-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Watery Eyes With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Ovarian Cysts With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

December 2025 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Moxibustion
How to Treat Dystonia With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Writer’s cramp? Foot cramps and spasms in your calf muscles? Cramps that cause your toes to curl up or big toe to stick up? These are signs of dystonia, a disorder that causes muscles to contract, causing painful spasms and uncontrollable twisting of body parts. Acupuncture can help relieve symptoms of dystonia and reduce cramping.
Dystonia is a movement disorder that can affect one part of the body, such as the hand, or several parts of the body, causing painful cramping and involuntary muscle contractions.
Dystonia most often affects the hands, feet, and neck (cervical dystonia or neck dystonia). When the cramping only happens in one area, this is known as focal dystonia, i.e. focal dystonia hand, or focal hand dystonia.
Acupuncture can help relieve symptoms of dystonia without injections or surgery.
Top 5 Kinds of Dystonia
Dystonia muscle cramping and spasming can happen in various parts of the body, including:
- Neck (Cervical Dystonia) – spasm pulls the head to one side forward or backward.
- Hand – usually triggered by a certain activity, like writing, playing an instrument, or playing golf.
- Jaw – (Oromandibular Dystonia) – causes trouble with chewing, swallowing or drooling, can happen concurrently with cervical dystonia.
- Eyelids (Blepharospasm) – spasms cause the eyelids to close, can also feel like dry eyes, sensitivity to light. Can be triggered by light, screens, and stress.
- Vocal Cords (Laryngeal Dystonia) – strained voice, only able to speak in a whisper.
For some people, dystonia does not cause pain, while for others, it can become increasingly painful. In some cases, dystonia may plateau; in others, it gets progressively more severe.
Over time, some types of dystonia can lead to the deterioration of joints and arthritis.
What Causes Dystonia?

Medical science is not entirely clear on the specific causes of dystonia. There may be some genetic predisposition for dystonia. Some types of dystonia show up without any seeming correlation to other issues (primary dystonia). Other kinds of dystonia manifest as symptoms of another disorder affecting the nervous system.
Muscle spasms can be a symptom of several different disorders, including:
- Huntington’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Stroke
- Brain injury or brain tumor
- Encephalitis
- Tuberculosis
- Carbon monoxide poisoning or heavy metal poisoning
Some types of dystonia can be brought on by a specific physical activity. Mental, emotional, and physical stress can also trigger an episode of dystonia cramping.
Some studies have suggested that there is a problem with motor programming, or a deficiency in the motor cortical network of the nervous system.
Treatment for Dystonia
The most common form of treatment for focal dystonia, such as the kind that causes “writer’s cramp,” is botulinum neurotoxin (BNT or Botox) injections. This is a localized treatment that helps relieve symptoms by blocking the release of chemicals involved in muscular contractions.
Patients feel their muscles relax within a few days or a week. The results of this treatment typically only last for a few months, and then another injection is needed.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical method used to treat dystonia. This involves the implantation of a stimulator that is somewhat like a pacemaker; it is controlled remotely and stimulates parts of the brain that affect muscular contractions.
Acupuncture can be a good alternative treatment modality for reducing the muscle spasms associated with dystonia.
Can Acupuncture Help Dystonia?

TCM theory views most health issues as being related to internal or external pathogenic forces causing imbalance within the organ systems. Organ systems in TCM are interrelated in ways that may seem counterintuitive from the “Western medicine” point of view. For example, in TCM, the actions of the muscles and tendons are related to the liver system.
Pathogenic forces like wind, damp, and heat can arise or attack the organ systems and cause problems. In the case of dystonia, excess wind in the liver affects the tendons and muscles, causing them to be overactivated.
In some cases, dystonia is triggered by emotional stress. If a patient is experiencing anxiety or depression, then that is also a factor that needs to be addressed.
Thus, the acupuncturist will create a treatment protocol designed to use different TCM modalities to address the root cause of the problem and the symptoms. Acupuncture to treat dystonia will address the liver wind and also be used to help relax the muscles. Treatment can also focus on relieving stress and balancing the person’s emotional state.
