-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Circulation
How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cal, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Fingers bent and can’t straighten? Dupuytren’s contracture is a condition in which the tissues under the skin of the fingers get thick and tight, making it hard to open your hand fully. Acupuncture and TCM offer alternative treatment for Dupuytren’s Contracture to help improve mobility in the fingers and hand.
Dupuytren’s Contracture is a progressive condition that causes the fingers—most often the ring and pinky fingers—to bend toward the palm, eventually interfering with hand function. Although it often develops slowly over several years, the impact on everyday activities can be significant.
What Is Dupuytren’s Contracture?
Dupuytren’s Contracture is a connective tissue disorder that affects the palmar fascia—the fibrous layer beneath the skin of the palm and fingers. Over time, this tissue thickens and shortens into tough, cord-like structures that gradually pull the fingers into a bent position.
This condition most commonly affects the ring and pinky fingers. While the condition is typically painless, it can significantly limit hand function, making it difficult to perform daily tasks like grasping objects, typing, or even shaking hands.
It is more common in older adults, particularly men, and often develops in both hands, though one may be more severely affected. Patients may also notice small nodules or puckering of the skin in the palm during the early stages.
Symptoms of Dupuytren’s Contracture
In the beginning, the condition might present as a small lump or thickened band of tissue in the palm. These fibrous cords become more pronounced over time, leading to increasing difficulty in extending one or more fingers.
Typically, the ring and little fingers are affected. As the disease progresses, the fingers are pulled inward toward the palm in a flexed position. This flexion limits hand mobility and can make everyday tasks, such as putting hands in pockets or wearing gloves, challenging. Additionally, the skin on the palm may appear puckered or dimpled, reflecting the tightening of the underlying fascia.
Top 5 Signs of Dupuytren’s Contracture
- A small lump or nodule in the palm or thickened bands or cords of tissue under the skin
- Difficulty fully extending one or more fingers
- Fingers (typically ring and pinky) pulled into a bent position
- Loss of hand function or reduced range of motion
- Puckering or dimpling of the skin on the palm
In the early stages, symptoms of Dupuytren’s Contracture may be subtle and not interfere much with hand use. As the contracture progresses, everyday tasks can become increasingly difficult.
What Causes Dupuytren’s Contracture?
Although the exact cause remains unknown, several risk factors are known to contribute to the development of Dupuytren’s Contracture. Genetics seem to play a significant role; people with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and epilepsy, have been linked to a higher incidence of Dupuytren’s. Lifestyle choices like smoking and heavy alcohol use may also contribute to the formation of these fibrous hand contractures by promoting inflammation and poor circulation.
Conventional Diagnosis and Treatment for Dupuytren’s Contracture
A medical diagnosis of Dupuytren’s Contracture typically involves a physical examination and a discussion of symptoms. One common clinical assessment is the “tabletop test,” in which the patient tries to lay their hand flat on a surface. Inability to do so often indicates the presence of contracture.
In early or mild cases where the fingers are still mostly functional, doctors may suggest observation. However, if the condition progresses to the point where hand function is compromised, treatment becomes necessary.
Conventional treatments include steroid injections to reduce inflammation in nodules, enzyme injections such as collagenase to weaken the cords and allow manual extension, and needle aponeurotomy, a technique that involves breaking up the thickened tissue with a needle. In more advanced cases, surgical removal of the diseased fascia, known as fasciectomy, may be required. Though these interventions can be effective in the short term, recurrence is common, and recovery—particularly from surgery—can be long and uncomfortable.
Can Acupuncture Help Dupuytren’s Contracture?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, Dupuytren’s Contracture is seen as a manifestation of internal imbalances that obstruct the flow of Qi and blood through the meridians of the hand. The condition corresponds with what TCM describes as “Bi syndrome,” or painful obstruction syndrome. According to TCM theory, this condition often arises from external pathogenic factors like Wind, Cold, and Dampness invading the meridians and causing stagnation. Over time, this stagnation leads to blood stasis and the formation of hard nodules and fibrous bands that contract the hand.
