-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- Acupuncture for Sciatica Pain
- Can Acupuncture Help With Bladder Control?
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

February 2026 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
Neuropathy
How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
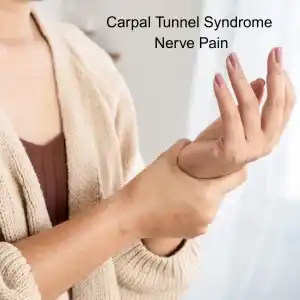
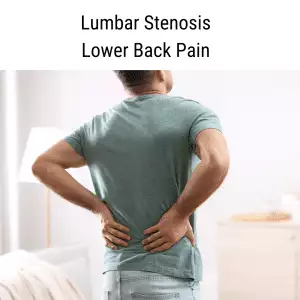
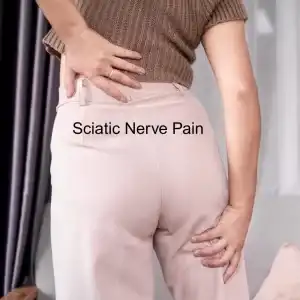
Struggling with sharp, burning, or tingling pain? Do your hands or feet feel numb or hypersensitive? Nerve pain—also called neuropathic pain—can be relieved with acupuncture treatment and other TCM modalities.
Nerve pain occurs when nerves are damaged or dysfunctional, sending incorrect pain signals to the brain. Unlike pain caused by injury or inflammation, nerve pain can persist without an obvious cause and may not respond well to common pain relievers.
Nerve pain can interfere with your ability to work, sleep, or enjoy your day-to-day life. The good news is that acupuncture can be an effective way to treat nerve pain.
What Causes Nerve Pain?
There are many possible underlying conditions that can lead to nerve pain. Here are some of the 10 most most common causes of nerve pain:
- Peripheral neuropathy – often due to diabetes, chemotherapy, or alcohol use
- Trigeminal neuralgia – intense facial pain due to nerve irritation
- Occipital neuralgia – shooting pain at the back of the head and neck
- Cervical radiculopathy – pinched nerves in the neck causing radiating pain
- Carpal tunnel syndrome – pressure on the median nerve in the wrist
- Spinal stenosis or Lumbar stenosis – narrowing of the spinal canal that compresses nerves
- Sciatica– pain radiating down the leg due to sciatic nerve irritation
- Postherpetic neuralgia – lingering nerve pain after shingles
- Dystonia and other movement disorders – can involve nerve dysfunction
- Multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases – affecting nerve conduction
Medical Treatment for Nerve Pain
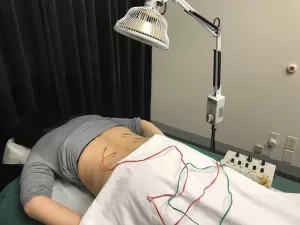
In Western medicine, the diagnostic process for nerve pain typically begins with a detailed health history and physical examination, focusing on neurological function. Physicians may conduct reflex tests, strength assessments, and evaluate your sensory response. Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans can help identify structural causes like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) may be used to assess how well the nerves and muscles are functioning.
Once nerve pain is diagnosed, treatment often involves medications aimed at disrupting the abnormal pain signals. Doctors may prescribe anticonvulsant drugs like gabapentin or pregabalin, which were originally developed to treat epilepsy but are now commonly used to relieve nerve pain.
Certain antidepressants, such as amitriptyline or duloxetine, are also frequently used—not for their mood-enhancing effects, but because they influence how the nervous system processes pain. In some cases, opioids may be prescribed, though they are generally considered a last resort due to the risk of dependence and side effects.
Topical treatments like lidocaine patches or capsaicin cream may offer localized relief for some people. Corticosteroid injections may be recommended if inflammation is contributing to nerve compression, such as in cases of radiculopathy or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Physical therapy can be useful for improving strength, mobility, and nerve function, especially when musculoskeletal imbalances are part of the problem. In more severe cases—such as when a nerve is severely compressed or damaged—surgical intervention may be considered.
While these treatments can sometimes provide temporary relief, they may not address the root cause of nerve dysfunction. Additionally, many patients find that medications come with undesirable side effects or offer only partial relief. That’s why more and more people are turning to acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) as a complementary or alternative solution for managing nerve pain holistically.
Can Acupuncture Help Nerve Pain?
In the Western medical model, nerve pain—also called neuropathic pain—is typically understood as the result of damage or dysfunction within the nervous system. This could be due to injury, chronic conditions like diabetes, infections such as shingles, or musculoskeletal issues like spinal stenosis or herniated discs.
