilator as treatment for some other illness or while recovering from surgery. When this happens, it is called hospital-acquired pneumonia, or health care-acquired pneumonia.
Top 5 Pneumonia Causes
Pneumonia can be caused by various types of infections: bacterial, viral, or fungal.
- Bacterial Pneumonia – also called pneumococcal pneumonia, or streptococcus pneumonia, this is the most common type of pneumonia, and is caused by strep germs that cause upper respiratory illnesses. Almost a million Americans get this kind of pneumonia every year. It can happen at the tail-end of a cold or flu, or after having surgery or being hospitalized for some other reason. People with respiratory problems like asthma or emphysema are at higher risk, as are people who are immunocompromised.
- Viral Pneumonia – this is caused by an influenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). This is the type that children may get more often. If a person who already has heart disease or lung disease, or someone who is pregnant, develops pneumonia after a flu, it can be very dangerous.
- Mycoplasma Pneumoniae (Walking Pneumonia) – this type of pneumonia is caused by a bacterial strain. This usually affects younger people who are living, working, or going to school, and is often mild enough that people think they just have a cold. This is sometimes called “atypical pneumonia,” but that doesn’t mean it isn’t common.
- Fungal Pneumonia – it is possible to get this kind of pneumonia if you are exposed to certain fungi in the environment, like those that live in soil and cause “valley fever,” or fungi that are found in bird droppings.
- Legionnaires Disease – legionella is a bacteria that can live in water or soil, and is sometimes present in plumbing, air conditioning systems, pools, or jacuzzis. People can sometimes breathe it in while gardening. If an at-risk individual breathes in this bacteria, they may develop a kind of pneumonia that also causes body aches. In some cases, people may go into septic shock or kidney failure.
People who have weakened immunity due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, or because they are going through chemotherapy for cancer, are at heightened risk for developing pneumonia, as are people who have trouble swallowing due to neurological conditions like stroke, Alzheimer’s disease/dementia, Parkinson’s disease, or ALS.
Smoking or using other drugs can also increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia, which can occur if a person breathes something–such as saliva, vomit, or food particles–into their bronchial tubes instead of swallowing it.
People with pre-existing lung conditions like emphysema/COPD or Cystic Fibrosis (CF), or other chronic illnesses, like diabetes, are also at higher risk for getting a serious case of pneumonia.
Medical Pneumonia Treatment
It is important to seek treatment if you believe you have pneumonia, because it can become very serious very quickly. First, doctors will do testing to determine what is causing the pneumonia. They will probably perform an x-ray to see where the lungs are inflamed.
Bacterial forms of pneumonia are typically treated with antibiotics, usually some form of amoxicillin. Pneumonia antibiotics cannot help if you have viral pneumonia, although some doctors may recommend medicines like Tamiflu, to help with symptoms.
Recovering from pneumonia takes time, no matter what kind of medication you take. It is normal to feel very tired, possibly for up to a month, or more. Rest, and drink lots of liquids, reduce your workload, and accept help whenever possible.
Acupuncture treatment and Chinese herb preparations can be very helpful for helping facilitate a more comfortable recovery from pneumonia.
Can Acupuncture Help Pneumonia?
According to TCM theory of disease, pneumonia is considered an invasion of the lungs by dampness and heat that leads to the production of phlegm. Wind and heat cause the fever and chills and sweating associated with the pneumonia.
TCM treatment for pneumonia can help on multiple levels: first, by addressing the infection in the lungs, second, by alleviating respiratory and gastrointestinal symptoms, and third, by helping to offset any negative side effects of conventional medical treatments.

Chinese herbal formulations can help to clear heat and congestion from the lungs, reduce fever, and relieve coughing. One study observed two groups of pneumonia patients: both groups were given conventional antibiotics, but one group also received acupuncture herbs, which increased the total effectiveness rate by 10%.
Acupuncture was found to help patients who were hospitalized with severe pneumonia, reducing the amount of time they needed to be on ventilator machines and improving their symptoms.
Another study of children being treated in the hospital for pneumonia found that those who had acupuncture treatment had shorter hospital stays and needed less medication.
TCM works effectively as preventive medicine, so coming in for a regular “acupuncture tune-up” can help you avoid the seasonal colds and flus that can turn into pneumonia. It can also help immunocompromised people and those at higher risk of aspiration pneumonia due to neurological conditions avoid becoming ill.
