-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
- Can Acupuncture Help Bad Breath?
- How to Treat Atopy with Acupuncture and TCM
- Plantar Fasciosis Treatment With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Protect Yourself When Air Quality Is Poor
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

September 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
Traditional Chinese Medicine
How To Prevent Miscarriage With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
Miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of pregnancy. While it is not talked about much, it is very common; 10-20% of pregnancies end in early miscarriage. TCM and acupuncture methods, well-known for helping women with infertility issues, can be used successfully to prevent threatened miscarriage.
Sometimes called spontaneous abortion, miscarriage at 12 weeks or earlier is often due to chromosomal abnormalities in the developing fetus. In some cases, miscarriage or recurrent miscarriages are caused by the mother’s health condition.
While miscarriage is common, and very early miscarriage, sometimes called chemical pregnancy, may even go unnoticed, women who have experienced this should seek out care. The spontaneous ending of pregnancy is emotionally difficult no matter the circumstances, and hormone imbalances can cause other problems if left unaddressed. Acupuncture treatment and TCM herbal supplements can help support a full recovery and lay a healthy foundation for getting pregnant after miscarriage.
Signs and Symptoms of Miscarriage
While some bleeding in the first trimester is common (about 20% of women experience this), it can be an indication that the pregnancy is at risk.
Other signs of miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding that is brownish or bright red
- Discharge that include clots
- Cramping or pain in the abdomen or lower back area, similar to menstrual cramps
- Contractions in the uterus that occur every 5-20 minutes, similar to labor pains
- Decrease in other early pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea and breast tenderness
In some cases, a miscarriage occurs without any signs of cramping or bleeding at all. Sometimes referred to as a missed miscarriage, missed abortion, or silent miscarriage, in this situation, a woman may not discover that she has miscarried until a doctor finds that there is no fetal heartbeat and checks via ultrasound and/or testing for HCG (pregnancy hormone) levels.
What Causes Miscarriage?
A positive pregnancy test usually can’t confirm a pregnancy until the third or fourth week, once implantation has occurred. It is estimated that miscarriage at 4 weeks or earlier, or when a fertilized egg has not successfully implanted, happens in up to 70% of conceptions. Miscarriage at 6 weeks or later is much less common; only about 5% of pregnancies end once this time when the heartbeat can be detected has passed.
Maternal age is one risk factor (20% of women over 35 might miscarry, while as many as 80% of pregnant women over 45 might miscarry). Chromosomal abnormalities in an embryo are more likely when a woman is older. The other most common reasons for a miscarriage to occur include:
- Hormonal imbalances – due to PCOS, low progesterone, diabetes, thyroid condition, etc.
- Thin or nutrient-poor endometrial lining
- Autoimmune issues
- Structural issues of the cervix or uterus, polyps, fibroid
- Exposure to toxins
- Smoking, alcohol, use of drugs
One of the primary reasons that a woman might miscarry during the second trimester is cervical insufficiency. In this case, there may be no prior symptoms, but the miscarriage begins with pressure or the water breaking. Once this weakness of the cervix has been discovered, doctors can treat this condition and protect subsequent pregnancies by making a “circling” stitch in the cervix at around the 12th week.
Recovering from a Miscarriage
The extent to which a woman may need medical intervention during miscarriage varies, depending on how advanced the pregnancy. If the pregnancy was still in the very early stages, and there is heavy bleeding, then the uterus may empty itself. However, if things have progressed further into the first trimester, and miscarriage at 12 weeks or thereabouts occurs, a woman may need medical attention to help expel all of the tissues from the uterus. This may be accomplished with medication (misoprostol, sometimes combined with mifepristone), taken orally or as a suppository, which will cause more cramping and the expulsion of the fetal and placental tissues. In other cases, it may be necessary for a doctor to perform a D & C (dilation and curettage), in which the tissues are surgically removed from the uterus.
Conventional medical treatment for miscarriage unfortunately does not offer much in the way of healing. The hormonal and emotional effects of a miscarriage can be profoundly upsetting. Feelings of grief, disappointment, and loss are very real, and if unresolved, can affect a woman’s mental and physical health going forward. Your acupuncture practitioner can provide holistic alternative care to help you recover from miscarriage. A program of acupuncture treatments, herbs, and caring support will focus on reestablishing a good flow of Qi and blood to the reproductive system while alleviating stress and anxiety. Balancing the hormones and emotions allows for the menstrual cycle to return to normal, and strengthens the organ systems so that subsequent pregnancy will start from a place of peak heath.
Can Acupuncture Help Prevent Miscarriage?

According to TCM theory, the vital energies–Jing (or essence), Qi (life force energy), Yin (female/cool energy) and Yang (male/warm energy)–must be balanced for optimal health, and this is especially true when a woman is preparing to bring a new life into the world. The quality of eggs and sperm depend on it. Naturally, as a woman ages, there will be some depletion of these energies, and this can be exacerbated by lifestyle habits: stress, overwork, diet, lack of sleep, etc.
Overall, TCM recognizes 4 differentiations of conditions that can lead to miscarriage:
- Kidney deficiency – Women with this type of deficiency may have experienced a late menarche (delayed first period), irregular cycles, anovulatory cycles (don’t always ovulate), long cycles. A woman might have been born with a kidney deficiency or it can develop due to exhaustion, heavy labor, or excessive sexual behaviors.
- Blood or Qi deficiency – This condition is related to the digestive system, when the stomach and/or spleen are not bringing enough nutrients to support and nourish the embryo.
- Excess Heat – If internal fire is too strong, it causes bleeding. This can cause the placenta to become detached and uterine contractions to begin, causing miscarriage.
- Injury – a fall or accident or excessive sexual activity during pregnancy can irritate the uterus, causing contractions.
Other causes could include: medications, antibiotics, food poisoning, or exposure to environmental toxins. Based on the presenting symptoms, an acupuncturist will determine which differentiation and create a treatment plan to address root causes. We can help to prevent miscarriage when there is spotting or cramping by calming the uterus to stop contractions and bleeding. Bed rest may be recommended, involving no exercise, no sexual activity, and no heavy labor.