Acupuncture treatment is often used to help stimulate muscle tone. In cases of dystonia, we will use acupoints on the meridians related to the affected muscles as a way of both suppressing muscle tone and activating it. Some of the muscles related to the area that is cramping up might be hypertonic (tight and rigid), while others might be hypotonic (not active or offering resistance).
One study that looked at acupuncture treatment for cervical dystonia used electromyogram to measure muscle activity, and it showed that shallow placement of acupuncture needles decreased excess activity in the muscles.
Another study looked at patients who had been receiving Botox treatment for their cervical dystonia. They then received a series of 6 sessions of acupuncture treatment. All of the patients reported improvement and two-thirds of the patients intended to continue acupuncture treatments for management of their condition.
Gua sha and other forms of Chinese massage can also be used to help with dystonia.
Moxibustion or moxa, which is a warming herb that is burned near the affected area, can also be helpful to relieve cramping.
Acupuncture Near Me for Dystonia
Dystonia can be a serious disruption to your daily life and activities, making you feel out of control in your body. In some cases, dystonia causes serious pain. If you have been experiencing severe muscle cramping in specific areas, please do not hesitate to reach out to us at Art of Wellness for help. Drs. Tan and Cai have over 35 years of experience helping to treat conditions of all kinds that affect the nervous system and cause musculoskeletal problems.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Sarcoidosis With Acupuncture and TCM
by Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Fever, fatigue, and muscle aches? Swollen lymph nodes, coughing, shortness of breath? Eye pain, or red eyes? These can all be signs of sarcoidosis, an autoimmune disorder. Acupuncture and TCM can help relieve sarcoidosis symptoms.
Sarcoidosis is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by the formation of granulomas—clumps of inflammatory cells—that can affect multiple organs in the body. It most commonly impacts the lungs and lymph nodes, but it can also involve the skin, eyes, heart, musculoskeletal system, and nervous system.
Sarcoidosis typically manifests in young adults, with the highest prevalence observed in individuals in their 20s and 30s, though it can affect people of any age. This condition’s exact cause remains unknown, but researchers believe it results from an overactive immune response to environmental or infectious triggers.
Sarcoidosis can cause serious and even life-threatening complications, especially when it is centered in the lungs. However, the good news is that many cases of sarcoidosis do eventually clear up or go into remission.
Acupuncture, herbs, and other TCM treatments for sarcoidosis can help address underlying issues that contribute to the formation of this autoimmune disorder, as well has help to relieve symptoms. TCM can also help with potential signs of dysautonomia (autonomic nervous system disorders) that can be caused by sarcoidosis.
Types of Sarcoidosis
There are different types of sarcoidosis depending on which organs are affected.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis, which targets the lungs, is the most common form and can lead to chronic respiratory issues.
Musculoskeletal sarcoidosis may cause joint inflammation (arthritis), muscle pain, or bone lesions, sometimes resulting in long-term complications such as osteoporosis.
Sarcoidosis can lead to vascular complications that involve inflammation of small, medium, or large blood vessels. These types of sarcoid-related vasculitis are rare but important to recognize, as they may present with overlapping features of other autoimmune or vascular conditions.
Small-vessel vasculitis in sarcoidosis primarily affects the skin. This type of vasculitis might coexist with sarcoidosis and manifests as petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin), purpuric spots (purple “blood spots” under the skin, due to broken blood vessels), or infiltrative erythema (raised rash, like welts on skin).
Medium-vessel sarcoid vasculitis often involves pulmonary lymphatic capillaries and may present with systemic symptoms, including fever, arthritis, and cutaneous manifestations (skin rash or lesions).
Sarcoidosis symptoms can vary widely but may include persistent fatigue, fever, shortness of breath, coughing, swollen lymph nodes, and joint pain. Because of its wide range of manifestations, sarcoidosis can be difficult to diagnose and often requires imaging tests, biopsies, and bloodwork.
New Diagnostic Methods for Sarcoidosis

Diagnosing sarcoidosis remains a complex challenge for clinicians because there is no single definitive test for the disease. The diagnosis is often made by combining a thorough clinical evaluation, imaging studies, laboratory tests, and biopsy results. However, emerging research has identified new biomarkers that may help streamline the diagnostic process.