Acupuncture Near Me for Pneumonia
If you are experiencing fever, chest pain when coughing, extreme fatigue, sweating, and/or looking blue around the lips, do not hesitate to get medical attention. Pneumonia requires urgent care. Once diagnostics have determined whether you have bacterial pneumonia or some other type, then it can be beneficial for you to add integrative care in the form of acupuncture and herbs to your recovery program. TCM methods can help clear phlegm from your lungs and help you regain your strength.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat the Common Cold With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Sneezing, runny nose, nasal congestion, cough? How can you tell if it’s a cold symptom, a flu, COVID-19, mononucleosis, croup, or maybe an allergy? All of these illnesses can cause fatigue and a stuffy nose. The common cold, however, does not cause a high fever, and the cough is usually mild, not a persistent cough. Acupuncture and TCM herbs offer a highly effective way to relieve common cold symptoms.
A cold is a kind of viral infection that affects your upper respiratory tract, centering mostly in the nose and throat. Different viruses can cause the common cold; rhinovirus is the most common kind of cold virus.
You can catch a cold virus when you are near someone else who sneezes or coughs, and you get droplets containing the virus into your own nose, mouth, or eyes, or you touch something they coughed or sneezed on, and then touch your own face.
Young children and people with weakened immune systems are more prone to catching colds, as are people who smoke. You’re more likely to catch a cold if you spend a lot of time in crowded places, like schools, airports, public transportation, etc. More people get colds during the winter, because more people are packed together indoors, but cold-causing viruses are circulating all through the year.
You will start feeling cold symptoms within a few days of being exposed to the virus. Typically, without any medical intervention, a cold will last about a week or ten days. For some people, though, a cold can lead to other, more serious infections, like an ear infection, asthma and wheezing, sinusitis/sinus infection, bronchitis, or even pneumonia.
Cold symptoms aren’t so much caused by the virus, but by the workings of the body’s own immune system to expel the virus. Coughing and a runny nose are the body’s way of getting the virus out of the respiratory system. While the common cold doesn’t necessarily require any medical treatment, it is best to take steps to strengthen your immune system and clear the virus as soon as you can.
Chinese herbs and acupuncture treatment are an excellent way to shorten the duration and lessen the severity of a cold. Regular acupuncture treatment also functions as preventive medicine, so that you and your family don’t catch cold nearly as often.
Top 10 Common Cold Symptoms

How can you tell if you have a cold or a flu? Usually, cold symptoms are more centered in the nose and throat, and are milder than flu symptoms. A flu is more likely to cause serious fatigue, chills and fever, and body aches than a cold is.
The typical symptoms of common cold include:
- Runny nose, stuffy nose, nasal congestion
- Sneezing
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Post-nasal drip
- Watery eyes
- Headache
- Body aches
- Low grade fever
- Fatigue, feeling tired
Sometimes people differentiate between head cold symptoms and a chest cold. A head cold describes the way most rhinovirus colds manifest in the upper respiratory organs: with a stuffed up nose, sniffling, headaches, and a red, sore throat.
If the cold “moves” down into the chest, causing inflamed bronchial tubes, and mucus production in the lungs, this is called acute bronchitis. This feels more like chest congestion, with a more persistent cough. Once a cold turns into bronchitis, you are more likely to have a serious cough, with or without coughing up phlegm.
How Is the Common Cold Usually Treated?
The accepted wisdom is that there is no cure for a cold; you just have to do whatever you can to make yourself more comfortable while the illness runs its course. Antibiotics only help get rid of bacterial infections. They do not help when you have a viral infection.
While it is true that there is no medication you can take to get rid of a cold, there are many remedies, both traditional home remedies for cough, and popular over-the-counter medicines and health store supplements that claim to take care of your cold symptoms.

Many people swear by things like Vitamin C, Zinc lozenges, or echinacea preparations. Other people will tell you to drink hot honey water and eat chicken soup. All of these natural cold remedies may have some benefits. At least, they don’t do any harm.
Other cold medicines may do more harm than good. Cough suppressants and nasal decongestants actually work against your body’s natural defenses. Your body is producing mucus and the cough reflex in order to expel the virus and keep it out of your lungs. Repressing these natural immune responses can prolong your cold.
Nasal decongestants like Sudafed can cause a fast heart rate and jittery feelings, especially in young children. Cough syrup with antitussive properties, or cough suppressant, can have negative side effects besides just making you drowsy or irritable. Some cough medicines can interact with other medications, making them inappropriate for people who have problems like high blood pressure, enlarged prostate (BPH), or glaucoma.
Trying to power on through your days with the help of OTC cold relief medications, caffeinated drinks, and sugary cough drops, without getting the rest you need, is not a good idea. Getting extra rest and drinking plenty of fluids are definitely tried and true ways to get over your cold.
Consider that acupuncture and herbal medicine developed over centuries of TCM tradition can help address cold symptoms without any side effects, and may help you recover more quickly than rest alone.
TCM for Colds: How to Get Rid of a Cold Fast

In TCM we consider some conditions to be external, meaning that they come from outside the body, in the form of pathogenic factors like heat, cold, wind, and dampness. Based on the environment, and the types of symptoms, we determine whether a cold follows a pattern of a cold-wind type, or a heat-wind type, or sometimes a hot-damp type as might occur during the summertime. An acupuncture practitioner will then base the treatment on the pattern of cold presented.