Additionally, internal imbalances—such as Liver Qi stagnation, which impairs the smooth flow of energy and affects the sinews, and Kidney deficiency, which weakens the bones and tendons—may underlie the development of this condition. These factors contribute to the gradual stiffening and deformity of the hand over time.
A TCM approach to treating Dupuytren’s Contracture focuses on restoring the proper flow of Qi and blood, relaxing tendons, and softening nodules. Acupuncture can help increase circulation, reduce inflammation, and relieve the tightness and rigidity in the fascia. Local needling around the palm and forearm is often combined with other points along the meridians to address systemic imbalances.
Moxibustion, the therapeutic application of heat using the dried herb mugwort, is sometimes applied over the affected area to dispel Cold and Dampness and improve local blood flow. This can help relieve stiffness and improve finger mobility. Tui Na, or Chinese medical massage, may also be used to manipulate the hand and fingers, helping to break up fibrous tissue and restore range of motion.
Herbal medicine—both internal formulas and topical liniments—can be customized to nourish the blood, dispel stasis, and promote tendon health.
Cupping therapy may also be incorporated to stimulate circulation and relax the contracted fascia. These methods, used together, provide a comprehensive, non-invasive way to manage symptoms and potentially slow the progression of Dupuytren’s Contracture.
One case study reported significant improvements in a patient’s hand mobility, along with reduced pain and thickening of tissue, after a series of six acupuncture treatments supported by moxibustion and herbal therapy.
Another published case study described how acupuncture and electroacupuncture helped a patient reduce the thickness of nodules and regain finger extension.
Research into acupuncture’s effectiveness in treating fibrotic and musculoskeletal disorders suggests that this modality may be especially well-suited for managing connective tissue issues. Acupuncture can promote fibroblast remodeling, modulate inflammation, and improve microcirculation—mechanisms that are directly relevant to the treatment of Dupuytren’s.
Acupuncture Near Me for Dupuytren’s Contracture in West Los Angeles
If you’re noticing a thickening in your palm or your fingers are beginning to curl inward, you don’t have to wait until surgery becomes necessary. Early intervention with acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine may help restore mobility, reduce discomfort, and potentially slow the progression of Dupuytren’s Contracture.
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West Los Angeles, we create personalized treatment plans that address the whole person—targeting both symptoms and the root imbalances underlying them. Contact us today to learn how we can help you regain full use of your hands with the help of TCM.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Bloody pee? Left side pain between your ribs and hip bone? Dizziness when you go to stand up? These can all be signs of Nutcracker Syndrome, or a compressed vein on your left side. Acupuncture and TCM can be used as an adjunct treatment for Nutcracker Syndrome to help relieve pain and improve blood flow.
What Is Nutcracker Syndrome?
Nutcracker Syndrome (NCS) is a rare vascular compression disorder that occurs when the left renal vein (LRV) becomes compressed, most commonly between the abdominal aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. This compression impedes blood flow from the left kidney, causing increased venous pressure that can lead to a wide range of symptoms.
Symptoms of Nutcracker Syndrome
The most common symptoms of NCS include chronic pain in the left flank or abdomen and/or blood in the urine.
Many patients also experience pelvic pain or a feeling of pelvic congestion, especially women during menstruation.
Men may develop a varicocele, a swelling of the veins within the scrotum. Other symptoms can include fatigue, dizziness, orthostatic intolerance (feeling lightheaded upon standing), and in some cases, headaches resulting from spinal vein congestion.
The most common signs of Nutcracker Syndrome include:
- Chronic left-sided flank or abdominal pain
- Hematuria (blood in the urine)
- Proteinuria (protein in the urine)
- Pelvic pain or congestion, often worsening with standing or during menstruation
- Varicocele in men
- Fatigue, occasional dizziness or syncope
- Orthostatic intolerance (lightheadedness upon standing)
- Headache
Because these symptoms can be non-specific and vary in intensity, NCS is often difficult to diagnose.
How Is Nutcracker Syndrome Treated?