One promising development involves the discovery of type 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1) as a potential biomarker for sarcoidosis. A study led by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania compared skin samples from sarcoidosis patients to those with granulomas caused by other conditions. They found that levels of ILC1 were significantly higher in sarcoidosis-affected tissues. This trend was also observed in lung granulomas and even in the bloodstream, where sarcoidosis patients showed a 12-fold increase in circulating ILC1 levels compared to healthy individuals.
Sarcoidosis Treatment
The main goals of treatment for sarcoidosis are managing symptoms, reducing the risk of organ damage, and improving the patient’s quality of life. In some cases, sarcoidosis may go into remission, meaning that the condition is no longer causing complications.
Patients with mild or no symptoms might not require treatment, just monitoring. When treatment is necessary, Western medicine focuses on reducing inflammation and suppressing the overactive immune system. These treatments can be highly effective but often come with potential risks and side effects.
Prednisone is usually the first-line treatment for sarcoidosis. This steroid medication suppresses the immune system and reduces inflammation, which can help to improve symptoms and prevent organ damage. However, long-term use of prednisone may lead to significant side effects, such as weight gain, bone loss, high blood sugar, and an increased risk of infection. For this reason, corticosteroid doses are typically tapered once symptoms improve, or alternative medications may be introduced to minimize steroid use.
Methotrexate, a drug commonly used for severe rheumatoid arthritis, is another option for managing sarcoidosis. It is particularly effective in patients with significant organ involvement, such as lung, skin, or joint manifestations. Methotrexate helps to suppress the immune system and can be used in combination with corticosteroids to reduce the need for higher steroid doses.
Drugs such as hydroxychloroquine, which are typically used to treat malaria, can be effective for sarcoidosis that primarily affects the skin or joints. These medications may also be helpful for managing chronic fatigue and muscle pain associated with the condition.
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, like infliximab or adalimumab, are biologic medications that help reduce inflammation. These drugs are often used in patients with severe sarcoidosis, particularly when other treatments have not been effective. TNF inhibitors can be administered intravenously or as an injection under the skin.
Corticotropin is a medication that stimulates the adrenal glands to produce natural steroid hormones. It can be injected under the skin to help manage inflammation and reduce immune system activity, offering an alternative to synthetic corticosteroids.
Acupuncture and other TCM treatments can be helpful for clearing inflammation and relieving symptoms related to sarcoidosis, as well as helping to manage the side effects that may be caused by other medications.
Can Acupuncture Help Sarcoidosis?
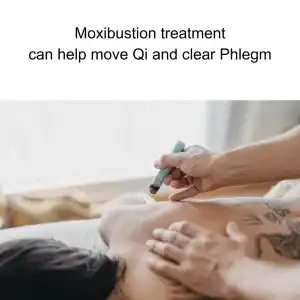
In TCM, sarcoidosis is viewed as a condition arising from underlying imbalances in the body. These imbalances are often associated with heat, phlegm, and stagnation of Qi and blood. Granulomas, for example, may be interpreted as accumulations of dampness and phlegm obstructing the free flow of Qi and blood. Furthermore, the systemic inflammation seen in sarcoidosis can be attributed to excessive heat in the body. TCM practitioners focus on identifying the root causes of these imbalances and tailoring treatments to the individual’s unique presentation.
Acupuncture treatments for sarcoidosis aim to reduce inflammation, support the immune system, and restore balance within the body. By stimulating specific acupuncture points, practitioners can promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood, reduce stagnation, and clear heat and dampness. This can help alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and joint pain, which are commonly experienced by those with sarcoidosis.
Research has shown that acupuncture can help modulate the immune system, reduce stress, and improve quality of life for people with chronic inflammatory conditions. For sarcoidosis patients, regular acupuncture sessions may not only provide symptom relief but also address the underlying imbalances contributing to the disease.
Chinese Medicine diagnosis is different from Western medicine diagnosis. An acupuncture practitioner will look carefully at each individual patient’s specific symptoms, medical history, and foundational constitution to discover the underlying causes of their particular presentation of disease.
In the case of sarcoidosis, possible TCM diagnoses might be:
- Lung Qi Deficiency – presents with symptoms like shortness of breath, weak lung sounds, throat rattling, spontaneous sweating, feeling cold, pale complexion, weak voice. Treatment will seek to tonify Lung Qi to strengthen respiratory function possibly with the inclusion of moxibustion treatment.