Acupuncture treatment influences the immune system’s response, and since that is what is actually causing the symptoms of a cold, the use of acupuncture points for cold and sore throat can really have a positive effect on reducing cold symptoms.
Cupping is a TCM modality that may be used to help treat colds and other respiratory conditions. Cupping helps to relieve congestion and gets lymph and blood circulation moving.
When you come in with a cold, your TCM provider will tailor your acupuncture treatment and prepare an herb formula specific to your needs. That said, our patients who have been coming into Art of Wellness for many years know that there is a

standard formula that is excellent for “knocking out” a cold if you can catch it at the very beginning. Right when you begin to feel that tickle in the back of your throat, that is the time to reach for your supply of Yin Chiao pills!
Ginger tea, made by simply slicing a bit of fresh ginger and steeping it in hot water, is also a great way to stop a cold in its tracks, before it gets worse.
Acupuncture Near Me for Common Cold in Santa Monica, West LA
Making time for regular acupuncture “tune-up” visits can help keep your body and mind balanced and your immune system in good working order. In the ancient TCM tradition, acupuncturists used to treat their patients for free when they caught a cold type illness, because it meant they hadn’t done their job of boosting immunity well enough. Prevention is certainly the best medicine when it comes to colds and flus. When you do begin to feel the first signs of a cold, though, it isn’t too late. Come in for a treatment, or call us at Art of Wellness to order some herbs to be shipped to you. We can help you get over your cold symptoms quickly.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat HIV/AIDS With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac.,Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

What does it mean to be HIV positive? HIV is a viral infection that harms the immune system over time and, if untreated, can eventually lead to AIDS, a syndrome that causes people to become weaker and get serious infections easily. There is no cure for HIV/AIDS, but there are various therapies that can slow the progression of HIV. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can help to improve immune function and relieve symptoms related to the side effects of other HIV/AIDS drug therapies.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an infection that affects the immune system by destroying the white blood cells (CD4 and T-cells) that are such an important part of the body’s immune response, causing people with HIV to be much more prone to all kinds of infections. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is the late stage of HIV, in which the CD4 cells have reached a critical low point and other infections are taking hold in the body.
Over a million people in the U.S. are currently living with HIV. Many more people may have HIV and not know it. People can have HIV for several years without feeling any symptoms, while the illness is in its early stages.
HIV is a progressive illness, which affects the functioning of the immune system over a long period of time.
4 Stages of HIV Infection:
- Infection – when a person contracts the HIV virus, it spreads quickly in the body, often causing flu-like symptoms: fever, headache, rash, sore throat. If you have these types of symptoms, and you think you may have had contact with an infected person or a needle recently, it is very important to go get tested for HIV. Early testing allows people to get treatment as soon as possible, and to know if they are contagious and can spread the virus to others.
- Asymptomatic – the HIV virus remains in the body, causing damage to cells and weakening the immune system, while the person may have no symptoms of HIV/AIDS. This latent stage of HIV can last for quite a long time, averaging 8-10 years. This is why many people do not realize they have HIV until they are tested.
- Symptomatic – Eventually, a person with HIV will begin to feel the effects: fatigue, mouth sores from oral candidiasis, diarrhea, and weight loss. Other infectious diseases can easily get into the body because of the weakened immune system; these are called opportunistic infections. Common co-infections associated with HIV include: tuberculosis (TB), cryptococcal meningitis, toxoplasmosis, hepatitis, and pneumonia.
- HIV progression to AIDS – In some cases, people with HIV who receive treatment to help boost their immunity are able to stave off progression into the AIDS stage of illness. However, if the CD4 cell count drops and other infections take hold, a person is considered to have progressed into the AIDS stage.
Being diagnosed with HIV can be emotionally devastating. Knowing you have a serious illness with no cure is naturally going to cause a lot of stress, feelings of anxiety, and even depression. With good health care, it is possible these days to live a long life with HIV. Putting together a team of caring health care professionals who can provide integrative care for HIV/AIDS will help you maintain the best physical and mental health possible. TCM provides holistic care for patients living with HIV or AIDS that works on all levels: keeping your mental outlook positive, helping you sleep better, boosting immune function, and relieving symptoms that are due to side effects of medical treatment, or caused by concurrent infections.
How Do You Get HIV/AIDS?
The HIV virus is carried through certain bodily fluids: blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breastmilk. In order for HIV to be transmitted from one person to another, one of these types of body fluids must have the infection present in it, and must get into the other person’s bloodstream through broken skin or mucous membrane.