Diagnosis of Nutcracker syndrome usually begins with imaging studies. A Doppler ultrasound is often used as an initial screening tool because it is non-invasive and effective at detecting abnormalities in blood flow. More detailed imaging with CT or MRI scans can confirm the compression of the renal vein and rule out other potential causes. In some cases, venography with pressure measurements is necessary to definitively diagnose NCS, as it can directly measure the pressure gradient across the compressed vein.
In Western medicine, treatment options for NCS depend largely on the severity of symptoms. For mild or moderate cases, especially in children and adolescents, conservative treatment may be advised. This can include observation, weight gain to alter the angle between the arteries, and medications such as ACE inhibitors to manage blood pressure and reduce proteinuria.
For more severe cases, particularly when quality of life is affected or there is significant hematuria or kidney function compromise, surgical intervention may be recommended. Surgical options include transposition of the renal vein, renal autotransplantation, or endovascular stenting. Each of these carries its own risks and benefits, and decisions are made on a case-by-case basis.
While these interventions focus on the anatomical problem, acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offer a complementary approach that addresses the systemic effects of the condition.
Can Acupuncture Help Nutcracker Syndrome?

Acupuncture is widely known for its ability to reduce pain and inflammation, and it has been used effectively to treat symptoms similar to those experienced by NCS patients. Although specific research on acupuncture for NCS is limited, there is growing evidence that acupuncture can help relieve flank pain, regulate blood flow, and improve autonomic function.
According to TCM theory, Nutcracker Syndrome can be understood as a combination of Qi stagnation, blood stasis, and deficiencies in the Kidney and Spleen systems. The Kidney in TCM governs water metabolism and structural integrity, while the Spleen is responsible for transporting fluids and maintaining overall balance in the body. When these systems are out of harmony, blood flow becomes sluggish and can lead to congestion and pain, like the impaired venous drainage seen in NCS.
Treatment with acupuncture typically involves selecting points that invigorate blood circulation, strengthen Kidney and Spleen Qi, and relieve pain.
Moxibustion may also be used to warm the Kidney area and promote circulation. In addition to acupuncture, Chinese herbal medicine can play a vital role. Customized herbal formulas may be prescribed to address individual patterns and promote healing.
Acupuncture Near Me for Nutcracker Syndrome in West Los Angeles
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture near Santa Monica, we offer a holistic approach to healing. For patients suffering from Nutcracker Syndrome, acupuncture and TCM offer a non-invasive, supportive pathway to symptom management and overall well-being. If you’re experiencing chronic pain in your side, hematuria, or other related symptoms and are looking for a natural, integrative approach, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West Los Angeles. We are here to help you find relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.
Persistent swelling in your arms, legs, or other areas of your body? This could be a sign of lymphedema, a condition caused by the buildup of lymphatic fluid. Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offer a gentle and effective way to promote lymphatic drainage and support the body’s natural detoxification process.
What Is Lymphedema?
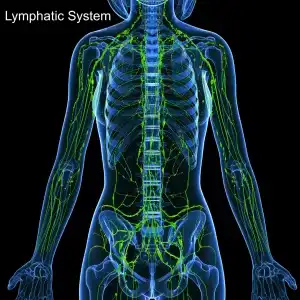
The lymphatic system is a complex network of nodes, tubes and ducts that move lymph fluid through the body, carrying immune cells (like T cells, B cells, and NK cells) that fight against bacteria, viruses, cancer cells, and damaged cells.
Lymphedema is a chronic condition that occurs when the lymphatic system is unable to properly drain lymph fluid, leading to fluid retention and tissue swelling. When the system is blocked or damaged, lymph can accumulate in the tissues, causing swelling and discomfort.
Top 10 Symptoms of Lymphedema
Signs of lymphedema, or lymphatic edema, can develop slowly over time or come on quite suddenly. At first, you may notice that a part of your body is a little swollen, or that your arm or leg just seems a little bit more swollen and stiff than the other one. Your clothes might seem a little bit tighter.
