-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Skin
How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Facial flushing? Persistent redness, tiny bumps, or a burning sensation across your nose and cheeks? These can be signs of rosacea, a common inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people. Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offer holistic rosacea treatment to address both the symptoms and the root causes of rosacea.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that most often appears in the middle of the face — the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. It can cause persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and small, painful pimples or red bumps on skin, like a red dot on face.
While facial rosacea is the most common form, there are some other skin conditions that can be related or sometimes mistaken for rosacea:
Pityriasis Rosea – Though the name is similar, this is actually a different condition caused by a viral infection. It leads to a scaly, pink rash that often appears on the torso and may be mistaken for rosacea, especially in its early stages.
Ocular Rosacea – In some patients, rosacea affects the eyes, causing symptoms like redness or “bloodshot eyes,” burning, stinging, dryness, or a gritty sensation. The eyelids may become inflamed, making the eyes appear bloodshot.
Perioral Dermatitis – considered by some practitioners to be a type of rosacea, this is a face rash that also appears on the face. “Dermatitis” is a general term that covers many types of inflammatory skin conditions.
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that will flare up at times, and at other times, appear to be improving (remission). If it is left untreated, rosacea can worsen over time and affect other areas, including the eyes.
Acupuncture and TCM can be used as a complementary or alternative treatment for roseacea.
Symptoms of Rosacea
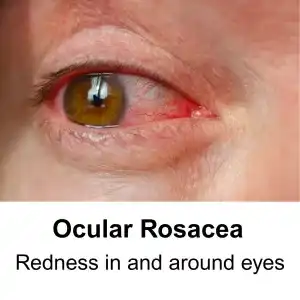
Common signs and symptoms include:
Facial Redness – Persistent redness or flushing, especially across the nose and cheeks.
Visible Blood Vessels – Tiny, broken blood vessels may appear near the surface of the skin.
Acne-like Bumps – Small, red, or pus-filled bumps that can be tender and painful.
Burning or Stinging Sensation – The skin may feel sensitive, warm, or sting when exposed to triggers like sun, wind, or skincare products.
Dry Skin – skin may appear dry, rough, scaly, or thickened (in severe cases).
Eye Symptoms – Red, irritated, or dry eyes (ocular rosacea)
Edema – puffiness or swelling in the face
What Causes Rosacea?
While the exact cause of rosacea is still not fully understood by medical science, many factors may play a role in the development of this skin condition. It is an inflammatory response that may be triggered by the immune system, certain foods, emotional stress, or environmental conditions like sun (U/V rays), heat, or wind. Genetics probably plays a role, as well.
Many people who suffer from rosacea have higher levels of mast cells. Some also have skin mites (Demodex mites). Demodicosis (face mite infestation) is not uncommon, but can show up in increased amounts in people who have rosacea and may be one of the factors that triggers the inflammatory response that contributes to rosacea flare-ups.
SIBO, or intestinal bacterial overgrowth, can sometimes contribute to rosacea.
Rosacea Treatment
A doctor or dermatologist typically diagnoses rosacea based on its characteristic signs and patient history. In some cases, a skin biopsy or other tests might be done to rule out other conditions like lupus or allergic dermatitis.
Common treatments include:
- Topical medications like metronidazole or azelaic acid. Some medications for rosacea constrict blood vessels to reduce redness, while others are antiparasitics
- Retinoids (Vitamin A)
- Oral antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline) to reduce inflammation
- Laser therapy for visible blood vessels
- Lifestyle and trigger avoidance (avoiding sun exposure, alcohol, spicy foods)
While these treatments can help manage symptoms, rosacea often returns when treatments are stopped, and long-term antibiotic use can affect gut health and immunity.
Can Acupuncture Help Rosacea?

In Traditional Chinese Medicine, rosacea is viewed as a result of internal imbalances that manifest as external skin changes. The skin is seen as an extension of the body’s internal state.
According to TCM theory, rosacea would usually be considered the result of stagnation of Qi, blood, and heat in the body.