The most effective preventive treatment happens pre-pregnancy. If a woman has one or two miscarriages or even three or more (habitual miscarriage), it is important that we take action to prevent problems before conception. Three months of treatment will prepare the body well to insure a full-term pregnancy. Ideally, a woman who is ready to get pregnant would seek acupuncture treatment and herbs to help strengthen all aspects of the reproductive systems for at least a few cycles before conceiving.
Acupuncture treatment can help prevent miscarriage by:
- Balancing hormones
- Treating PCOS
- Improving the quality of endometrial lining
- Calming contractions early in the pregnancy
- Improving blood flow and preventing clotting
- Regulating immune responses
- Reducing stress and anxiety
Top 5 Tips to Prevent Miscarriage

Self care is always important, but during pregnancy, it is especially vital to prioritize your health and wellness. The need to eat and rest appropriately cannot be overemphasized during this crucial time.
- Eat cooling foods – During pregnancy, women carry more heat in the body and often feel hot. It is best not to have anything too spicy; spicy food can encourage bleeding and trigger contractions. Cooling foods include: cucumbers, melons, citrus fruits, celery, leafy greens, soy and mung beans, eggs, millet, buckwheat, whole wheat.
- Avoid warming foods – Warming foods raise yang energy and body temperature. Be moderated from: deep fried food, coconut, leeks, onions, roasted walnuts, pistachios and pine nuts, and spices like cinnamon, cloves, pepper, ginger, garlic, mustard, chili pepper, or add more cooling food if there is warming food.
- Stay away from alcohol and coffee. Try chrysanthemum tea or peppermint tea as an alternative.
- Make sure you are getting the right balance of calcium and magnesium. Most people get more calcium than magnesium. Foods high in magnesium include spinach, beans, brown rice, and fish like halibut and salmon.
- If you experience bleeding or cramping, cease all activities, including manual labor, exercise and sex.
Acupuncture Near Me for Miscarriage Prevention
At Art of Wellness, our doctors have over 30 years of expertise in women’s healthcare through TCM and acupuncture. We specialize in helping women fulfill their dream of a healthy, full-term pregnancy from infertility treatment, to miscarriage prevention and complete pregnancy care. If you or someone you love is concerned about threatened miscarriage, please contact us to arrange an initial consultation and get started with a treatment plan right away.
We recommend that any woman who is seeking to start a family should begin partnering with her TCM practitioner before conceiving–ideally, for three months or menstrual cycles. This allows for any underlying health issues that may affect things to be addressed and gives the best chance for a full-term, healthy pregnancy.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Neuropathy With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.
Neuropathy pain and tingling, often in the hands or feet, is caused by damage to the nervous system. Dysfunction of the sympathetic nervous system can also interfere with autonomic internal processes like blood pressure and digestion. Relieve the effects of nerve damage with integrative care that includes acupuncture and TCM.
Neuropathy refers in general to the dysfunction or disease of one or more nerves, causing pain, sensitivity, and/or degenerative atrophy in parts of the body, usually the extremities. The most common form of neuropathy is peripheral neuropathy, in which damage to the peripheral nervous system–the signalling system that allows the brain and spinal cord to communicate with the rest of the body–leads to a breakdown in communication.
Peripheral neuropathy is believed to affect about 30 million people in the U.S. In some cases, neuropathy causes severe pain and can be disabling. Neuropathy in feet may be the most recognizable form of this condition, but different kinds of nerve damage can affect many parts of the body.
Symptoms of neuropathy vary widely from person to person, so it can be challenging to get a specific diagnosis. Some types of neuropathy develop slowly over many years (chronic neuropathy), while others can come on quite suddenly (acute neuropathy). There is currently no cure for neuropathy, and conventional medicine has limited ways of addressing the underlying causes of most neuropathies. Medical treatment mostly focuses on relieving painful symptoms with medications.
Studies have shown that acupuncture and TCM present an effective form of complementary or alternative treatment that can work upon the deeper dysfunctions that led to the degeneration of the nervous system in the first place.
Symptoms of Neuropathy
The signs of neuropathy can be subtle or severe, and appear in widely different combinations. The most common symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Burning or sharp pains in the limbs
- High sensitivity to touch, temperature
- Conversely, an inability to sense temperature or external pressure–loss of sensation
- Lack of coordination, balance, tendency to fall
- Muscle twitching, cramping, or weakness
- Lightheadedness or dizziness when rising to standing position
- Problems with control of the bladder and/or bowel
- Loss of sexual function
- Unintentional weight loss
Diagnosis of neuropathy usually involves a combination of electrodiagnostic tests to measure the electrical activity of nerves and muscles and blood tests to determine deficiencies, toxicity and/or abnormal immune responses. Quantitative Sensory testing can help determine the extent of nerve damage that exists, and Autonomic testing can assess whether there is damage to the autonomic nervous system, which controls things like blood pressure and sweating to manage body temperature.
Top 10 Types of Neuropathy
In general, the major types of neuropathy are known as: peripheral, proximal, cranial, autonomic and focal. There are over 100 different kinds of specific neuropathies that affect different parts of the body in various ways, depending on where nerve damage has manifested. The most common types are discussed in detail below.
-

carpal tunnel syndrome is a type of compression neuropathy Peripheral neuropathy – The peripheral nervous system transmits messages from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.The somatic nervous system is made up of the cranial nerves and spinal nerves, which send messages between the brain and the periphery regarding voluntary movements, such as rising, walking, and picking up objects. When these systems sustain damage and become compromised, symptoms such as tingling, burning, numbness in the extremities, extreme sensitivity to touch, muscle weakness, loss of balance and coordination, or even paralysis can result.
- Autonomic neuropathy – The autonomic nervous system controls the body’s basic functions, such as the pumping of blood, the emptying of the excretory organs, and the digestive processes. When the small fibers of nerves lose their function, the fine movements necessary for the contraction of blood vessels are compromised, leading to inabilities of the organs to perform their usual activities.
- Sympathetic Nervous System Neuropathy – The sympathetic nervous system controls the body’s ability to react under urgent circumstances, triggering the “fight or flight” response. The rush of hormones causes a rise in heart rate and extra blood to flow to the muscles. Problems with the nerves that control this response are especially common in patients with diabetes and can have a negative impact on cardiovascular function, impairing coronary blood flow.