HIV is not transmitted through saliva, sweat, urine, or feces, and is not carried in the air in droplets. You cannot get HIV through water or air, or by touching surfaces. The way that HIV is most often passed from person to person is through sexual contact. Other ways you can get HIV are by sharing needles while using drugs, getting a tattoo with a needle that wasn’t properly sanitized, or a blood transfusion. (As a reminder: we only use single-use, disposable, sterile needles for acupuncture treatment.) A woman could also pass HIV to her baby when breastfeeding. Using condoms during sex and only using sterilized needles are the primary ways to prevent HIV infection.
Top 10 Symptoms of HIV
Most people with HIV will go through a long phase of having no noticeable symptoms. Eventually, after the virus has spread slowly, people with HIV will begin to show symptoms such as:
- Fatigue, feeling tired all the time
- Fever, or feeling hot even if you don’t show a fever
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia, night sweats
- Weakness, dizziness
- Weight loss, wasting, loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Skin rash, or purple spots on skin, bruise easily
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen lymph glands
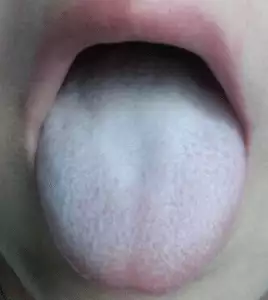
Oral candidiasis, also known as thrush or oral candida, is also common among people living with HIV because the suppressed immune system makes it easier for the fungal infection to take hold. Burning sensation or pain in the mouth cavity and redness with white patches are the signs of oral candidiasis. Long-term use of antifungal medication (Fluconazole) to control thrush can cause side effects and eventually cease to be effective as the body develops a resistance to it.
HIV can also lead to neurological problems, like peripheral neuropathy, in which the signals between the brain and the rest of the body are compromised, causing symptoms like: muscle twitching, loss of balance and coordination, tingling or burning sensations, or numbness.
Medical Treatment for HIV and AIDS
Advances have been made in medical treatment for HIV/AIDS. Different combinations of medications that block the replication of the virus can help to slow the progression of HIV in the body. This type of drug therapy for HIV used to be called HAART, short for “highly active antiretroviral therapy.” Now, it is usually referred to as ART or cART, which stands for “combination antiretroviral therapy.” This form of treatment for HIV can increase chances of survival and quality of life, but is not well-tolerated by all patients. Lifelong use of the medication is required, which, for some, makes HIV a manageable chronic illness. For other patients, the side effects of cART may not be tolerable. Side effects of HIV medications can involve gastric problems, headaches, fatigue, and peripheral neuropathy. Medications can cause liver dysfunction, damage to the liver, and bone marrow suppression, meaning fewer blood cells are being made by the bone marrow.
While a person is still in the asymptomatic phase of HIV, doctors may not begin using antiretroviral therapy because of concerns related to side effects and resistance. However, taking some steps to optimize immune function can potentially help stave off progression into symptomatic and AIDS stages. TCM herbs and acupuncture can be helpful during this phase to help strengthen the immune system and hopefully slow down the progression of disease.
Acupuncture and herbal treatment with TCM may also be used as an adjunct therapy during later phases in order to help people tolerate cART better by reducing nausea and other gastrointestinal effects of the medication and helping to improve appetite. For patients with HIV, TCM treatment is designed to help strengthen the body’s immune defenses in the hopes of preventing advancement to the AIDS stage of disease. For patients in the AIDS stage, TCM treatment focuses on helping to alleviate symptoms of opportunistic infections and to mitigate the side effects of other medications.
TCM for HIV/AIDS

What is HIV from the TCM perspective? TCM puts a lot of emphasis on the prevention of disease by maintaining a balance of yin and yang energies in order to protect the body’s Vital Qi. It is Vital Qi that keeps invasive illnesses like viruses from getting into the body and taking hold there. There are no TCM historical records that point specifically to AIDS, but we do have centuries of practice treating various kinds of invasive viral infections. Modern TCM practitioners apply this knowledge when treating patients with HIV/AIDS.
Syndrome factors of HIV according to TCM:
- Qi deficiency
- Blood deficiency
- Yin deficiency
- Yang deficiency
- Phlegm
- Dampness
- Qi stagnation
- Essence deficiency
An invasion of heat causes the early symptoms of HIV infection: fever, itching (pruritis), and fatigue. Then, later on, as the virus moves deeper into the body, toxic heat causes problems with the organ systems of the stomach, spleen, kidneys, and liver that lead to the weight loss and poor appetite indicative of later stages of HIV and AIDS. Herbal formulations can help relieve the diarrhea that is often reported by patients with AIDS/HIV. Herbs that work to help strengthen the spleen can improve fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, diarrhea, and skin rash.