Diagnostic patterns that an acupuncturist might observe as being the root cause of rosacea might include:
- Wind-heat of the lung meridian
- Damp heat of spleen and stomach
- Heat stagnation in the liver channel
Heat and toxicity in the lungs and stomach can create excess internal heat, which may rise to the surface, causing redness, flushing, and pustules.
Stagnation of Qi and blood, along with chronic stress, hormonal changes, and dietary habits can impede the flow of qi and blood, leading to stagnation and visible capillaries.
In some patients, dampness combined with heat can cause swelling, acne-like bumps, and increased oiliness.
In long-standing rosacea, depletion of yin (cooling, moistening energy) can cause lingering redness and sensitivity.
How TCM Treats Rosacea
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine take a personalized approach to rosacea, focusing on restoring balance within the body and addressing both internal and external symptoms.
Acupuncture works by:
- Reducing systemic and local inflammation
- Improving blood flow and microcirculation
- Regulating the autonomic nervous system
- Helping balance the gut-skin connection
- Calming the body and reducing stress, a common rosacea trigger
Research supports acupuncture as an effective therapy for rosacea. A review and analysis of studies found that a complementary treatment for rosacea combining conventional treatment and TCM therapy reduced the recurrence of symptoms. Acupuncture can reduce flushing, redness, and skin lesions associated with rosacea by modulating inflammatory pathways and promoting tissue healing.
One published case study demonstrated that a patient who had gone through 18 months of conventional treatment for rosacea with unsatisfactory results experience significant improvement after 3 acupuncture treatments, with no recurrence of a flare up in the subsequent six months. Laser Doppler showed increased blood microcirculation (blood flow) in the localized area of the skin rash.
Chinese herbs can be used both internally and externally to reduce redness, clear heat, and support overall skin health. The herbs in one TCM herbal remedy often used to treat rosacea—Liang Xue Wu Hua Tang—for example, works to remove toxins, cool and activate blood, and disperse wind. A traditional formula may be modified to suit the patient’s specific presentation, making TCM highly individualized.
Skincare for Rosacea
In addition to acupuncture and herbs, a TCM practitioner will recommend:
Avoiding rosacea triggers like alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods.
- Incorporating cooling, anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., leafy greens, cucumber).
- Managing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine using gentle, hydrating products.
By addressing the root causes of rosacea and working with the body’s natural balance, acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine can help reduce the frequency and severity of rosacea outbreaks, often yielding long-lasting results.
Acupuncture Near Me for Rosacea in West Los Angeles
If you’re tired of dealing with rosacea and want a natural approach that supports both your skin and overall health, we’re here to help. At Art of Wellness Acupuncture, we specialize in treating rosacea and other skin conditions with personalized acupuncture and herbal therapy. Contact us today to book your consultation and take the first step toward calmer, clearer skin.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac.

Itchy red bumps around mouth, nose, or under eyes? Perioral dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin condition that shows up as a red, bumpy rash on the face. Acupuncture and TCM offers a holistic way to help get rid of perioral dermatitis.
What Is Perioral Dermatitis?
Perioral dermatitis is a type of face rash that primarily affects the area around the mouth (perioral), though it can also show up around the nose (perinasal dermatitis) and eyes (periorbital dermatitis). This condition is most commonly seen in women aged 20–45, but it can affect men and children as well. It’s considered a form of rosacea or a rosacea-like condition by many dermatologists, though it has its own distinct features.
Unlike acne, the red bumps in perioral dermatitis don’t contain pus, and unlike eczema, the rash is not typically scaly or flaky. It often appears suddenly and can be persistent, sometimes lasting for weeks or months.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), including acupuncture and herbal therapy, offers a natural approach to different types of dermatitis that focuses on healing the skin and addressing underlying imbalances that cause this condition.