- Central neuropathic pain syndrome – due to damage to the central nerve system or spinal nerves, usually caused by a spinal cord injury, brain injury, or stroke. Can cause sharp, burning pain in localized areas, or throughout the body. Sometimes accompanies other chronic conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease.
- Compression mononeuropathy – Damage to a single nerve can cause pain, numbness, and/or loss of use of a specific part of the body, as in carpal tunnel syndrome, which affects the hand, wrist and arm, cubital tunnel syndrome (ulnar neuropathy), in which ulnar nerve entrapment compresses the ulnar nerve of the elbow, radial tunnel syndrome compressing the radial nerve, and femoral nerve dysfunction, which affects the leg, causing numbness in thigh or femoral nerve pain.
- Neuropathic arthropathy or Charcot’s Joint – a progressive condition that causes severe damage to the bones, cartilage, and soft tissues of joints, usually the ankle and foot area. This extreme form of arthritis occurs when a person has nerve damage to the extent that they cannot feel the grinding of bone on bone.
- Neuropathies of the 12 Cranial Nerves – damage to the nerves of the brain and brainstem can lead to dysfunction of the muscles that manage the movements of the eyes (optic nerve), or Bell’s Palsy, which affects the muscles of the face.
- Thoracic and Lumbar Radiculopathy – A rare type of neuropathy, pinching or damage of the spinal nerves can cause pain around the chest (thoracic) or pain that radiates from the lower back (lumbar).
- Proximal Neuropathy – causes pain and weakness in the muscles of the hip, thigh and/or buttock, usually on just one side of the body.
- Unilateral Foot Drop – compression of the peroneal nerve in the leg causes difficulty in lifting the front part of the foot. People with this type of neuropathy, sometimes called “drop foot,” may drag their toes along the floor as they walk.
What Causes Neuropathy?
Chronic neuropathy is usually a secondary condition related to some other form of chronic disease. Diabetes is the most common and well-researched cause of neuropathies. Upwards of 60% of people with diabetes experience some form of nerve damage. Over time, high blood sugar levels cause weakening of the blood vessels that provide nutrients to nerve endings.
The main factors that can lead to various neuropathies include:
- Diabetes
- Traumatic injury that damages nerve tissues
- Side effects of medications or chemotherapy
- Autoimmune and inflammatory conditions
- Cardiovascular disease – narrowing of the arteries
- Kidney problems
- Poor diet, overuse of alcohol
- Exposure to toxins
Damage to peripheral nerves is a common side effect of chemotherapy treatment for cancer. Many people who undergo chemotherapy experience some form of neuropathy that continues long after the round of treatment has ended.
Medical treatment of neuropathy often involves the management of the related chronic conditions, especially diabetes, with lifestyle changes. Proper management of diet can certainly help prevent and improve neuropathy symptoms, but it is difficult for most medical practitioners to spend much time counseling patients on nutrition and behavioral modification. Medications such as Lyrica, Neurontin, Cymbalta and Elavil are often prescribed to help manage the painful symptoms of nerve damage. These can help dull pain, but do not fundamentally treat the condition, and possible negative side effects include leg swelling, weight gain, and fatigue.
Acupuncture and TCM offer a safe alternative for treating neuropathy symptoms stemming from diabetes, chemotherapy, inflammatory and other conditions.
How Does Acupuncture Help Neuropathy?
According to TCM theory, peripheral neuropathy is related to dampness hampering the smooth flow of Qi and blood to the limbs. Acupuncture treatment, therefore, will focus both on resolving the underlying condition causing the dampness to accumulate and clearing the blockages in the energy pathways (meridians) so that Qi and blood can move freely again.
Nutrition is an integral part of TCM, and a qualified acupuncturist will be able to give specific advice for each individual on how to modify diet to help address underlying conditions affecting the health of the nervous system. Your acupuncturist will likely also introduce herbs that provide additional nutrients to balance the system. These medicinal herbs are sourced from plants and contain properties we do not get from the and vegetables we eat on a daily basis. TCM considers herbal supplements to be an important extension of the diet to enhance health.
One study conducted with patients with Type 2 diabetes compared results of patients using medications only versus those who also received acupuncture treatment. The acupuncture group saw vast improvement over the medication-only group, not only in relief of painful symptoms, but in disability scores as well.
A study comparing a group of patients who got acupuncture versus those who received sham acupuncture showed that the people who had real treatment showed improvement in sensory and motor function in a fifteen-day period.
Another study designed to look at the long-term effects of acupuncture on neuropathy pain showed that people who had received ten weeks of acupuncture treatment were able to reduce their use of medications, and the majority of patients reported that they were still feeling the benefits up to a year later.
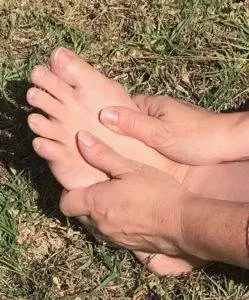
Top 5 Tips for Care of Neuropathy in Feet
People with neuropathy are highly susceptible to seemingly small injuries to the feet that can quickly turn into serious infections. Because sensation is diminished, sometimes a small stub is not felt until it has already become problematic.
- Wash feet and dry them carefully every day. Check for any sores or swelling, and address immediately with ointment and appropriate bandaging.
- Massage your feet every day. Rub the tops and bottoms until they are warm. This encourages circulation and stimulates good sensitivity.
- Wear socks and shoes that provide support and cushioning without compression or irritation.
- Move the feet regularly. Even when you must sit for long periods, make a point of removing your shoes to stretch and wiggle your toes. Elevate the feet when possible.
- Don’t go barefoot or wear flimsy shoes. It is so easy to injure the feet this way, and you may not be conscious of a small abrasion until it is already infected.
Acupuncture Near Me for Neuropathy
Our doctors at Art of Wellness have over 30 years of experience helping patients with chronic pain and neurological conditions. If you or a loved one has been suffering with neuropathy pain, please contact us to set up an initial consultation. We partner with you and other members of your healthcare team to provide the very best in integrative care.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Acid Reflux with Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Acid reflux, also known as heartburn, is the most common symptom of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), a chronic disease in which the contents of the stomach move upwards into the esophagus, irritating the lining of the food pipe and causing burning pain in the chest, among other symptoms.