TCM, on the other hand, views nerve pain through a holistic lens, focusing on the flow of energy—known as Qi—through the body’s channels or meridians. In this system, pain is often caused by Qi and blood stagnation, which leads to blockages along these pathways. This stagnation can arise from a deficiency in the liver or kidney systems, which in TCM are believed to support and nourish the body’s nerves.
External influences like wind, cold, or dampness may also disrupt the body’s internal balance, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or sharp, radiating pain. Instead of targeting only the site of discomfort, TCM aims to correct underlying imbalances and restore smooth, harmonious flow throughout the body.
Treatment for nerve pain in TCM often involves acupuncture to stimulate specific points that promote circulation and healing. Herbal medicine is frequently used in combination, with formulas designed to nourish blood, strengthen the liver and kidneys, and dispel pathogenic factors. Other traditional therapies, such as moxibustion (a warming technique using mugwort) or cupping, may be applied to enhance circulation and relieve tension. TCM practitioners also offer guidance on diet, lifestyle, and emotional health to support the body’s natural healing processes and prevent further pain episodes.
A 2023 meta-analysis of 16 studies involving over 1,000 patients with neuropathic pain found that acupuncture significantly reduced pain intensity compared to sham or no treatment.
Acupuncture can modulate receptors and ion channels in peripheral nerves, reducing spontaneous nerve activity that leads to pain.
Studies have shown that acupuncture stimulates the release of neurotrophic factors like nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which support nerve regeneration and repair.
Acupuncture Near Me for Nerve Pain in West Los Angeles
If you’re struggling with nerve pain and looking for a natural, holistic approach to healing, acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine may offer the relief you’ve been hoping for. At Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West Los Angeles, we specialize in helping patients manage complex, chronic pain conditions by addressing the root causes—not just the symptoms. Whether your nerve pain stems from an injury, a chronic condition, or something undiagnosed, we’ll work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that supports your body’s natural healing processes. Don’t let nerve pain control your life—reach out today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward lasting relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Wrist Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac. Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Wrist pain when you bend it? Is it hard to open jars or doors? Popping sound in wrist? Pain at the base of the thumb? Wrist or fingers swollen? Wrist pain can be caused by a variety of joint issues, including tendinitis of wrist, or De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Acupuncture and TCM can help treat the root cause of wrist pain.
The wrist is a complex joint composed of several small bones, tendons, ligaments, muscles, and nerves. In medical terminology, the thumb side of the wrist is the radial wrist (wrist pain on thumb side, radial thumb pain, or inner wrist pain), while the little finger side is the ulnar wrist (wrist pain on pinky side, ulnar wrist pain, or outer wrist pain).
Injuries, such as a wrist fracture, are a particularly common cause of acute wrist pain, as people will often try to catch themselves with an outstretched hand when falling, which can easily lead to wrist injury. Wrist fractures can result in wrist pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to move the wrist normally.
Fractures may also damage nearby ligaments, nerves, and tendons, which can complicate healing and prolong discomfort. Proper alignment and stabilization are essential for healing, and if not treated correctly, a fracture can lead to chronic pain and arthritis in the wrist.
Acupuncture treatment can certainly be helpful for reducing inflammation, relieving acute pain, and helping to speed the healing of a wrist fracture.
Other, more chronic conditions can also cause wrist pain.
Top 5 Causes of Wrist Pain

Certain chronic health conditions that build up slowly over time can ultimately lead to wrist pain and dysfunction. Some of these include:
- Arthritis of the Wrist – Osteoarthritis of the wrist and rheumatoid arthritis can both be causes of wrist pain. Osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear on the cartilage of the wrist joint. This condition usually develops slowly over time, especially in individuals who have experienced previous injuries or repetitive stress on the wrist. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the wrist joints, leading to pain, warmth, and eventual joint damage. Both types of arthritis can severely limit the range of motion and strength in the wrist, making even simple activities painful.
- Repetitive Stress Injury (RSI) – Repetitive stress injuries in the wrist are caused by continuous or repetitive movements, such as typing, gripping, or lifting, which can strain the tendons and ligaments in the wrist. Over time, this repetitive strain can lead to inflammation, pain, and decreased mobility. Carpal tunnel syndrome and tendonitis (discussed further below) are common forms of repetitive strain injury that cause wrist pain. RSI often requires rest and modification of activities to allow the wrist to heal, as continuous stress can worsen the condition and lead to long-term issues.