Top 5 Symptoms of Perioral Dermatitis
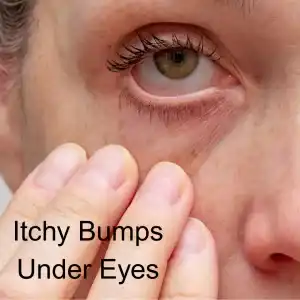
Perioral dermatitis can sometimes be mistaken for other health issues that cause skin rashes or other skin conditions, such as: acne, herpes, rosacea, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, discoid lupus, and papula sarcoidoisi. The most common signs of Perioral Dermatitis include:
- Red, inflamed bumps around the mouth, nose, or eyes
- Burning or itching sensation in the affected area
- Dry, tight, or peeling skin
- Clear fluid or pus in some bumps (though usually not like acne)
- Rash that spares the skin directly around the lips (creating a clear border)
Typically, perioral dermatitis will become worse with use of corticosteroid creams or heavy moisturizers.
It is important to recognize this condition, so that it can be treated appropriately.
What Causes Perioral Dermatitis?
The exact cause of perioral dermatitis is not fully understood, but several triggers and contributing factors have been identified. People who already suffer from eczema may be more prone to developing perioral dermatitis, because eczema can affect the skin barrier. Here are some of the things that might trigger an perioral dermatitis outbreak or flare up:
Topical corticosteroid use – This is the most common trigger. Long-term use of steroid creams, even over-the-counter hydrocortisone, can lead to this rash.
Hormonal changes – Many people who menstruate notice flare-ups around their menstrual cycle or during times of hormonal fluctuation.
Use of heavy facial creams or cosmetics – Occlusive skin products may block pores and irritate the skin.
Fluoridated toothpaste – Some people find their symptoms worsen with fluoride-containing toothpaste.
Environmental triggers – Sun exposure, wind, and heat can aggravate the skin.
Microbial imbalance – Overgrowth of certain bacteria or yeast on the skin may play a role.
Stress – Emotional stress can weaken the immune system and disrupt skin balance.
Dietary factors – Some people report flares related to certain foods, like spicy foods or alcohol.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Perioral Dermatitis
In a conventional medical setting, diagnosis is typically made based on a visual exam and patient history. A dermatologist may ask about what kinds of skincare products you use, medications (especially steroid use), and recent lifestyle changes.
Standard treatments include:
Discontinuation of steroid creams – Although this may cause a rebound flare, it is essential to stop steroid use.
Topical antibiotics or anti-inflammatory creams – Such as metronidazole or clindamycin.
Oral antibiotics – Like tetracycline or doxycycline, especially for more stubborn cases.
Skin care guidance – Patients are usually advised to stop all current products and switch to a minimalist routine with gentle cleansers and no makeup.
While these treatments can be effective, they don’t always address the root cause, and relapses are common—especially if underlying imbalances are not corrected.
TCM for Perioral Dermatitis

Traditional Chinese Medicine sees perioral dermatitis not just as a skin problem, but as a sign of deeper internal disharmony. In TCM, the health of the skin is closely related to the health of the Lung, Stomach, and Spleen organ systems. When there is heat, dampness, or toxicity trapped in the body, it can manifest as inflammation on the skin.
For example, a rash around the mouth is often related to Stomach Heat or Spleen Dampness, especially if digestion is weak or the diet is rich in spicy or greasy foods. If the rash appears around the nose and cheeks, Lung Heat or Wind-Heat may be contributing factors.
TCM also considers emotional stress and hormonal imbalance as key factors in skin conditions. Emotional stress can create stagnation in the Liver system, while hormonal changes may disrupt the balance of Yin and Yang in the body, leading to heat and inflammation.
Can Acupuncture Help Perioral Dermatitis?
Acupuncture and TCM therapies aim to treat the root cause of perioral dermatitis while also calming the skin and promoting healing.
Acupuncture helps regulate the immune system, reduce inflammation, and rebalance the organ systems involved. Specific acupuncture points may be used to clear heat, drain dampness, and support the Spleen and Lung.
Chinese herbal medicine can be customized to each patient’s individual pattern. Herbal formulas will be customized for each individual, depending on the presentation.
Dietary and lifestyle recommendations are often part of treatment, helping patients avoid inflammatory foods, support digestion, and reduce stress.
Facial gua sha and herbal washes can be used as topical therapies to calm redness, promote lymphatic drainage, and soothe irritated skin.