It is estimated that at least 40% of adults experience heartburn symptoms at some point in their lives, while up to 20% experience heartburn at least weekly, making GERD one of the most commonly diagnosed digestive disorders in the US. If a person is experiencing GERD symptoms frequently, doctors will usually try to treat acid reflux with medications called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and lifestyle changes. However, in many cases, patients will continue to suffer with symptoms beyond chest pain and regurgitation, often in concert with other common digestive complaints like dyspepsia (indigestion), IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), and ulcers in the stomach, necessitating further investigation and treatment.
TCM and acupuncture offer an alternative course of action to deal with acid reflux and many other digestive disorders. Acupuncture treatment has been shown to be even more effective than medications for heartburn relief. Acupuncture and herbal natural remedies for heartburn provide long-term positive results for GERD symptoms by helping to resolve the digestive disorder at its origin.
Acid Reflux Symptoms
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is characterized mainly by the reverse flow of digestive fluids up into the esophagus. When this occurs regularly over time, it can damage the lining of the esophagus and cause other problems. The sensation of “heartburn” is the most commonly known symptom of acid reflux, but it is possible to have GERD and not experience this burning sensation. GERD can occur with other non-acidic digestive fluids and may not cause the type of pain caused by acidic stomach juices. GERD symptoms include:
- Burning in chest, worse after eating and when lying down
- Chest pain, even when you haven’t eaten
- Difficulty swallowing
- Regurgitation of food or sour-tasting liquid
- Excessive salivation
- Sensation of a having a lump in the throat
- Excess gas in stomach and bloating
- Intolerance of certain foods and beverages
- Bad breath, or a constant sour taste in the mouth
- Hoarse voice or laryngitis
- Constant need to clear the throat
- Chronic dry, sore throat
- Burning sensation in the mouth
- Inflammation of the gums and other dental problems
Acid reflux symptoms may appear at the same time as other symptoms like stomach pain, stomachache, and stomach cramps. These may be stomach ulcer symptoms, gastritis symptoms, or signs of dyspepsia, as it is common for two or more of these digestive issues to coexist.
Heartburn Causes

While there is no single clear cause of GERD, it is usually related to the functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle that separates the esophagus from the stomach. The LES, when it works correctly, allows chewed food matter to pass into the stomach, then closes to prevent matter from the stomach from flowing upwards. When this sphincter is relaxed or weakened, the contents of the stomach can breach this barrier. This can happen due to pregnancy or excess weight in the belly pushing upwards on these organs. Sometimes it may be due to a hiatal hernia, which can cause the upper part of the stomach and LES to push through the diaphragm muscle into the chest area.
Heartburn can be triggered by eating spicy or acidic foods, by smoking or inhaling second-hand smoke, or the use of aspirin or ibuprofen, as well as some blood pressure medications. If abstaining from these triggers does not help, patients may be referred to a gastroenterologist for investigative testing to pinpoint the problem. Endoscopy of the upper GI tract can show whether there is a hiatal hernia, stomach ulcers, or damage to the esophagus.
Acid Reflux Treatment
Many people take over the counter antacids (like Tums, Rolaids, Maalox, or Mylanta) to try to get heartburn relief. These may help alleviate the burning sensation temporarily, but using antacids frequently can actually exacerbate the problem by creating more stomach acid. Histamine (H2) blockers (like Pepcid and Zantac) can help reduce production of acid, but they don’t work for everybody. PPIs (like Prevacid, Prilosec, and Nexium) work by blocking the production of stomach acids.
These GERD medications can help with healing stomach ulcers and reducing acid reflux, but there are downsides. These drugs are very expensive, and many people end up using them on a daily basis. PPIs also inhibit the output of certain enzymes, which creates a negative interaction with common heart disease medications. They can also reduce absorption of calcium in the digestive tract, which can lead to weaker bones and increased risk of fractures. PPIs can also affect kidney function and increase the levels of bacteria in the stomach; if this bacteria makes its way up into the chest area due to reflux, it can get into the lungs and cause higher risk of pneumonia and other respiratory infections.
Asthma and GERD are often considered to be related conditions, because acid reflux can irritate tissues that trigger asthma attacks, while asthma attacks can cause a weakness in the LES that triggers reflux. Asthma medications like theophylline can also cause heartburn attacks. People who suffer from both GERD and asthma need to manage both conditions in tandem.
Prescribed medications called prokinetics cause the stomach to empty more quickly, reducing the chances of reflux. However, they can also cause side effects like nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, anxiety and depression, as well as having contraindications with other prescriptions.
All of these medical treatments focus on the stomach acids that cause heartburn. Currently, there is no conventional treatment that helps to restore the normal functioning of the LES. Research has indicated that acupuncture treatment, in addition to helping regulate gastric secretions, may help to strengthen the motor function of the LES.
Acupuncture and Herbs for GERD
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a holistic system of medicine founded on over 3000 years of recorded research and practice. In TCM, all health problems are viewed as imbalances caused by blockages of Qi (life force energy) in the body. Disorders of the organ systems are often linked to emotional disturbances. According to TCM, acid reflux and other digestive problems are influenced by stress and anxiety. Long-term, ongoing feelings of worry, frustration, and anger impact the liver, spleen and stomach, increasing acidity and inflammation in these organ systems.
An “upset stomach” and feelings of tightness and pain in the chest are caused by Qi rising inappropriately, causing the backflow of acids. Acupuncture treatment for GERD focuses on calming anxiety, and restoring the downward flow of Qi, while toning the stomach and LES to improve their motor function.
TCM uses herbal formulations, developed over many centuries, to support the proper functioning of the internal organs on a deep nutritional level. Herbal remedies for acid reflux in TCM work to increase healthy mucus in the esophagus, soothing and healing damage from stomach acids.
An acupuncturist is also likely to ask questions about dietary habits, as certain foods are likely to be part of the problem. Working together with a qualified TCM practitioner to plan meaningful lifestyle changes, specific to each individual, will also help resolve heartburn, stomach pain, and indigestion.