You might notice that you can’t see veins in your limbs, when you used to be able to. Your joints just may seem stiff. It can be easy to attribute mild symptoms of lymphedema to hot weather, general inflammation, or simply aging.
As lymphedema progresses to more severe stages, you may begin to notice that the affected areas are always stiff and swollen, firm to the touch, and that the skin in those areas is becoming noticeably thicker.
Common symptoms of lymphedema include:
- Swelling in the arms, legs, fingers, toes, face, or trunk
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected area, restricted range of motion
- Aching or discomfort in the swollen limb
- Recurring infections in the affected area
- Hardening or thickening of the skin (fibrosis), redness, itchy skin, rosacea
Symptoms of lymphedema may worsen over time if they are not addressed. Acupuncture and TCM offer a holistic way to treat lymphedema and manage the underlying conditions that cause swelling.
Common Causes of Lymphedema
There can be many different factors that lead to a buildup of lymphatic fluid. A few of the most common causes of lymphatic edema include:
- Surgical removal of lymph nodes (commonly due to cancer treatment)
- Radiation therapy that damages lymph vessels or nodes
- Infections that cause inflammation and blockage of lymphatic vessels
- Cancer that spreads to or blocks lymph nodes
- Injury or trauma to the lymphatic system
- Congenital malformations or underdeveloped lymphatic vessels (primary lymphedema)
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle that impair lymph flow
Treatment for Lymphedema

Conventional treatment for lymphedema typically focuses on symptom management and improving quality of life. This may include a recommendation to wear compression garments like sleeves or stockings to encourage lymph flow. Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD): A specialized massage technique performed by trained therapists to move lymph fluid manually.
Gentle, regular physical activity may be recommended to help stimulate lymphatic circulation.
Machines known as Pneumatic compression devices, such as inflatable sleeves worn on the limbs, can mimic manual drainage.
In some cases, procedures to remove excess tissue or improve drainage pathways.
While these methods can help manage the symptoms, they often need to be maintained consistently and may not address the underlying systemic imbalances.
TCM View of Lymphedema
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, lymphedema is viewed as a disruption of the body’s natural flow of Qi (vital energy) and fluids. According to TCM theory, the spleen plays a central role in fluid metabolism. When the spleen Qi is weak or deficient, it cannot properly transform and transport fluids, leading to dampness and phlegm accumulation. This internal dampness can settle in the limbs and cause swelling.
Lymphedema may also be related to stagnation of Qi and blood, particularly in the channels (meridians) that traverse the affected area. External factors like trauma, surgery, or radiation can block the flow of Qi and blood, creating what TCM refers to as “blood stasis.”
Key TCM patterns that may contribute to lymphedema include:
- Spleen Qi deficiency
- Damp accumulation
- Qi stagnation
- Blood stasis
Can Acupuncture Help With Lymphatic Drainage?
Acupuncture helps to regulate the flow of Qi and blood through the meridians. When specific points are stimulated, they can promote circulation and encourage the movement of stagnant fluids.
Herbal medicine and acupuncture treatments can strengthen the spleen’s function of fluid transformation and transport. Strengthening the kidneys also helps resolve chronic dampness and supports the body’s ability to detoxify.
Research has shown that acupuncture has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. For patients experiencing pain, heaviness, and aching due to lymphedema, acupuncture can provide relief.
A healthy lymphatic system is essential for immune function. Acupuncture has been found to modulate immune activity and may help reduce the frequency of infections associated with lymphedema.
Gentle massage techniques like Tui Na and Gua Sha can be applied along the meridians to manually stimulate lymphatic drainage. Unlike deep tissue massage, these methods work with the body’s energy system to promote gentle, effective movement of fluids without overwhelming the tissues.
One study of women who had breast cancer related lymphedema found that twice weekly acupuncture sessions over the course of four weeks helped reduce swelling in their arms.
A review of studies on acupuncture treatment for cancer patients showed that acupuncture not only helped with lymphatic swelling, but also helped to relieve anxiety and depression, nausea and vomiting, and chemotherapy induced neuropathy.