In many cases, patients find that their rash improves significantly with a few weeks of consistent acupuncture and herbal therapy—without the side effects of antibiotics or topical steroids.
While studies specifically on acupuncture for perioral dermatitis are limited, research shows that acupuncture is effective in treating other inflammatory skin conditions like eczema, acne, and rosacea. These studies demonstrate that acupuncture can reduce inflammation, balance hormones, and modulate the immune system, which are all key factors in healing perioral dermatitis.
A review found that acupuncture reduced itch, redness, and lesion count in patients with atopic dermatitis. Another study noted improvement in acne symptoms with acupuncture and herbal medicine, especially in women with hormonal imbalances.
Acupuncture Near Me for Perioral Dermatitis in West Los Angeles
If you’ve been struggling with persistent or recurring perioral dermatitis and are looking for a more holistic, drug-free way to manage your symptoms, acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine offer a safe and effective alternative. By treating both the surface symptoms and the internal imbalances, we help the skin heal from the inside out.
At Art of Wellness Acupuncture, we specialize in treating chronic skin conditions like perioral dermatitis using the principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Every treatment is tailored to your unique constitution and lifestyle, so you can heal naturally and prevent future flare-ups. If you’re dealing with red, itchy bumps around your mouth or face, don’t wait—reach out today to schedule your consultation and get started on the path to clearer, calmer skin.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Edema With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Swollen feet and ankles? Fluid retention in legs? These are signs of edema. Acupuncture and TCM offer natural diuretic herbs and alternative treatment for swelling in legs and feet.
Edema refers to when excess fluid in body tissues, or water retention, leads to swelling. Edema most commonly causes swollen ankles and swollen feet. But edema can occur in many parts of the body.
Blood vessels have tiny valves that work to push blood from the lower body back up to the heart. When this process isn’t working properly, blood and other fluids will gather in the legs and cause swollen feet and ankles.
Edema causes puffiness under the skin, and when you press on the skin, it leaves an imprint. The skin may be shiny and stretched because of water retention.
Other edema symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness in the legs, and a swollen belly or distended abdomen.
Everyone experiences edema once in a while; for example, after a long airplane flight, which causes fluids to pool in the legs and feet, or the day after eating particularly salty foods, which can cause water retention. Edema is also common during pregnancy, when increased blood volume and pressure from the growing uterus can cause edema in the legs.
Occasional edema can often be prevented or remedied by reducing salt intake, drinking more water, and wearing compression garments.
Some health conditions can cause edema, in which case, both the underlying issue and the edema itself need to be addressed.
Acupuncture and Chinese herbs can help relieve swollen ankles and feet due to water retention, as well as helping to address the root cause of edema.
Causes of Edema

Edema can happen when a person stays in one position for a long time and fluids build up in the lower body due to gravity. This type of swelling can be helped by getting up and moving around regularly and/or wearing compression socks that prevent water retention from causing swollen ankles and feet.
Cardiovascular issues having to do with heart function or the health of blood vessels can cause edema. When the heart doesn’t pump blood effectively, it can cause fluid buildup in the legs, ankles, and feet. Venous insufficiency, or weakness in the veins, can prevent blood from being pushed back to the heart properly, which leads to varicose veins and blood buildup in the legs.
Kidney disease and liver disease can contribute to edema. Damaged kidneys are less able to remove excess fluid, leading to swelling. Conditions like cirrhosis can increase pressure in blood vessels and reduce proteins that keep fluid in the bloodstream, causing edema.
Blocked or damaged lymph nodes can prevent lymph fluid from draining well, causing localized edema. This is known as lymphedema. Lymphedema can be related to cancer treatments, when lymph nodes are removed.
People may experience edema after a stroke or cardiac event like a heart attack.
Side effects from some drugs, including those for high blood pressure and corticosteroids, can cause fluid retention.
Conditions such as cellulitis or arthritis can cause inflammation and localized swelling.
When there are underlying conditions like cirrhosis, kidney problems, and vascular issues, they must be addressed in order to resolve the edema.