TCM for Heartburn During Pregnancy
Many women experience acid reflux, which can happen at any time during pregnancy. This is due to hormone changes that can relax the LES so that it doesn’t close completely. In the later stages of pregnancy, the uterus pushes up on the digestive organs and diaphragm. According to TCM, stomach fire, indicated by a craving thirst for cold drinks, may need cooling. Stagnation in the digestive organ system can cause belching and bloating. Acupuncture treatments can be tailored to address these conditions, improving digestive flow and balancing hormones. Acupuncture can also help if baby is showing signs of colic or infant reflux.
Top 10 Tips for GERD Diet and Lifestyle

Creating and maintaining balance between Yin (cool) and Yang (warm) energies in the body and spirit is central to treating heartburn with TCM.
- High fiber diet – eat oatmeal and plenty of cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower and broccoli.
- Avoid citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits) and emphasize melon, bananas, apples and pears. Tomatoes and pineapple are also highly acidic and can cause problems, as can onions and garlic. Citric acid is also a common food additive and should be avoided.
- Eat several small meals per pay – eating larger amounts at one time increases the chance of the stomach becoming distended.
- Reduce fatty foods – high-fat foods stay in the stomach longer. Avoid fried foods, dairy ingredients and marbled meats.
- Avoid alcohol, especially red wine
- Avoid caffeinated drinks: coffee, tea and sodas can all trigger heartburn.
- Drink ginger or chamomile tea, which are both soothing to the stomach. Green tea can also positively stimulate the LES.
- Don’t lie down after you eat. Eat at least two hours before you intend to go to bed.
- Watch your workout positions: movements that affect your abdomen can cause reflux. Crunches, sit-ups, leg lifts, headstands, downward dog and other poses should be done carefully if at all. Never exercise on a full stomach.
- Sleep with your head elevated above your feet. A wedge-shaped foam lift will work much better than stacking pillows. Or, attach risers to the feet at the head of your bed.
Best Acupuncture Near Me for Heartburn Relief
Acupuncture treatment for heartburn is a safe and effective acid reflux remedy. If you or someone you know is suffering from GERD, acid reflux, gastroparesis, stomach pain, or symptoms of ulcer, we hope that you will not hesitate to find an acupuncturist in your area to schedule an initial consultation. We are practicing at Art of Wellness in Santa Monica, one of the top 20 acupuncture clinics in the greater Los Angeles area.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Shoulder Pain by Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Shoulder pain is one of the most common types of musculoskeletal pain amongst adults, affecting about one in four people in their lifetime. Almost 20% of disability cases related to chronic pain are due to disorders of the shoulder, such as frozen shoulder (also known as adhesive capsulitis), torn rotator cuff, and tendonitis in shoulder. Neck and shoulder pain can be caused by injury, overuse, arthritis, or degeneration of tissues over time.
Shoulder pain is usually treated first with medications to reduce pain and swelling, and suggested activity modifications. Often people are referred to physical therapy (PT) or sports medicine specialists, so that a specific regimen of exercise can strengthen and stabilize the joints. In more severe cases, surgery may be required to repair torn tendons or cartilage. Acupuncture and other TCM modalities can be used to complement these conventional treatments, helping to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, speed healing and improve range of motion.
In this article we will discuss some of the causes of shoulder pain, how it is usually treated with conventional methods, and how acupuncture and TCM can help reduce and prevent recurrence of shoulder pain.
Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder is generally thought of as a “ball and socket” joint, but in fact, this part of the body has such a high level of utility and mobility because it is made up of several bones and a complex system of muscles, tendons, and bursae–little fluid-filled sacs that provide cushioning between the bones.
There are really three joints that make up the shoulder: the acromioclavicular joint (AC joint), where the collarbones (clavicle) and shoulder blades (scapula) meet, the glenohumeral joint, where the ball-shaped head of the long arm bone (humerus) fits into a shallow socket (glenoid), and the sternoclavicular joint, where the clavicle meets the sternum. These bones are held together by the “rotator cuff,” a collection of four major muscles and tendons.
The unique construction of the shoulder allows for a wide range of motion, including flexion and extension, adduction and abduction, and both medial (internal) and lateral (external) rotation of the socket joint. The scapula joint allows for protraction and retraction, elevation and depression. All of this amazing mobility comes at a price, however. It is up to the muscles and tendons to provide stability, and when these soft tissues are injured or weakened, the shoulder can become unstable and/or lose part of that mobility.
The 10 Most Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
The most common cause of shoulder pain is a problem with the rotator cuff. When the tendons are torn, or even just inflamed, it can be difficult and painful to lift the arm. This can be caused by repetitive motions executed during manual labor (especially overhead motions, as with painting or construction) or sports-related injuries (especially common with baseball and tennis). In some cases, the tendons of the rotator cuff tear, either due to a sudden injury (acute torn rotator cuff), or degeneration of tissue that occurs over a long period of time (chronic shoulder pain). Other causes of shoulder pain can be related to the bursae, or a disorder of the way the tendons and bones fit and move together.
Common causes of shoulder pain include:
- Torn rotator cuff – A tear or tears in the muscles and/or tendons of the shoulder joints generally causes a dull pain that worsens when you sleep on it. It can cause difficulty performing simple actions such as combing your hair, and all of the actions of the arm may be weakened. A tear can be caused by a sudden injury, but is more commonly due to repetitive motions related to physical engagement in work or sports over a long period of time. Rotator cuff problems should not be ignored. Some tears are best treated with surgery before they become larger. Without adequate treatment and changes in movement behaviors, torn rotator cuff tendons can lead to serious degeneration of the tissues and permanent loss of mobility.
- Frozen Shoulder – Also known as adhesive capsulitis, which refers to the capsule of tissues that surrounds the shoulder joints. When these tissues tighten and become more rigid, it creates a stiffness and severe pain in the shoulder and arm, making it increasingly hard to move without shoulder pain lifting arm. This condition is more common in women, and is seen more often in people between the ages of 40 and 60. PT can be effective for improving flexibility.
- Tendonitis – this refers to inflammation of the tendons that attach the muscles to the bones of the shoulder joints. When the tendons become inflamed, the area feels tender and achy, and normal activities can be difficult.Tendonitis in shoulder can often resolve itself with rest and reduction of the inflammation.
- Bursitis – this occurs when the small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae become inflamed, again, either due to injury, repetitive movements, or other conditions that cause inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis. This can cause even small movements, like pushing open a door, to hurt. Usually patients are cautioned to rest, and perhaps even wear a brace to restrict movement until the inflammation is resolved.