Acupuncture Near Me for Lymphatic Drainage in West Los Angeles
Lymphedema can be a chronic and frustrating condition, but there are holistic options that go beyond symptom management. Acupuncture and TCM offer time-tested methods to support lymphatic drainage, strengthen the body’s natural detox systems, and relieve discomfort. If you’re living with lymphedema or chronic swelling, reach out to us at Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West Los Angeles. We’d be happy to create a personalized treatment plan to help you feel lighter, more comfortable, and more energized again.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Sarcoidosis With Acupuncture and TCM
by Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Fever, fatigue, and muscle aches? Swollen lymph nodes, coughing, shortness of breath? Eye pain, or red eyes? These can all be signs of sarcoidosis, an autoimmune disorder. Acupuncture and TCM can help relieve sarcoidosis symptoms.
Sarcoidosis is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by the formation of granulomas—clumps of inflammatory cells—that can affect multiple organs in the body. It most commonly impacts the lungs and lymph nodes, but it can also involve the skin, eyes, heart, musculoskeletal system, and nervous system.
Sarcoidosis typically manifests in young adults, with the highest prevalence observed in individuals in their 20s and 30s, though it can affect people of any age. This condition’s exact cause remains unknown, but researchers believe it results from an overactive immune response to environmental or infectious triggers.
Sarcoidosis can cause serious and even life-threatening complications, especially when it is centered in the lungs. However, the good news is that many cases of sarcoidosis do eventually clear up or go into remission.
Acupuncture, herbs, and other TCM treatments for sarcoidosis can help address underlying issues that contribute to the formation of this autoimmune disorder, as well has help to relieve symptoms. TCM can also help with potential signs of dysautonomia (autonomic nervous system disorders) that can be caused by sarcoidosis.
Types of Sarcoidosis
There are different types of sarcoidosis depending on which organs are affected.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis, which targets the lungs, is the most common form and can lead to chronic respiratory issues.
Musculoskeletal sarcoidosis may cause joint inflammation (arthritis), muscle pain, or bone lesions, sometimes resulting in long-term complications such as osteoporosis.
Sarcoidosis can lead to vascular complications that involve inflammation of small, medium, or large blood vessels. These types of sarcoid-related vasculitis are rare but important to recognize, as they may present with overlapping features of other autoimmune or vascular conditions.
Small-vessel vasculitis in sarcoidosis primarily affects the skin. This type of vasculitis might coexist with sarcoidosis and manifests as petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin), purpuric spots (purple “blood spots” under the skin, due to broken blood vessels), or infiltrative erythema (raised rash, like welts on skin).
Medium-vessel sarcoid vasculitis often involves pulmonary lymphatic capillaries and may present with systemic symptoms, including fever, arthritis, and cutaneous manifestations (skin rash or lesions).
Sarcoidosis symptoms can vary widely but may include persistent fatigue, fever, shortness of breath, coughing, swollen lymph nodes, and joint pain. Because of its wide range of manifestations, sarcoidosis can be difficult to diagnose and often requires imaging tests, biopsies, and bloodwork.
New Diagnostic Methods for Sarcoidosis

Diagnosing sarcoidosis remains a complex challenge for clinicians because there is no single definitive test for the disease. The diagnosis is often made by combining a thorough clinical evaluation, imaging studies, laboratory tests, and biopsy results. However, emerging research has identified new biomarkers that may help streamline the diagnostic process.
One promising development involves the discovery of type 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1) as a potential biomarker for sarcoidosis. A study led by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania compared skin samples from sarcoidosis patients to those with granulomas caused by other conditions. They found that levels of ILC1 were significantly higher in sarcoidosis-affected tissues. This trend was also observed in lung granulomas and even in the bloodstream, where sarcoidosis patients showed a 12-fold increase in circulating ILC1 levels compared to healthy individuals.
Sarcoidosis Treatment
The main goals of treatment for sarcoidosis are managing symptoms, reducing the risk of organ damage, and improving the patient’s quality of life. In some cases, sarcoidosis may go into remission, meaning that the condition is no longer causing complications.