Treatment for Swollen Legs and Feet
Conventional medical treatments for edema typically focus on addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms. Typical medical treatment for edema may include:
- Diuretics to help the body expel excess fluid through urine.
- Compression stockings to help reduce swelling by promoting fluid movement in the legs.
- Elevating the affected limbs above the level of the heart can help reduce swelling.
- Lowering sodium in the diet can help prevent fluid retention.
- Regular exercise to improve circulation and help reduce swelling.
- Addressing heart, kidney, or liver issues can help manage edema.
Using diuretic medications may seem to alleviate swelling in the short term, but these drugs create a kind of dependency. As soon as a person stops taking the diuretics, the water retention will return.
Chinese herbal formulations can act as natural diuretics, while addressing the root cause of edema.
By integrating acupuncture and TCM into your treatment plan, you may find a holistic approach that addresses not only the symptoms of edema but also its cause, providing lasting relief from edema swelling.
Can Acupuncture Help Edema?

TCM theory for the treatment of edema goes back over 2000 years. The Yellow Emperor wrote about edema treatment in his medical text before 100 B.C., describing the disruption of fluid movement in the body. In the second century A.D., another well-known Chinese doctor Zhang Zhong-Jing detailed treatments for edema with herb formulas, which are still considered classics today.
Edema can be related to imbalances in Yin and Yang. Yin edema affects the spleen and kidneys, while Yang edema affects the spleen and lungs. Yin edema symptoms tend to start in the lower body, with swollen feet and ankles, while Yang edema symptoms tend to start in the upper body, with the tendency to have tight, shiny skin.
According to TCM, the organ systems of the Spleen, Kidneys, and Lungs must be balanced in order to restore proper functioning of fluid metabolism. An acupuncture treatment protocol would be directed towards clearing wind, heat, dampness, and other pathogenic forces, while balancing Yin and Yang, and regulating Qi and Blood.
Different pathologies of edema can be described by TCM diagnoses, including:
- Blood stasis
- Qi stagnation
- Damp heat
- Heat toxins
- Wind-cold or Wind-heat in the lungs
Recent research shows that ancient herb formulas can help regulate fluids and have a positive effect on vascular function.
Moxibustion, a TCM modality that involves warming acupoint areas by burning mugwort herb near the skin, is often used to help relieve edema. Moxa treatment can help improve blood flow by warming and dispersing dampness and phlegm and invigorating the spleen and kidneys.
One study of patients suffering from swelling in legs and ankles showed that moxibustion helped relieve swelling in the legs.
Breast cancer treatment often involves radiation treatment that affects the lymph nodes, or the removal of lymph nodes, which can lead to lymphedema. This type of lymphedema often affects one arm, or both arms. It can also affect other parts of the body.
One study involved using acupuncture treatment twice a week to help relieve lymphedema after cancer treatment. More than half of the patients experienced a significant improvement in lymphedema, as measured by arm circumference. The conclusion was that acupuncture is a safe treatment that can help reduce swelling.
Acupuncture treatment improves blood flow and the movement of fluids in general, while nourishing the kidneys and spleen. Moxibustion can be used to further stimulate the flow of blood and Qi.
Acupuncture Near Me for Edema in West Los Angeles
Edema is a common problem, but it requires an individualized approach, as it can have many different root causes. Experienced acupuncture practitioners like Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in Westwood, CA can help patients find relief from edema swelling and water retention in legs through a combination of acupuncture, moxa, herbs, and personalized nutrition counseling.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Pruritus With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Itchy skin, hives all over the body, or skin rashes that itch? Pruritus, commonly known as itching, is an irritating and persistent condition that affects many people. Acupuncture and TCM herbs can offer a holistic approach to alleviate itching.
Pruritus is simply a medical term that means “itching,” or that feeling that you need to scratch your skin. It can refer to itchy skin on one part of the body, or systemic itching that feels like it moves around or affects the whole body. The sensation can be mild, even ticklish, or painful and constant to the point that it is debilitating.
The sensation of itching all over body can significantly impact one’s quality of life, as it can be painful, distracting, and make it difficult to concentrate, relax, or sleep.