- Arthritis – when cartilage and the synovial lining that lubricates the joints begin to wear away over time, the bones of the joints begin to rub against each other. This generally happens in older people, and they begin to feel deep aching that sometimes gets worse when the weather changes. Along with rest, PT, and anti-inflammatories, patients are often treated with corticosteroid shots to temporarily reduce pain and inflammation.
- Shoulder Impingement – Some of the muscle and tendon tissue of the shoulder is sandwiched between the bones. When the movement of the shoulder causes parts of the soft tissue to be pinched by the bones, causing pain, it is called subacromial impingement. This can be caused by swelling of those tissues due to overuse, or because of a tear in a tendon or the labrum, or because of arthritis causing a change to the shape of the bone. In some cases the congenital shape of the acromion or coracoid bones can make someone more susceptible to impingement. The development of a bone spur could also cause this problem. In these cases, surgery to remove bone and create more space in the joint may be indicated.
- Dislocation – This occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) pops out of the cup of the socket bone (glenoid). This can happen when the arm is suddenly pulled or twisted sharply, or when a person falls on their outstretched arm. The shoulder is the joint most commonly dislocated, and this injury happens more often in young people. It causes severe pain, swelling, bruising, and loss of mobility. Once the displaced arm bone is reset in the socket, mobility returns, but it can take a long time to regain strength. A person may be prone to dislocating the shoulder again without physical therapy, and in some cases, reconstructive surgery is required.
- Separation – This is an injury that causes AC joint pain, in which the ligaments that connect the collarbone to the shoulder blade are torn. This most commonly happens because of a fall right onto the shoulder. This often causes a bump or bulge on the top of the shoulder, where the clavicle is sticking up at an odd angle while the scapula drops down. A mild sprain causing clavicle pain may be healed with rest and restriction of movement with a sling. More severe cases may require surgery. Either way, physical rehabilitation is indicated to help restore mobility and strength.
- Broken collarbone – The collarbone/clavicle, which connects the arm to the ribcage, is a fairly exposed and delicate bone. It commonly breaks due to a fall. This injury causes collarbone pain and makes it hard to move the arm, causes the shoulder to sag, and creates a lot of bruising and swelling. If the break is clean, the shoulder can be immobilized with a sling until it heals. If the broken ends of the bone have shifted apart, though, surgery may be necessary to realign them. PT rehabilitation will then help through a long healing process.
- Labral tear – the labrum is a rounded rim made of cartilage that helps hold the top of the arm firmly in the shoulder girdle. Sometimes the labrum is stretched or torn due to injury or overuse, causing the joint to become loose and unstable. This can feel like a gentle shoulder pop or locking sensation when you move, or it can produce a severe pain when you try to lift the arm. A labral tear can cause loss of strength and range of movement. This condition is usually diagnosed by a specific imaging technique called an MR arthrogram. A labral tear may be helped by lifestyle changes to prevent aggravation, anti-inflammatory medications, cortisone, shots, and physical therapy. In some cases, a severe or complicated case may require surgery to repair the tear or tighten the joint capsule.
Other types of sore shoulder include: a pinched shoulder nerve in the neck area that can cause radiating neck and shoulder pain, or a muscle pull in the upper back or top of the arm, as in trapezius pain, rhomboid pain, or deltoid pain. Problems with the jaw, or TMJ disorders, can also contribute to shoulder pain.
Acupuncture and TCM for Shoulder Pain

As you can see, resolving shoulder pain relies heavily on the reduction of inflammation. It may be that inflammation with a separate root cause (such as heart disease or an autoimmune disorder) created a problem with the soft tissues of the shoulder joints in the first place, or it may be that an injury to the shoulder is the primary source of the inflammation. Either way, reducing the inflammation is the key to relieving shoulder pain and restoring mobility to the joints.
Acupuncture is a highly effective modality for reducing inflammation, without the sometimes severe side effects that can arise from other conventional treatments like steroid injections. Cortisone shots can reduce pain and swelling temporarily, but repeated shots can cause damage to the area, and in some cases, infections at the site. Cortisone can also raise blood sugar levels, increasing the risk for diabetes.
Scientific evidence suggests that acupuncture treatments reduce inflammation by stimulating the pituitary gland to release more cortisol naturally. It is also hypothesized that acupuncture affects the release of neuropeptides from the peripheral nerve endings, which is a key part of the body’s inflammatory response.
In TCM vocabulary, we consider inflammation to be due to a stagnation of Qi and blood, not only in the area immediately affected, but also in related organ systems. In the case of the shoulder, the corresponding organ system is often that of the large and small intestines. To relieve shoulder pain and restore freedom of movement, it is also necessary to “re-train” the shoulder muscles to move together smoothly. Physiotherapy can be very helpful for this, but there are also TCM practices that can be integrated to help achieve better mobility. One study compared patients with frozen shoulder who were performing exercises to improve the condition with patients who exercised and received regular acupuncture treatments. The patients treated with acupuncture scored significantly higher in improved mobility and reduced pain, and the positive effects lasted for months after treatment ended.
Tuina and Gua Sha, specific forms of therapeutic massage administered by doctors of TCM, can also be used as part of comprehensive treatment for relieving stiffness in the shoulder.
Chinese herbs have been used for thousands of years to help reduce inflammation in the body.More recent scientific studies have demonstrated the direct anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Chinese herbal formulations. Specifically, herbs have been shown to inhibit the swelling caused by cytokine production that is typical of chronic joint diseases.
Top 3 Tips for Relief and Prevention of Shoulder Pain
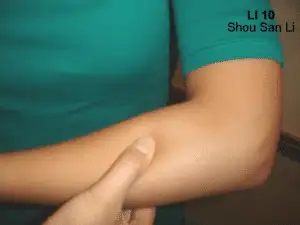
The best way to relieve and prevent shoulder pain from recurring is to manage inflammation. Regular acupuncture treatments are beneficial, but there are also some excellent self-care techniques you can use to relieve pain and improve function.
- Acupressure point for shoulder pain: LI10 (large intestine meridian). Find this point on the front side of the forearm, about three inches below the elbow. Apply gentle pressure while breathing deeply to relieve stiffness and pain in the shoulder, neck, and elbow.