Strengthening deficient Qi is central to TCM treatment for HIV and can help to improve immune responses in the body. Chinese herbal formulations can aid in reducing the spread of the infection with results similar to those of cART medicines, while simultaneously having a positive effect on the immune system overall. Herbs do not come with the negative side effects associated with drug therapy for HIV/AIDS.
In addition to the other immune-related problems, people living with HIV/AIDS are also likely to have systemic inflammation. HIV can cause damage and inflammation in the gut, and cause blood clotting, making people more susceptible to cardiovascular problems and heart disease. Acupuncture has been shown to help reduce systemic inflammation in HIV patients. Some studies have suggested that herbs may help AIDS patients to live longer, and improve chances of long-term survival. Treatment of HIV with acupuncture and herbs can help to relieve symptoms and reduce the side effects of other treatments.
Acupuncture Near Me for HIV/AIDS in the Los Angeles Area
If you or someone you love is living with HIV, getting the best care possible as soon as possible is vital for improving the long-term outcome. Putting together a program of complementary health care for HIV/AIDS can help offer the best chances for survival, quality of life, and peace of mind.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat UTI With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. & Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Why do I feel like I have to pee all the time? A urinary tract infection, usually referred to as UTI, is a bacterial infection that affects the bladder and/or other parts of the urinary system, causing urinary urgency, often accompanied by a burning pain when you go to the bathroom. Acupuncture and TCM is a good way to get to the root causes of frequent urination, including recurrent UTIs.
Urinary frequency, or an unusual urgency to urinate, can be caused by several different health conditions. A common cause of bladder pain, pressure on the bladder, or a burning sensation when peeing is a bacterial infection in the urinary tract, or UTI. But there can be many other reasons for constantly feeling like you have to pee, including diabetes, interstitial cystitis (IC), pregnancy, prostate problems, ovarian cysts, and more.
Over half of all adult women have experienced a UTI (also called cystitis) at some point in their lives. Many women get UTIs frequently, making them the most common type of non-hospital-related infection in the U.S. Up to 6% of all doctor visits are related to UTIs. A UTI can occur when bacteria, usually E. coli, gets into the urethra and travels up into the bladder, or further into the urinary tract. This can happen because of hygiene habits, after sex or exercising, or the use of contraceptives or period products. It can also happen when urine sits in the bladder for too long, or because a person has a weakened immune system.
While UTI treatment at home remedies such as drinking cranberry juice are popular, most women recognize that once they get that constant urge to pee, they have no choice but to rush to the doctor for antibiotics. Typical UTI medical treatment almost always involves confirming the infection by lab analysis, and a prescribed course of antibiotics, along with analgesic medicine (such as Pyridium) to help the UTI pain in bladder. Unfortunately, many women keep getting UTIs. Infections that are antibiotic resistant are increasingly common, and antibiotics do not get to the root of the problem.
Interstitial cystitis (IC), or painful bladder syndrome, is a condition that causes a constant sensation of having to pee, or bladder pressure, even when there is no infection present. Recurrent UTI and IC are a significant source of anxiety and depression for women, as they can cause almost constant pain and an inability to leave the house due to the constant urge to urinate.
UTI in men is not as common as UTI in women. The more common cause of frequent urination in men is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), in which an enlarged prostate presses on the urinary organs, blocking the flow of urine, and causing backup that can lead to bacterial urinary tract infection men.
Sometimes what feels like a UTI might be something else. Growths in the pelvic area, such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, or tumors can cause pressure in the bladder, bladder pain, or urinary frequency at night. Even when there is no infection, there may urinary symptoms such as:
- Strong urge to pee frequently (more than 8 times per day)
- Difficulty urinating
- Urine is different color than usual
- Pain during peeing, or burning sensation when peeing
- Nocturia, frequent urination at night
The conventional medicine answer to UTI is antibiotic treatment, but this is not the only answer for everyone. TCM methods of acupuncture and herbs can help with improving the function of bladder and kidney systems, reducing symptoms from recurrent UTIs, as well as helping to address the deeper problems that cause inflammation and pressure in the bladder.
Top 10 Urinary Frequency Causes
There are many possible causes of frequent urination.
- UTI (urinary tract infection, also called cystitis, or bladder infection)
- Kidney infection – when bacteria move further up into the urinary tract, the kidneys can become infected. Sometimes people with nerve damage in the spine cannot feel UTI symptoms (neurogenic bladder), so the infection becomes more widespread.
- Bladder stones – when the bladder does not empty completely, urine can crystallize and form hard stones, causing pain during urination.
- Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome) – a syndrome of urinary pain symptoms, the exact cause of which is unknown. Inflammation of the bladder lining may be due to trauma (from surgery or delivery/birth), overdistension, or dysfunction of the pelvic floor muscles.
- Prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate accompanied by irritation of the nerves in the area; not necessarily an infection, although a bacterial infection of the prostate can occur.