Persistent itching requires treatment that takes many possible underlying factors into consideration. This is why acupuncture and TCM can be a good alternative treatment for pruritus.
What Causes Pruritus?
Pruritus can stem from various causes. It can be a primary condition, arising due to a skin problem or skin allergy, such as:
- Atopic dermatitis
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Hives, urticaria
- Folliculitis
- Dry skin
- Hemorrhoids
- Head lice infestation
Pruritus can also be caused by many other conditions, such as nerve damage, renal disorders that require dialysis, blood diseases like polycythemia vera, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, infections like chicken pox and shingles, HIV, thyroid disorders, MCAS, pregnancy and perimenopause.
Top 10 Pruritus Causes
Because the sensation of itching, like that of pain, can be influenced by so many factors, there are many possible causes of pruritus. Itchy skin can be caused by a wide variety of conditions, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Common allergens include certain foods, medications, and insect stings or bites. Immune system disorders like MCAS can cause pruritus.
- Dermatitis: Conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema) and contact dermatitis can lead to persistent itching.
- Skin Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can cause itching.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Often exacerbated by environmental factors, dry skin can cause itching.
- Internal Diseases: Liver disease, chronic kidney disease, thyroid problems, and certain cancers can cause systemic itching. Chronic kidney disease that require dialysis treatment, in particular, can cause a condition known as Uremic Pruritus.
- Nervous System Disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, pinched nerves, and postherpetic neuralgia can lead to pruritus. Brachioradial pruritus, for example, is a condition in which irritation of the cervical nerves (C5-C8) causes itching on one or both of the the upper arms.
- Mental Health Issues: Stress, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder can manifest with itching.
- Pregnancy: Some women experience pruritus during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
- Perimenopause: Some women experience pruritus during perimenopause and menopause due to a reduction in estrogen levels.
- Reactions to medications: Many drugs can cause pruritus as a side effect, including antibiotics like penicillin, amoxicillin, erythromycin, blood pressure medications, statins, or cholesterol medications, analgesics like aspirin, and tricyclic antidepressants.
Treatment for Pruritus

Conventional medicine typically treats pruritus by trying to find and address the underlying cause, while using medications to alleviate the symptom of itching. This may include topical treatments like over-the-counter or prescription creams and ointments that contain corticosteroids, menthol, or capsaicin to soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. These creams may help relieve localized itching for a time, but they cannot do much to control widespread, systemic itching.
Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine or cetirizine, may be prescribed to reduce allergic reactions and relieve itching. These can be helpful in some acute cases of pruritus, but again, they do not resolve the problem of chronic itching. Overall, most people with chronic pruritus do not get adequate relief from antihistamine treatment for itching.
For severe itching, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and immune response.
TCM and acupuncture can be an effective alternative or adjunct treatment for itching, as TCM addressed both underlying conditions and the symptoms of itchy skin.
Can Acupuncture Help Pruritus?
TCM methods like acupuncture and moxibustion have been used for over 2000 years to help relieve itchy skin conditions and systemic pruritus. Now, scientific research is beginning to show that Chinese medicine is an effective alternative treatment for itching.
The mechanisms that cause the sensation of itching often stem from the brain and the peripheral nervous system. Acupuncture has been shown to have an effect on the nervous system, and specifically, to help reduce the activation of the itch response in the brain.
Itching responses are also activated by the behavior of mast cells, like cytokines. Acupuncture, particularly electroacupuncture, has been shown to help regulate the activity of cytokines, which can help reduce inflammation and sensation.
Acupuncture is well known, now, to help relieve pain by stimulating receptors in the brain. This same action can help to reduce itchy sensations, as well as pain.
The chemical and mechanical activations that cause itching can lead to a chronic problem referred to as the “itch-scratch vicious cycle,” which occurs because of a neural loop in the spinal cord. Acupuncture can potentially help to disrupt this chronic loop of activations that causes the urge to scratch.

Acupuncture and TCM herbal remedies can also help to clear up skin conditions that are directly causing itching, and can help to address deeper underlying conditions, such as liver and kidney ailments, that can be the secondary cause of systemic itching.