- Practice stretching and strengthening exercises for the shoulder joints. Start slowly, with gentle movements to improve range of motion, then move up to using some light weights to help strengthen the muscles.
- Pendulum – Lean forward with one arm hanging loosely. Use the other arm to brace against a chair for support. Gently swing the hanging arm from side to side, forward and back, and in a circular motion. Slowly return to a standing position. Repeat on the other side.
- Wall angels – Stand with your back to a wall, with the arms at your sides, whole arm and back of the hand pressed to the wall. Slowly raise your arms, keeping them pressed to the wall, and lower them in a “snow angel” motion.
- Follow an anti-inflammatory food program – avoid foods that cause inflammation, including fried foods, refined carbohydrates (flour, sugar, etc.), red meat, and processed fats like margarine and shortening. Consume lots of leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables, fresh fruits, especially berries and cherries, emphasize fish as a primary protein source, and use high quality olive oil. Your acupuncture provider will be able to give you more specific directions for how to eat best to improve your condition.
Acupuncture Near Me for Shoulder Pain
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & TCM in Santa Monica, California, was recently chosen as one of the top 20 acupuncture clinics in Los Angeles. Our doctors have over 30 years of experience both in China and here in the United States. Dr. Tan is a specialist, with training in both TCM and conventional medicine, in orthopedic, musculoskeletal, neurological, and chronic pain disorders of all kinds. We work in an integrated fashion with your other medical practitioners to help you achieve the best results. If you or someone you know is suffering from shoulder pain, call us at 310-451-5522 to schedule a consultation.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
Acupuncture and TCM for Cancer – Integrative Oncology
By Dr. Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
Until very recently, it seemed cancer was the one illness that had touched everyone’s life in some way. Cancer is the leading cause of death in the world. Almost 40% of the population will be diagnosed with some form of cancer at least once in their lives. We have all lost friends and relatives to this seemingly relentless form of disease. Doctors, scientists, researchers, and organizations have worked tirelessly in recent decades to develop life-saving treatments, and millions of people go on to live full lives as cancer survivors.
Cancer is a broad term that refers to the unchecked growth of abnormal cells in the body. When the body’s mechanisms for getting rid of old cells begins to break down, these damaged cells begin to divide, in some cases forming masses, or tumors. These types of cancer are usually classified by the organs affected by the tumor, including gynecological cancers such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, and endometrial cancer, as well as prostate cancer in men, lung cancer, cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatic, stomach, esophageal, colon, rectal), thyroid, brain, spine, bladder, liver, and kidneys. Carcinomas refer to cancers affecting the skin, and sarcomas to cancers affecting the musculoskeletal system. Hematological cancers involve the proliferation of abnormal blood cells, including leukemia, lymphomas and multiple myeloma.
Written records of Traditional Chinese Medicine detection and treatment of cancerous growths go back over 2000 years. In recent decades, TCM has become more recognized as a way to complement and enhance contemporary methods of treating cancer. Integrative Oncology, in which the latest technological and pharmacological advances are combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine techniques and philosophy, forms a holistic way of working with cancer patients.
Cancer Treatment Options
Cancer screening is a vital component of modern health care, as early detection offers the best chances for successful treatment. Data show that of the 18 million new cases detected in 2018, 5 million could have been discovered sooner and treated more effectively if we had higher rates of screening. Unfortunately, almost half of colorectal and cervical cancers and a third of breast cancers are not diagnosed until the disease is already in later stages, which makes them harder to treat.
When a cancerous growth is still localized, surgery and/or radiation treatment can remove or destroy much or all of the abnormal growth. When cancer has advanced to a later stage, and cells have spread through the body, then more systemic treatments are used, such as:
- chemotherapy, which uses cytotoxic drugs to kill tumor cells
- immunotherapy, a newer type of treatment, uses specifically designed synthetic antibodies to boost the body’s immune system.
- targeted therapy seeks to destroy the cancer cells without harming healthy tissues surrounding tumors.
New treatment options are constantly being researched and tested, giving patients a better chance at stopping the cancer in its tracks.
However, most cancer treatments themselves can cause serious side effects that dramatically impact quality of life. Positive outcomes also vitally depend on a person’s ability to strengthen the body’s immune system while fighting the disease, as well as coping with the severe emotional stresses involved. Research has shown that acupuncture can significantly mitigate side effects of chemotherapy, radiation treatments and other conventional methods of treating cancer.
Chemotherapy and radiation work by killing cancer cells. As these chemicals do not distinguish between normal and malignant cells, they can also damage surrounding tissues, creating more blockages. The synthetic drugs used also increase toxicity levels within the body. Acupuncture can help increase the production of white blood (immune) cells, detoxify the body and increase energy, so that the cancer can be eradicated, and new, healthy cells can flourish. Acupuncture can also improve sleep and relieve anxiety, so that hope and confidence can outweigh fears and exhaustion.
Acupuncture and TCM can be valuable for cancer patients throughout every stage of treatment, recovery and beyond, not only alleviating the pain and nausea associated with cancer treatments, but also boosting immune function, relieving anxiety and depression, and even helping to prevent the cancer from coming back.
How Can Acupuncture Help with Cancer Treatment?
Acupuncture operates based on the philosophy that the body is powered by Qi – a life force energy – that runs along pathways throughout the body called meridians. Pain and diseases are caused by blockages in these pathways that prevent Qi and nutrient-rich blood from reaching and adequately supplying the organ systems of the body. When the body is balanced and functioning smoothly, the immune system is able to detect and eradicate pathogens on its own. Our bodies do this all the time. While genetic predisposition may increase some people’s cancer risk, the truth is everyone is susceptible to the formation of cancerous cells. When the body is healthy, it can sweep away mutated cells. But when the body is in a weakened state and energies are blocked, cancer cells are able to take hold, multiply, and grow.
Acupuncture can help relieve symptoms caused by the disease itself, as well as the side effects of treatment, including but not limited below:
- neuropathy
- pain
- nausea/vomiting
- dry mouth
- fatigue
- insomnia
- depression & anxiety
In addition to providing palliative care for these symptoms, acupuncture treatment works on a deeper level to strengthen Qi, revitalize blood, and restore healthy functioning to the organ systems. The combination of acupuncture treatment to stimulate specific points and herbs to act on chemical/elemental imbalances can approach the root cause of the abnormal cell growth.