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis – De Quervain’s tenosynovitis (also known as Quervain disease or styloid tenosynovitis) affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed, leading to pain and tenderness, particularly during movements that involve gripping or pinching. This condition is often the result of repetitive thumb movements, such as those used in typing or texting. De Quervain’s disease tenosynovitis can cause sharp pain on the radial (thumb) side of the wrist, and people may find it difficult to grasp or hold objects.
- Tendonitis (or Tendinitis) of the Wrist – Tendonitis of the wrist refers to inflammation of the tendons that cross the wrist joint. It is commonly caused by repetitive motion, excessive strain, or sudden injury. Tendonitis can affect various tendons depending on the type of movement that led to the condition. Pain and swelling are typical symptoms, and the affected area may feel warm to the touch. Wrist tendonitis is often seen in athletes and individuals who perform repetitive tasks with their hands and can result in decreased wrist function and grip strength.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – Carpal tunnel syndrome is a type of neuropathy, or nerve pain, caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. This compression leads to pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is often associated with repetitive wrist movements and can be exacerbated by activities that involve gripping or bending the wrist. If left untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to permanent nerve damage and reduced hand function.
Other possible causes of wrist pain could include: bursitis (small, fluid-filled sacs that form between bones), ganglion cysts (fluid-filled cysts that form near joints), or Kienbock’s disease (in which the lunate bone of the wrist begins to break down).
Treatment for Wrist Pain
When a patient presents with wrist pain, diagnosis usually begins with a physical examination to identify the specific cause of pain. The doctor will assess the patient’s range of motion, grip strength, and any areas of tenderness or swelling in the wrist. Imaging via X-rays, MRI or ultrasound may be used to confirm a diagnosis, especially if a fracture, ligament tear, or nerve compression is suspected.
For nerve-related issues like carpal tunnel syndrome, a nerve conduction study (NCS) or electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to assess the functionality of the median nerve. This can help differentiate between arthritis, repetitive strain injuries, or specific tendon and nerve issues.
Conventional treatments for wrist pain depend on the specific diagnosis. In cases of arthritis, anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, or physical therapy are commonly recommended to manage pain and improve joint mobility.
For fractures, immobilization with a cast or splint is typically required, and surgery may be necessary for more severe breaks. Repetitive stress injuries like tendonitis or De Quervain’s tenosynovitis often respond to rest, ergonomic modifications, and anti-inflammatory treatments.
Physical therapy exercises to strengthen and stretch the affected muscles and tendons can be helpful. In cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, wrist splints are often used to keep the wrist in a neutral position, particularly at night, and corticosteroid injections may be administered, aimed to reduce inflammation.
If these methods do not relieve symptoms, surgical intervention, such as carpal tunnel release, might be recommended to decompress the median nerve.
While typical treatment usually involves pain medication, rest, and possibly physical therapy, acupuncture treatment can be an excellent adjunct or alternative treatment to relieve wrist pain.
Can Acupuncture Help Wrist Pain?

Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) can offer natural pain relief for injuries and chronic pain conditions, by reducing pain and inflammation, improving circulation, and supporting the body’s healing process.
According to TCM theory, the health of the internal organ systems is related to the rest of the body parts. For example, the spleen is responsible for transforming Qi and blood. If the spleen is weak, it can cause blockages in blood flow that create stasis, stiffness and pain in the limbs and joints. The liver governs the tendons of the body. When the liver is not functioning well, often due to emotional stress, than there may be pain and dysfunction in the tendons and joints.
Therefore, an acupuncturist does not only treat the painful area, but also looks at the deeper root cause and addresses them with acupuncture treatment, Chinese herbs, and other therapeutic modalities, to help relieve pain and inflammation and bring about healing.
A systematic review of trials showed that acupuncture treatment led to significant pain reduction for patients treated for rheumatoid arthritis affecting the wrist. It also concluded that acupuncture brought about pain relief and functional improvement for patients with tenosynovitis and carpal tunnel syndrome.
One study separated patients with carpal tunnel syndrome into two groups: one group received pain medication for wrist pain and the other group had 12 acupuncture treatments. Comparatively, the acupuncture group had greater reduction in pain, tingling, and numbness and greater functional improvement.
Studies of MRI results after acupuncture have suggested that acupuncture for carpal tunnel syndrome actually has a positive impact on nerve function in the wrist and changes the way the brain and nerves are signaling pain.
A trial involving patients treated for De Quervain’s disease tenosynovitis with five acupuncture sessions over the course of two weeks showed improvement in pain and grip strength, and the results were still maintained at a ten week follow up visit.