Uremic pruritus, which is associated with dialysis treatment for chronic kidney disease or renal failure, affects many people. This type of pruritus can cause sleep problems and affect patients on a daily basis and is believed to be caused by severe dryness of the skin, along with sweating, and chronic inflammation. It may also be related to opioid receptors and inappropriate nerve signaling that triggers the release of cytokines. A review of studies about acupuncture treatment for chronic kidney disease suggests that TCM is highly effective for reducing itching related to uremic pruritus.
One specific study looked at patients undergoing dialysis who were given acupressure treatment. The conclusion was that acupressure was both helpful for relieving itching and cost effective as a treatment alternative.
Acupuncture treatment has an impact not only on the autonomic nervous system, but also on histamine release, and studies have shown that acupuncture is more effective at controlling histamine-related itching than many antihistamine medications.
One study done with 16 patients suffering from brachioradial pruritus (itching on the upper arm/s) found that the majority experienced total resolution of their itching, while the remaining patients experienced partial relief of itching.
Acupuncture Near Me for Pruritus in West Los Angeles
Acupuncture can be beneficial for itchy skin conditions like hives, dermatitis, and rashes. During pregnancy and perimenopause, acupuncture can help balance hormones to relieve itching and insomnia. Acupuncture can also help relieve anxiety, PTSD and panic disorders that can sometimes exacerbate itching sensations. Liver problems, kidney problems, and side effects of cancer treatment can all be addressed with TCM, which may help relieve persistent pruritus.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat MCAS With Acupuncture and TCM
By Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Shortness of breath, dyspnea? SIBO or fungal infections? Sensitive to smells? Signs of orthostatic low blood pressure? Itchy skin rash or hives? Musculoskeletal pain, joint pain? These can be some of the many different MCAS symptoms. Acupuncture and TCM can offer alternative treatment for MCAS, or mast cell activation disorders.
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) is a complex and often underdiagnosed condition characterized by the inappropriate activation of mast cells, which are immune cells involved in allergic and inflammatory responses throughout the body.
In short, mast cells are what cause people to have an allergic reaction to something. When mast cells encounter an allergen (or sometimes a medication, infection, or insect venom), antibodies inside them surface and send out “mediators.” Mast cells can produce hundreds of different types of mediators. These include histamine, leukotrienes and cytokines.
In MCAS, mast cells release excessive amounts of mediators, leading to a wide range of symptoms affecting various organ systems throughout the body. There are so many different mediators that science is not yet able to pinpoint which mediators may be causing which symptoms, in many cases.
This systemic activation of mast cells can occur spontaneously or in response to triggers such as stress, exercise, medications, infections, or environmental factors.
The symptoms of MCAS can vary widely among individuals and may mimic those of other conditions, making diagnosis challenging. There are five categories of MCAS symptom, affecting different parts or systems of the body:

Skin-related MCAS Symptoms:
Itching (pruritus)
Hives (urticaria)
Flushing or redness of the skin
Rashes or eczema-like lesions
Swelling (angioedema), particularly of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
Gastrointestinal MCAS Symptoms:
Abdominal pain or cramping
Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhea or constipation
Acid reflux or heartburn
Bloating or abdominal distension
Respiratory MCAS Symptoms:
Wheezing or difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
Chest tightness or pain
Coughing or throat clearing
Nasal congestion or runny nose
Sneezing or postnasal drip
Cardiovascular MCAS symptoms:
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
Low blood pressure (hypotension)
Fainting or near-fainting episodes (syncope)
Fluctuations in blood pressure upon standing (orthostatic hypotension)
Raynaud’s phenomenon (abnormal blood vessel spasm in response to cold or stress)
Neurological MCAS symptoms:
Headaches or migraines
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Cognitive dysfunction or brain fog
Anxiety or panic attacks
Fatigue or malaise
These symptoms can vary in severity and may occur intermittently or chronically.
What Causes MCAS?
Medical science is unclear about the underlying cause of MCAS. Mastocytosis is a different mast cell disorder, in which people have an elevated number of mast cells. However, with MCAS, people have a normal number of mast cells; they just behave in an exaggerated manner when triggered.