- Urinary incontinence – leakage of urine, occurs when the urethral sphincter that controls the flow and stoppage of urine is weak. More common in women and older people.
- Vaginitis – inflammation of the vagina, usually due to infection. Candida, or yeast infection, is one type of vaginitis.
- Diabetes – can cause a variety of urinary problems, due to the body producing more urine to process blood sugar, and nerve damage that leads to urinary retention and incontinence. Constant thirst is also a sign of diabetic urinary symptoms.
- Side effects of cancer treatment in pelvic area – cancer treatments that affect the pelvis, including radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and surgeries to remove pelvic organs, can all cause irritation or damage to the bladder.
- Overactive bladder (OAB) – a group of symptoms, including frequent urination, leakage, nocturia (getting up to pee at night), and primarily, a strong urge to urinate often. Considered to be caused by inappropriate signalling of the nerves that communicate between the brain and the urinary tract organs.

Causes of frequent urination vary somewhat according to biological sex. Frequent urination in men is often caused by prostate problems, while frequent urination in women may be due to pregnancy or other womens’ health conditions related to the ovaries or uterus.
Pressure on the bladder because of pregnancy, or from other organs, can also cause urinary frequency and discomfort. This can happen due to an anterior prolapse, when the pelvic floor is weakened, and the uterus, intestine, or bladder drop from their normal position. When a woman is pregnant, the heavy uterus often causes more frequent urination, or, in some cases, urinary retention. Damage or trauma to the pelvic floor can occur during delivery, so many women experience weak pelvic floor muscles, prolapsed uterus or bladder, and ongoing urinary urgency after they have had a baby.
In men, an enlarged prostate or prostatitis (infection and inflammation of the prostate) can put pressure on the bladder and other parts of the urinary system.
A frequent need to pee can also be caused by drinking too much coffee or alcohol, or taking diuretics.
Can Acupuncture Help Frequent Urination?
In Chinese Medicine, urinary problems come under the classification of “Lin Syndromes.” Lin disorders generally involve painful, “dribbling” urination and are caused by disharmonies in the Bladder and Kidneys, as well as involving other major organs like the Heart, Liver, and Spleen. Dampness and Heat are the primary pathogenic factors, so we use acupuncture treatment and herbal formulations to clear heat and dampness from the body.
Top 5 TCM differentiations of UTI:
- Damp Heat – characterized by frequent urination, burning sensation when peeing, painful pressure in bladder, dark urine or cloudy urine that smells unusual, feelings of nausea, bitter taste in mouth
- Heart Fire – frequency and urgency, thirst, hot, red face and chest, trouble sleeping/insomnia, irritability, anxiety, heart palpitations
- Liver Fire – excess heat causes painful burning during urination, headaches, ringing in ears/tinnitus, constipation, feelings of anger and frustration, redness in eyes and face.
- Fatigue Lin – covers urinary disorders that involve incomplete emptying of the bladder, due to prostate enlargement or prolapsed pelvic organs.
- Stone Lin – obstructions of the urinary system due to buildup of minerals that create stones in the bladder, kidney stones, etc.
Patients who have problems with recurring UTIs may be resistant to the antibiotics they’ve been given. TCM herbs can be used as an additional or alternative remedy from antibiotics and help to strengthen the immune system overall. One review of studies involving the use of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) for UTIs concluded that the herbs, whether used alone or in conjunction with antibiotics, worked better than antibiotics alone.
One study showed that women who were prone to getting UTIs who were treated with acupuncture as preventative care only got a UTI one-third as often as women who didn’t receive acupuncture. Acupuncture has also been shown to be highly effective for bladder pain due to interstitial cystitis. Studies have also shown that TCM treatment can relieve the blockage of urine caused by an enlarged prostate (BPH).
Top 5 Tips for Preventing UTI

What a relief! Now that you’ve gotten over that urinary tract infection, it’s important to take steps to prevent getting another UTI. Here are some natural ways to prevent UTIs:
- Drink more water – This may seem counterintuitive, as you don’t want to have to pee even more. But you do want to be constantly flushing bacteria out of the urinary tract. Avoid drinks like coffee and soda, which can be irritating to the bladder.
- Go when you feel you need to – Some therapies for overactive bladder or IC involve training yourself to hold urine, but for most people, this is not a good idea. Retaining urine for too long contributes to bacterial growth and causes overdistension of the bladder.
- Hygiene – be sure to wipe from front to back when you go to the bathroom. Change clothes and underwear often, especially after sweating. During your menstrual period, change your pad and tampon frequently.
- After sex – always go to the bathroom and urinate before falling asleep.
- Avoid chemical products – Avoid using deodorants, douches, or scented wipes around the genital area. Consider whether contraceptive products like spermicides might also be part of the problem.