The combination of acupuncture and moxibustion can be particularly helpful for treating Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
Overall, the evidence shows that acupuncture and other TCM modalities can be a relatively low cost, non-invasive way of helping to treat wrist pain, without surgery or the unwanted side effects of pain medications or steroid injections.
Acupuncture Near Me for Wrist Pain in Los Angeles
Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in West L.A. have over 35 years of experience helping people recover from sports injuries, repetitive stress injuries, and orthopedic pain conditions of all kinds. Acupuncture treatment for wrist pain can be used in addition to your medical protocol to help speed recovery and bring about pain relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Raynaud’s Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac. Ph.D.

Fingers numb? Numbness in fingers and toes? Fingers turning white, poor circulation in fingers, cold fingers and toes? Raynaud’s disease, or Raynaud’s phenomenon, causes poor circulation in the extremities due to constriction of the blood vessels, usually triggered by cold weather or stress. Acupuncture can help relieve Raynaud’s disease symptoms.
Raynaud’s disease is a condition characterized by occasional narrowing of the blood vessels, primarily in the fingers and toes. The small arteries that supply blood to the skin of the fingers and toes (and sometimes, to the ears and the tip of the nose) become constricted in cold conditions.
Raynaud’s syndrome causes the tips of the fingers and/or toes to turn white due to the lack of circulation, and there may be numbness in fingers or tingling in toes. A “Raynaud’s attack” or episode lasts until the person warms up, at which point, there may be a burning sensation, and the affected skin may flush and turn red as blood flow returns.
Raynaud’s can occur in two forms: primary and secondary.
Primary Raynaud’s, also called Raynaud’s disease, is the more common form and isn’t usually related to another medical condition. Raynaud’s is considered to be an exaggerated response to cold, emotional stress or anxiety, leading to spasms in the small arteries.
People with primary Raynaud’s phenomenon usually begin to experience symptomatic episodes during their teenage years. Women are more likely to have Raynaud’s.
Secondary Raynaud’s is less common but more serious. It is associated with other diseases, typically autoimmune diseases or connective tissue disorders, like scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders, or lupus.
Secondary Raynaud’s can be linked to conditions that directly damage the arteries or affect blood flow, like carpal tunnel syndrome. In these cases, it is considered a symptom rather than a separate condition.
Raynaud’s Syndrome Causes

For most people with Raynaud’s syndrome, there is probably a combination of genetic, physiological, and environmental factors at play.
Vascular abnormalities, or dysfunction in the blood vessels, involving excessive narrowing (vasospasm) and poor dilation in response to stimuli, may be involved.
Overactivity of the nerves controlling the blood vessels (sympathetic nervous system) may cause spasms.
Raynaud’s can tend to run in some families. If someone is already susceptible, then the numbness in fingers and toes may be triggered by cold temperatures, or a stressful situation. Smoking cigarettes can also cause Raynaud’s symptoms.
In secondary Raynaud’s, underlying autoimmune conditions can lead to inflammation and damage to blood vessels.
An injury to one of the limbs, like a broken wrist, or damage to the tissues from frostbite, could also trigger Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Some prescription medications, such as beta blockers, ADHD medications, medications for migraine headaches, and even some cold and flu medicines, could cause Raynaud’s symptoms.
Acupuncture treatment can help to relieve Raynaud’s syndrome symptoms and also address the underlying condition that may cause Raynaud’s.
Top 10 Raynaud’s Disease Symptoms
Raynaud’s symptoms may show up differently for each person. Symptoms of Raynaud’s disease can vary in severity and may include:
- Skin changes color: pallor (pale skin, white skin, or yellow skin) in the affected fingers or toes during an episode
- In rare cases, Raynaud’s phenomenon can affect other areas, such as the nose, ears, and lips.
- Some people may experience Raynaud’s in their nipples, which can cause a severe throbbing pain.
- Bluish discoloration (Cyanosis) as blood flow decreases
- Affected areas feel cold and/or numb during an episode
- Throbbing or tingling in the fingers or in the toes
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures, leading to more frequent episodes in cold weather.
- In severe cases, recurrent or persistent episodes of reduced blood flow can lead to skin sores or ulcers, particularly on the fingertips or toes.
- Changes in the texture and color of the nails, including nail beds that turn white and then blue during an episode.
- Some individuals may experience joint pain, particularly if there is an underlying connective tissue disorder.
Emotional stress, anxiety, or rapid changes in temperature can trigger Raynaud’s symptoms.