Patients with mild or no symptoms might not require treatment, just monitoring. When treatment is necessary, Western medicine focuses on reducing inflammation and suppressing the overactive immune system. These treatments can be highly effective but often come with potential risks and side effects.
Prednisone is usually the first-line treatment for sarcoidosis. This steroid medication suppresses the immune system and reduces inflammation, which can help to improve symptoms and prevent organ damage. However, long-term use of prednisone may lead to significant side effects, such as weight gain, bone loss, high blood sugar, and an increased risk of infection. For this reason, corticosteroid doses are typically tapered once symptoms improve, or alternative medications may be introduced to minimize steroid use.
Methotrexate, a drug commonly used for severe rheumatoid arthritis, is another option for managing sarcoidosis. It is particularly effective in patients with significant organ involvement, such as lung, skin, or joint manifestations. Methotrexate helps to suppress the immune system and can be used in combination with corticosteroids to reduce the need for higher steroid doses.
Drugs such as hydroxychloroquine, which are typically used to treat malaria, can be effective for sarcoidosis that primarily affects the skin or joints. These medications may also be helpful for managing chronic fatigue and muscle pain associated with the condition.
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, like infliximab or adalimumab, are biologic medications that help reduce inflammation. These drugs are often used in patients with severe sarcoidosis, particularly when other treatments have not been effective. TNF inhibitors can be administered intravenously or as an injection under the skin.
Corticotropin is a medication that stimulates the adrenal glands to produce natural steroid hormones. It can be injected under the skin to help manage inflammation and reduce immune system activity, offering an alternative to synthetic corticosteroids.
Acupuncture and other TCM treatments can be helpful for clearing inflammation and relieving symptoms related to sarcoidosis, as well as helping to manage the side effects that may be caused by other medications.
Can Acupuncture Help Sarcoidosis?
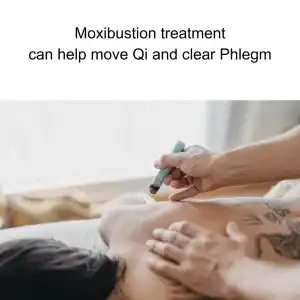
In TCM, sarcoidosis is viewed as a condition arising from underlying imbalances in the body. These imbalances are often associated with heat, phlegm, and stagnation of Qi and blood. Granulomas, for example, may be interpreted as accumulations of dampness and phlegm obstructing the free flow of Qi and blood. Furthermore, the systemic inflammation seen in sarcoidosis can be attributed to excessive heat in the body. TCM practitioners focus on identifying the root causes of these imbalances and tailoring treatments to the individual’s unique presentation.
Acupuncture treatments for sarcoidosis aim to reduce inflammation, support the immune system, and restore balance within the body. By stimulating specific acupuncture points, practitioners can promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood, reduce stagnation, and clear heat and dampness. This can help alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and joint pain, which are commonly experienced by those with sarcoidosis.
Research has shown that acupuncture can help modulate the immune system, reduce stress, and improve quality of life for people with chronic inflammatory conditions. For sarcoidosis patients, regular acupuncture sessions may not only provide symptom relief but also address the underlying imbalances contributing to the disease.
Chinese Medicine diagnosis is different from Western medicine diagnosis. An acupuncture practitioner will look carefully at each individual patient’s specific symptoms, medical history, and foundational constitution to discover the underlying causes of their particular presentation of disease.
In the case of sarcoidosis, possible TCM diagnoses might be:
- Lung Qi Deficiency – presents with symptoms like shortness of breath, weak lung sounds, throat rattling, spontaneous sweating, feeling cold, pale complexion, weak voice. Treatment will seek to tonify Lung Qi to strengthen respiratory function possibly with the inclusion of moxibustion treatment.
- Lung Yin Deficiency – symptoms: breathlessness, night sweats, 5-center heat (warmth in palms, soles, and chest), dry throat, non-productive cough, malar flush, red skin lesions. Treatment goals include nourishing Lung Yin and clearing heat.