Acupuncture for Cancer Treatment Side Effects
The most common side effects of cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy are gastrointestinal in nature. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea are caused by the medications involved, which may be administered intravenously or by mouth. The extent to which a patient feels nauseated depends on many factors: the location of the cancer being treated in the body, the dosage of the medications, the timing of administration, and a person’s prior susceptibility to nausea and vomiting. Treatment for tumors in the brain, liver, or gastrointestinal tract–such as esophageal, pancreatic, colon, or stomach cancers–is more likely to cause vomiting. Women, in general, are more likely to experience severe nausea. Antiemetic drugs or stomach acid-reducing medication like Esmeprazole can sometimes help with the nausea, but they don’t work in many cases. One controlled study showed that acupuncture given to patients undergoing chemotherapy reduced the duration and frequency of unpleasant gastric upsets. The TCM providers in this case used acupuncture points to reduce spasming of the stomach and intestines, while strengthening liver and spleen function to improve digestion and absorption. The patients given acupuncture ended up spending less time in the hospital.
Using acupressure point PC6, located below the wrist on the inner forearm in between the two tendons, is very effective for controlling nausea. Relief of retching and vomiting helps patients withstand chemotherapy sessions better and helps keep appetite and proper nutrition up.
Another side effect of chemotherapy is neutropenia, or low white blood cell count. This is especially prevalent amongst patients being treated for bone marrow cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. The low level of bacteria-fighting immune cells puts people at higher risk for developing infections during the course of their treatment, especially invasive candida infection. A study involving women with ovarian cancer suggested that acupuncture treatment helped patients maintain higher levels of white blood cells and neutrophils. The study also suggested that acupuncture measurably reduced cortisol levels, positively impacting patients’ stress.
Protecting cancer patients from side effects of chemotherapy such as neutropenia and severe nausea allows them to adhere more closely to their treatment programs, which can improve outcomes.
Acupuncture for Late Stage Cancer Pain and Neuropathy
Pain is, unfortunately, the most pervasive symptom experienced by people with cancer, yet this pain is often inadequately treated with analgesics. Recent epidemic-level problems with opiate use mean that doctors and patients are hesitant to use these powerful medications, which can lead to addiction. Acupuncture offers an alternative method for reducing pain naturally, without any additional risks involved.
Cancer pain can be pathophysiologically caused by tumorous growths themselves causing compression around other tissues and nerves. It can also be caused by secondary tissue damage created by chemotherapy, radiation, hormone therapy, or surgeries. When nerves are damaged, neuropathy pain can result.
To manage all of the different types of pain, patients are often prescribed some combination of acetaminophen, opiates, anti-inflammatories, anticonvulsants, corticosteroids, and antidepressants. All of these can cause serious side effects, and some patients will build up a tolerance to the medications, reducing their efficacy. Some people develop a dependence or addiction.
Pain, as a subjective experience, affects emotional and mental health as much as it does the physical body. Pain can be amplified by the very real fear that it will only get worse or never end. Adequate pain management is vital to keeping a positive frame of mind and hopeful attitude. When pain is reduced, attention and energy can be freed up for increased healing and motivation to maintain healthy behaviors that will improve the chances for recovery and prevent recurrence.
Most people who seek out acupuncture do so for chronic pain conditions. While much of how TCM works is still unproven by scientific study, many research studies have shown that acupuncture is an effective modality for pain relief, such that it is now widely accepted as an adjunct by the medical community. Acupuncture treatment can be used on its own to help alleviate pain, or in addition to pain medications, in which case it will help both to address the pain and to mitigate the side effects of the drugs.
Top 3 Tips for Cancer Prevention

TCM is preventative medicine. It is always best to manage lifestyle for maximum health in order to prevent disease from forming in the first place. While some people are more at risk for developing certain kinds of cancer than others, everyone can benefit from healthy habits that reduce these risks. Regular acupuncture treatments help balance Qi and maintain good flow between the organ systems of the body. But it is up to each individual to eat in such a way that the cells receive abundant nutrient-rich blood, to avoid toxins whenever possible, and to move the body frequently and with intention.
- Green tea contains chemicals called polyphenols, especially EGCG. These antioxidants inhibit the kind of cell damage that leads to cancer growth. Green tea has less caffeine than coffee or black tea, and can be drunk throughout the day.
- Exercise – Many studies have shown that increased physical activity reduces the risks of specific types of cancer, such as: pancreatic, endometrial, breast, colon cancer, esophageal, kidney, and stomach cancer. Exercise prevents cancerous growth by helping to regulate hormone levels, preventing high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and obesity, and reducing inflammation throughout the body.
- Healthy diet – A well-rounded food program lowers the risk of cancer. Focus on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Salmon is full of omega-3 fatty acids that have been shown to help fight cancer. Other fish that can help reduce the risk of endometrial cancer in women include halibut, sardines and tuna. Cruciferous vegetables are especially full of nutrients and fiber. Included in this family of vegetables are broccoli, cauliflower, radishes, brussel sprouts, kale, cabbage, and bok choy. Cruciferous vegetables are high potent anti-cancer phytochemicals. Studies have shown that this vegetable group has the ability to stop the growth of cancer cells for tumors in the breast, uterine lining, lung, colon, liver, and cervix. And studies that track the diets of people over time have found that diets high in cruciferous vegetables are linked to lower rates of prostate cancer. Eat fruits and vegetables raw or only lightly steamed so they retain their cancer fighting phytochemicals. Go for at least one of these greens on a daily basis: arugula, beet greens, bok choy, broccoli, brussel sprouts, cabbage, Napa cabbage, collard greens, daikon, rutabaga, chard, watercress, pea shoots, spinach.
Acupuncture Near Me for Cancer Support
Acupuncture provides palliative care for the many intense discomforts of cancer and cancer treatment. But TCM goes beyond pain relief. Regular acupuncture treatments combined with lifestyle changes can improve patients’ ability to defeat cancer now, and to prevent cancers in the future.
When you or a loved one is fighting cancer, building a team of doctors who will work together to provide integrative health care can increase the chances of survival and recovery.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