Acupuncture Near Me for UTI
While it is rare for a UTI to become so serious that you have a fever or become nauseated, urinary problems should be taken seriously before they become worse. If your UTIs keep coming back, or you constantly feel like you have to pee, it may be a sign that there is something deeper going on. As people age, urge incontinence, prolapsed organs due to weak pelvic floor muscles, and nerve damage can lead to more serious bladder problems. TCM provides a holistic way to treat urinary tract issues, as well as other, possibly hidden conditions in the pelvic region. Urinary urgency may be a signal of something else, so don’t ignore it. Consult with your acupuncturist to find urinary frequency relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Irregular Heartbeat With Acupuncture and TCM

Does if feel like your heart “skips a beat,” or your heart is “fluttering?” Maybe you feel your heart beat is fast or slow, compared to your normal heart rate. Lots of things can cause your resting heart rate to be uneven. Acupuncture and TCM can be beneficial as both an adjunct or alternative to drug therapy for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and other types of arrhythmia that cause heart palpitations or a fast heart rate.
The pulse rate is controlled by electrical impulses that originate in the sinus node, which is located in the right atrium, or upper chamber, of the heart. The feeling that your heart rhythm is off, or different from your normal pulse rate is called Arrhythmia. The average resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. A fast heart rate–more than 100 beats per minute–is called tachycardia. A slow heart rate–less than 60 beats per minute– is called bradycardia.
It is natural to have a slightly high heart rate during or just after exercise, or or a slow heart rate during sleep or times of relaxation, as when meditating. In some cases, a rapid heartbeat is related to anxiety or panic attacks. Sometimes a rapid or irregular heart rate may be related to caffeine consumption or a side effect of some medication. Other times, it may be a sign of heart disease or other chronic condition that needs to be addressed. Other symptoms related to irregular heartbeat include: shortness of breath, chest pain, sweating, and dizziness.
The heart is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are called the atria, into which blood is received, and the two bottom chambers, the ventricles, from which blood is pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body. Medical science classifies deviations from a normal resting heart rate both according to their rapidity and the chamber of the heart that seems to be problematic.
There are different medications available to help restore the regular rhythm of the heart, as well as therapies that deliver electrical impulses to the heart through a catheter, and devices, such as pacemakers or defibrillators.
In many cases, arrhythmia is not a serious problem. But in other cases, it can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and other life-threatening conditions. It is advisable to consult a medical professional if you are having an irregular heartbeat often enough to be concerned.
Acupuncture and TCM offer a natural way to help restore heart function and a good resting heart rate without the unwanted side effects of medications or invasive procedures.
Top 10 Types of Irregular Heartbeat

There are many different terms that describe deviations from a regular, healthy heart rate. Some irregular heartbeat issues are due to congenital conditions, while others may occur due to trauma, disease, or aging.
- Atrial flutter – an accelerated heart rate that occurs in an organized and rhythmic way due to rapid electric impulses in the atria.
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib or AF) – a rapid heart rate, also caused by increased electrical impulses in the atria that happen in a chaotic, arrhythmic way. Fibrillation refers to the rapid and irregular movement of muscles. In the case of AFib, the upper chambers of the heart quiver quickly. This condition is associated with stroke. AFib with RVR (rapid ventricular response) is a condition that occurs when patients are critically ill, often in the ICU, when the atrial fibrillation causes the ventricles to beat faster.
- Ventricular fibrillation – rapid impulses in the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart) cause ineffective pumping of blood out to the body.
- Supraventricular tachycardia – this refers to types of arrhythmia that originate in the atria (above the ventricles) and cause brief episodes of accelerated heart rate.
- Ventricular tachycardia – a fast but regular heart rate that does not allow the ventricles to fill with as much blood as usual.
- Sick sinus syndrome – more common among older people, this is when the sinus node is malfunctioning and may sometimes cause a fast heart rate, and other times, a slow heart rate.
- Long QT Syndrome – a heart disorder found in people with a particular genetic mutation that causes rapid heartbeat and fainting spells.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome – some people are born with an extra electrical pathway that can cause extra or irregular signalling to occur.
- Conduction Block – a block of the electrical pathways that sometimes results in a slower heart rate.
- Premature ventricular contractions – this is when an extra heartbeat beat originates from the ventricles, rather than the atria. It can feel like a “skipped” beat, or your heart pounding or jumping in your chest, but it is actually a kind of extra beat. This can happen occasionally due to drug stimulants like caffeine or nicotine, or other medications like decongestants or antihistamines. It can also be due to heart disease creating scarring in the ventricles or in the structural parts of the heart that hold the pathways for electrical impulses.
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of blood clots and strokes because blood is not being effectively pushed from the atria into the ventricles, so blood pools or collects in the atria.
What Causes Irregular Heartbeat?