- Lung Qi Stagnation – symptoms: chest congestion/blockage, difficulty breathing, emotional grief or melancholy, trouble letting go of the past, and constipation. Treatment will help improve circulation of Lung Qi to relieve stagnation and promote emotional well-being.
- Phlegm in the Lungs- symptoms: Chronic phlegm retention contributing to fibrous tissue and scarring, which can parallel conditions such as chronic bronchitis. There may also be phlegm-related symptoms like congestion or rattling breath. Treatment will seek to nourish Lung Qi, transform phlegm, and circulate Qi to reduce stagnation.
These differential diagnoses reflect the diverse ways in which TCM approaches pulmonary dysfunctions and can be used to tailor treatments for individuals with sarcoidosis, ensuring that the root causes and symptoms are addressed holistically.
Acupuncture for Sarcoidosis Near Me in West Los Angeles
If you or someone you know is suffering with sarcoidosis, or perhaps has some of the symptoms mentioned above, but has not been able to get adequate diagnosis or treatment for their condition, it may be appropriate to seek care from a qualified TCM doctor. Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in Los Angeles, just east of Santa Monica, have over 35 years of experience helping people with all types of autoimmune disorders, skin conditions, respiratory problems, and musculoskeletal pain. We can help you find relief and better health.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Pelvic Congestion Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Pelvic pain that gets worse after standing for a long time? Urinary pain and urgency? Lower back pain and sciatica? Bloated stomach after eating? These can all be symptoms of pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS), or vaginal varicose veins. Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative treatment for pelvic congestion syndrome.
What is Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS)?
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS) is a chronic condition caused by varicose veins in the pelvis—similar to varicose veins that commonly occur in the legs. These dilated veins in the pelvis can cause severe pelvic pain, particularly a feeling of heaviness or aching pain that worsens over the day. PCS pain can often get worse after standing for long periods.
Pelvic congestion is one of the most common causes of chronic pelvic pain, but PCS often goes undiagnosed because the symptoms can mimic other conditions, such as:
- Endometriosis
- uterine fibroids/leiomyoma of the uterus
- bladder pain/interstitial cystitis
- ovarian cysts
- Generalized back pain, lower back pain, hip pain, or groin pain
All of these conditions can cause chronic pain in the pelvic area.
In Pelvic Congestion Syndrome, dilated veins around the ovaries and the vulvovaginal can happen due to venous obstruction, problems with valves in the blood vessels, and/or changes in hormone levels.
PCS does not only affect women. Men can also suffer from pelvic congestion syndrome and experience chronic pelvic pain.
Pelvic pain conditions related to vascular issues and blood flow are complicated. Most health conditions related to pelvic pain in relation to reproductive organs, and in particular CPS, are still not very well understood by modern medicine.
TCM offers a holistic approach to reproductive healthcare. Acupuncture treatment can help address the many factors involved in pelvic congestion syndrome.
Top 10 Pelvic Congestion Syndrome Symptoms
PCS symptoms can vary from patient to patient, but the most common signs of PCS include:
- Pelvic pain that gets worse as the day goes on. Discomfort tends to accumulate as the day progresses due to the pooling of blood in the pelvic veins, leading to increased pressure.
- Pelvic pain that worsens when standing for long periods. Many women report that standing for extended periods increases the feeling of pressure and pain in the pelvic region.
- Pelvic pain after eating, abdominal pain after meals. Eating can trigger pain and bloating, making meals uncomfortable.
- Urinary incontinence, an inability to control urination, especially when coughing or lifting something heavy.
- Painful urination (urinary pain),burning during urination, often confused with a UTI (urinary tract infection).
- Urinary urgency, sudden need to urinate, sudden, intense urge to urinate, which can feel similar to bladder conditions.
- IBS symptoms, alternating constipation and diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain.
- Lower back pain, radiating pain in the lower back, often mistaken for sciatica or musculoskeletal problems.
- Throbbing in the legs, achy legs after standing for a long time, poor circulation in the lower extremities, causing aching, swelling, and throbbing in the legs.