MCAS is “primary” when there is a particular genetic mutation, which may happen due to mastocytosis or monoclonal mast cell activation syndrome (MMAS,) in which there is a clonal line of mast cells.
In some cases, when a person also has a diagnosed autoimmune disorder, allergy, or infection the MCAS is considered “secondary,” meaning that the overactive mast cell activity may be stemming from that other primary condition.
A diagnosis of “Idiopathic MCAS” indicates that neither of the above factors is present.
MCAS can begin at any point in a person’s life, including during childhood.
MCAS Treatment

Treatment for Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) in Western medicine typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications aimed at stabilizing mast cells and alleviating symptoms.
Antihistamines, such as H1 receptor blockers (e.g., loratadine, cetirizine) and H2 receptor blockers (e.g., famotidine, ranitidine), are commonly prescribed to reduce the effects of histamine released by mast cells.
Mast cell stabilizers, such as cromolyn sodium, can help prevent the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells and may be used as preventive therapy. In cases of severe or refractory symptoms, corticosteroids or leukotriene inhibitors may be prescribed to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Medications to manage specific symptoms, such as gastrointestinal distress or cardiovascular symptoms, may be recommended.
Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding known triggers, managing stress, and following a healthy diet, may also play a crucial role in managing MCAS symptoms.
It’s important for individuals with MCAS to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. Acupuncture and TCM can provide adjunct treatment for MCAS that address each patient’s unique symptoms and needs.
Can Acupuncture Help MCAS?
One of the central concepts of Traditional Chinese Medicine, which dates back many centuries, is that of the meridian system. The 12 meridians are channels of energy, or Qi, that flow throughout the body. Along the meridians are many acupoints: spots where Qi is activated when thin acupuncture needles or acupressure are applied to them.
But do the meridians exist as physical entities, or are they metaphorical?
Scientific research in the twentieth century sought to explain the various phenomena produced by the activation and manipulation of acupoints. It was found that both blood vessels and nerves are located near the acupoints in greater concentration than in other areas of the body. These studies suggested that acupuncture treatment functions through the vascular and nervous systems.
Later, further studies showed that acupuncture has effects on the production and releasing of hormones, such as endorphins, which has a analgesic effect of reducing pain.
The sensations that people feel as a result of acupuncture treatment cannot be fully explained by saying they are related to blood vessels, nerves, or hormones. Further questioning continued, asking if other cells or tissues could also be involved in how acupuncture works.
One female scientist, researcher, and professor in China, Jimei Song, hypothesized that activity around acupoints may be related to mast cell activation. This idea was Song’s Mast Cell Theory of Acupuncture (now called Song’s MC Theory for short, originally published in the Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in 1977.

Studies suggest that when an acupuncture needle penetrates the skin, mast cells are released, which then in turn, affect the blood vessels and nerves, leading to both sensations experienced by the patient in the moments, and systemic effects on the release of histamines, serotonin, and other chemicals than go on to create systemic effects. This is now considered a milestone in TCM research.
Acupuncture has been shown to have a positive effect on histamine response. Specific Chinese herbal formulas have also been shown to be effective in dampening mast cell activation. Compounds found in some herbs can help inhibit the production of cytokines.
An acupuncturist is able to address the problem both at its root, and help take care of the wide variety of symptoms a person may be experiencing. Acupuncture treatment can help relieve problems like itchy skin rash, sensitivities, orthostatic low blood pressure, and joint pain, all in one treatment session. A personalized herb formula can be prescribed to suit each individual patient.
Acupuncture Near Me for MCAS in Los Angeles
MCAS can mimic many other conditions and be difficult to diagnose and treat. This is what makes acupuncture, herbs, and moxibustion excellent modalities for helping to relieve MCAS symptoms such as: dizziness, headaches, musculoskeletal pain, insomnia, anxiety, hives, GERD, SIBO, IBS, interstitial cystitis bladder pressure, and more. Acupuncture and TCM can offer an adjunct or alternative treatment for MCAS symptoms.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.