In general, most types of arrhythmia are caused by some disorder of the electrical conduction system that controls the beating of the heart valves, or weakness of the heart itself, which is known as cardiomyopathy.
Causes of tachycardia include:
- Not enough blood nourishing the muscles of the heart.
- Dilation or one or more valves of the heart, meaning that the muscle tissue becomes thinner and the chamber becomes enlarged.
- Thickening of the walls of the heart chamber makes them stiff; this is known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Scar tissue makes the heart tissue more rigid (restrictive cardiomyopathy or dysplasia). This can happen due to inflammation, high levels of iron or protein in the tissues, sometimes as a side effect of cancer treatments (radiation and/or chemotherapy). Arrhythmic right ventricular dysplasia may be an inherited condition.
Causes of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter include:
- High blood pressure
- damage to the heart from a heart attack or heart surgery
- Coronary artery disease
- Congenital heart defects
- Hyperthyroidism
- Lung disease, infections, or pneumonia
- Sleep apnea, snoring
- Smoking or overuse of other chemical stimulants
Chronic conditions like diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, kidney problems, alcoholism, Parkinson’s disease, or a family history of heart problems increase a person’s risk for developing an arrhythmia.
Treatment for Irregular Heartbeat
There are several different types of medications to treat irregular heartbeat. Tachycardia may be treated with antiarrhythmic drugs, which work by suppressing or depressing the electrical impulses that are misfiring or transmitting signals too quickly. Beta blockers slow down the heart rate and reduce blood pressure by reducing the production of adrenaline. AFib treatment often involves anticoagulants or blood thinners, which prevent the formation of blood clots. In some cases, these medications can work to help people maintain a steady heart rate and prevent serious events like strokes. The downside is that they must be taken daily on an ongoing basis, and in some cases, they can actually cause the heartbeat to become even more erratic.
Medical procedures that are designed to help irregular heartbeat include: electrical cardioversion, in which an electric shock is used to help “reset” the heart rate, and ablation, in which the tissues that contain the electric impulse pathways are intentionally scarred in order to reduce their output. Implantable devices such as defibrillators or pacemaker monitor the heart rate and deliver small “shocks” to alter the rhythm of the heartbeat. For some people, these methods work to keep the heart functioning. In some cases, though, the surgery to implant the device causes complications or damage to critical tissues around the heart or lungs.
Can Acupuncture Help Irregular Heartbeat?

In conventional medicine, and indeed, in Western culture, the heart is seen as one of the most important, if not the most important, organ in the body. Not only does it supply the whole body with oxygenated blood, but it also is associated with our deepest emotions. TCM also views the heart as a central organ that governs the blood and vessels, and also the mind and spirit.
The traditional diagnostic methods employed by TCM practitioners can tell us a lot about the health of the heart. The feeling of the pulse gives us detailed information about the strength, quality, and speed of the heart rate. According to TCM theory, the heart “opens” out into the face, and so observing the pallor or color of the face, the brightness of the eyes, and the appearance, especially, of the tongue, also gives the acupuncturist vital information about the heart.
TCM providers classify different causes of irregular heartbeat by looking at the whole concert of presenting symptoms:
- Heart Qi deficiency or Blood deficiency: may happen after a long illness or loss of blood and be marked by heart palpitations, dizziness, memory problems, and/or insomnia. The pulse will be weak, and the tongue pale pink.
- Kidney yin deficiency with Heart Fire: chronic illness can deplete the kidneys so that they can no longer manage the balance of fluids and heat, so heat rises and disturbs the Heart. With this presentation, a person may be experiencing strong feelings of fear or anger, depression, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and stomach problems.
Depending on the type of arrhythmia, the acupuncturist will choose acupuncture points and herbs to clear heat and dampness, nourish the blood, and calm and strengthen the heart. Specific herbal formulae work to activate and maintain blood flow, removing stasis, while also helping to protect the spleen and stomach.
A controlled study that compared patients with arrhythmias and tachycardias who were treated with medication (Lopressor) versus patients treated with both the medication and acupuncture and Chinese herbal formulations. The patients who received integrative care showed statistically very significant improvement over the patients using medication only.
A systematic review of randomized trials that compared acupuncture treatment versus typical medication treatment found that both types of treatment were equally effective for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, that acupuncture in addition to medication was effective for ventricular premature beat, and that acupuncture was beneficial over no treatment at all for sinus tachycardia.
Acupuncture Near Me for Irregular Heartbeat
Unfortunately, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death among Americans. Over five million people in the U.S. experience atrial fibrillation, or heart flutter. The conventional methods of treating heart problems such as AFib and other types of arrhythmia can work, but they require people to become completely dependent upon medications or devices. These methods of treatment are also very expensive. Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative or adjunct approach that can help improve heart function and restore a healthy heart rate without side effects.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.