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia), pain during or after sex due to the increased pressure and swelling of the pelvic veins.
What Does Pelvic Congestion Pain Feel Like?
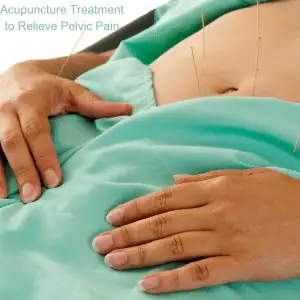
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS) and Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS) are two conditions that cause debilitating pain in the pelvic region, yet they are distinct in the way they present.
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS) is primarily caused by varicose veins in the pelvis, leading to blood pooling in the veins and creating chronic pelvic pain, particularly in women of childbearing age. PCS pain tends to worsen after long periods of standing, physical activity, or after sexual intercourse.
PCS is often associated with hormonal changes and pregnancy, but it is also underdiagnosed because the symptoms can overlap with other pelvic disorders besides pregnancy.
Diagnostic tools like Doppler ultrasound or venography are often needed to identify the underlying venous issues, which may be treated with hormone therapy, vein embolization, or surgery.
Medications that suppress estrogen may be prescribed to help relieve symptoms. These include Depo-Provera, Implanon, or Goserelin. These are all drugs that also prevent pregnancy, so they are not helpful for people who may be hoping to get pregnant, or who want or need to avoid taking hormonal birth control for whatever reason.
Ovarian vein embolization is a procedure that blocks or ties off veins so that blood isn’t flowing or pooling in areas of the pelvis.
Acupuncture offers an natural treatment for pelvic congestion syndrome, without side effects of hormonal birth control.
Can Acupuncture Help Pelvic Congestion Syndrome?

Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), particularly acupuncture, can be an effective modality for treating conditions like Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS) and Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS).
Acupuncture has been widely adopted in both Eastern and Western countries for managing pain syndromes. The central mechanism behind acupuncture’s effectiveness in these cases is its ability to stimulate specific acupoints, improving local blood circulation and reducing inflammation, which ultimately helps in alleviating pain.
The muscles and fascia inside the pelvis play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the pelvis and spine. The fascia in the pelvis can be compromised by trauma, postural stress, pregnancy, anxiety, and other subtle factors.
This is one of the reasons the pelvic pain and congestion can be difficult for conventional medicine to address properly. Visceral pain in the pelvic may not be easily “visible,” as it can be caused by microtraumas, adhesions, scar tissue, and pain referring from one area to another.
Acupuncture treatment can help relieve this type of pain, as placing needles in acupoints has an analgesic, as well as a calming, effect.
Research has demonstrated that acupuncture can release certain neurochemicals like adenosine, which exerts an analgesic effect during stimulation of acupoints, offering relief from pain in conditions like CPPS. This mechanism helps reduce inflammation and regulate pain by influencing inflammatory mediators, which play a significant role in chronic pelvic pain disorders.
Clinical trials have specifically shown that acupuncture improves symptoms in both men and women suffering from CPPS, with better outcomes than placebo or sham treatments.
One study looked at male patients with pelvic pain and venous congestion. After five weekly sessions of acupuncture treatment, patients reported significant reduction in pain, and MR venography showed reduction in intrapelvic venous congestion.
Specific formulations of Chinese herbs have been developed to help address the root cause of pelvic congestion, while also relieving painful symptoms.
Acupuncture’s ability to relieve pain through modulation of inflammatory processes makes it an excellent alternative or complementary therapy for chronic pelvic pain conditions.
Acupuncture Near Me for PCS in West LA
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture and TCM in Santa Monica, we have over 35 years of experience helping people with all kinds of chronic pain conditions. We offer highly specialized care for people experiencing reproductive issues, pregnancy, pelvic pain, referred back pain, lower back pain, hip pain, and groin pain. Our team of practitioners spend time with each patient to provide holistic care that takes the whole person into account: physical, mental, and emotional. If you or someone you know is experiencing chronic pelvic pain, please do not hesitate to reach out to us.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.