Raynaud’s disease is generally considered a benign condition, but repeated episodes can lead to more serious problems, like skin sores, chilblains, or even gangrene, which can cause permanent damage to tissues.
Raynaud’s Syndrome Treatment

Diagnosis of Raynaud’s disease may involve a test called nailfold capillaroscopy. This is a non-invasive test that allows the doctor to see the capillary size and action in the tips of the fingers and nail bed. This can help to determine whether the person has Primary Raynaud’s, or may have a connective tissue disorder, like lupus or Sjogren’s syndrome.
The standard medical treatment for Raynaud’s phenomenon aims to manage symptoms, improve blood flow, and prevent complications. While there is no cure for Raynaud’s, various medications and lifestyle modifications can be employed to alleviate symptoms and enhance circulation.
Medications that relax and widen blood vessels, known as vasodilators, are commonly prescribed. Calcium channel blockers, such as nifedipine, are often used to help dilate the small blood vessels in the extremities, reducing the frequency and severity of Raynaud’s episodes.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors like sildenafil (which is also commonly prescribed to help erectile dysfunction, ED) can sometimes be beneficial in promoting blood vessel dilation and improving blood flow.
In some cases, topical nitroglycerin cream may be prescribed to increase blood flow to the affected areas.
Endothelin receptor antagonists, such as bosentan, may be considered in cases where blood vessel constriction is severe. These medications target endothelin, a substance that can cause blood vessels to narrow.
Antiplatelet agents like aspirin may be recommended to reduce the risk of blood clots and improve blood circulation.
If Raynaud’s is secondary to another condition, treating the underlying cause is crucial. For example, if it is associated with an autoimmune disorder, immunosuppressants might be considered.
Lifestyle changes play a significant role in managing Raynaud’s symptoms. Patients are typically advised to dress warmly.
Quitting smoking is strongly recommended, as smoking constricts blood vessels.
Can Acupuncture Help Raynaud’s Syndrome?
TCM has acknowledged Raynaud’s phenomenon as a condition of severe cold in the limbs for centuries. According to TCM theory, a deficiency of Qi and blood circulation is the root cause of Raynaud’s symptoms. In TCM, we consider that Qi (life force energy) and blood work together; Qi moves the blood throughout the body, and blood carries the Qi throughout the body.
In TCM, we are always looking at both external factors and internal factors that contribute to a condition. In the case of Raynaud’s disease, cold acts as a pathogenic factor that can be already present inside the body, and then, when a person is exposed to cold temperatures as an external factor, this triggers an extreme reaction.
So, in many cases, a person suffering from Raynaud’s is already dealing with too much cold and poor blood circulation. Herbs can be used to help warm the body internally and increase blood flow.
Some people develop Raynaud’s symptoms in response to stress. In this case, the liver may be involved. In TCM, the liver is associated with strong emotions, and when the liver is distressed, it can trigger muscular contractions that squeeze the blood vessels, restricting blood flow. In these cases, we will use herbal formulas and acupuncture points to help restore balance in the liver.
When there is an autoimmune disease also present, such as scleroderma or lupus, then there may also be blood stasis, and a thickening of the blood and tissues. TCM can address those conditions at their roots, as well.
An acupuncturist will make careful observations about how each individual is experiencing Raynaud’s symptoms, and address it according to the pattern presenting.
Top 3 Tips for Managing Raynaud’s Syndrome Symptoms

You can help prevent Raynaud’s attacks by keeping your whole body warm, especially your hands and feet.
- Protect your hands and feet. Wear mittens or gloves, thick socks and lined boots, and use hand and foot warmers in cold weather. Consider wearing gloves or oven mitts when reaching into the refrigerator or freezer.
- Exercise regularly, both to stimulate healthy blood circulation, and to help manage stress levels.
- If hands and/or feet do begin to feel cold or numb, take action to warm them up immediately by wiggling them, running them under warm water, massaging them, or putting your hands in your armpits or against your abdomen under your clothing.
Acupuncture Near Me for Raynaud’s Syndrome in West Los Angeles
It is important to address Raynaud’s disease to avoid damage to the nerves and skin tissue in your extremities, and to be sure whether or not Raynaud’s symptoms are related to an underlying autoimmune disorder. The acupuncturists at Art of Wellness Acupuncture in West L.A. have over 35 years of experience helping people with autoimmune conditions, circulatory problems, and nerve pain and tingling. The combination of herbs and acupuncture treatment can help relieve Raynaud’s phenomenon symptoms and address any autoimmune disease or nerve conditions.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.