- Lung Yin Deficiency – symptoms: breathlessness, night sweats, 5-center heat (warmth in palms, soles, and chest), dry throat, non-productive cough, malar flush, red skin lesions. Treatment goals include nourishing Lung Yin and clearing heat.
- Lung Qi Stagnation – symptoms: chest congestion/blockage, difficulty breathing, emotional grief or melancholy, trouble letting go of the past, and constipation. Treatment will help improve circulation of Lung Qi to relieve stagnation and promote emotional well-being.
- Phlegm in the Lungs- symptoms: Chronic phlegm retention contributing to fibrous tissue and scarring, which can parallel conditions such as chronic bronchitis. There may also be phlegm-related symptoms like congestion or rattling breath. Treatment will seek to nourish Lung Qi, transform phlegm, and circulate Qi to reduce stagnation.
These differential diagnoses reflect the diverse ways in which TCM approaches pulmonary dysfunctions and can be used to tailor treatments for individuals with sarcoidosis, ensuring that the root causes and symptoms are addressed holistically.
Acupuncture for Sarcoidosis Near Me in West Los Angeles
If you or someone you know is suffering with sarcoidosis, or perhaps has some of the symptoms mentioned above, but has not been able to get adequate diagnosis or treatment for their condition, it may be appropriate to seek care from a qualified TCM doctor. Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in Los Angeles, just east of Santa Monica, have over 35 years of experience helping people with all types of autoimmune disorders, skin conditions, respiratory problems, and musculoskeletal pain. We can help you find relief and better health.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Wrist Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac. Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Wrist pain when you bend it? Is it hard to open jars or doors? Popping sound in wrist? Pain at the base of the thumb? Wrist or fingers swollen? Wrist pain can be caused by a variety of joint issues, including tendinitis of wrist, or De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Acupuncture and TCM can help treat the root cause of wrist pain.
The wrist is a complex joint composed of several small bones, tendons, ligaments, muscles, and nerves. In medical terminology, the thumb side of the wrist is the radial wrist (wrist pain on thumb side, radial thumb pain, or inner wrist pain), while the little finger side is the ulnar wrist (wrist pain on pinky side, ulnar wrist pain, or outer wrist pain).
Injuries, such as a wrist fracture, are a particularly common cause of acute wrist pain, as people will often try to catch themselves with an outstretched hand when falling, which can easily lead to wrist injury. Wrist fractures can result in wrist pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to move the wrist normally.
Fractures may also damage nearby ligaments, nerves, and tendons, which can complicate healing and prolong discomfort. Proper alignment and stabilization are essential for healing, and if not treated correctly, a fracture can lead to chronic pain and arthritis in the wrist.
Acupuncture treatment can certainly be helpful for reducing inflammation, relieving acute pain, and helping to speed the healing of a wrist fracture.
Other, more chronic conditions can also cause wrist pain.
Top 5 Causes of Wrist Pain

Certain chronic health conditions that build up slowly over time can ultimately lead to wrist pain and dysfunction. Some of these include:
- Arthritis of the Wrist – Osteoarthritis of the wrist and rheumatoid arthritis can both be causes of wrist pain. Osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear on the cartilage of the wrist joint. This condition usually develops slowly over time, especially in individuals who have experienced previous injuries or repetitive stress on the wrist. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the wrist joints, leading to pain, warmth, and eventual joint damage. Both types of arthritis can severely limit the range of motion and strength in the wrist, making even simple activities painful.
- Repetitive Stress Injury (RSI) – Repetitive stress injuries in the wrist are caused by continuous or repetitive movements, such as typing, gripping, or lifting, which can strain the tendons and ligaments in the wrist. Over time, this repetitive strain can lead to inflammation, pain, and decreased mobility. Carpal tunnel syndrome and tendonitis (discussed further below) are common forms of repetitive strain injury that cause wrist pain. RSI often requires rest and modification of activities to allow the wrist to heal, as continuous stress can worsen the condition and lead to long-term issues.
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis – De Quervain’s tenosynovitis (also known as Quervain disease or styloid tenosynovitis) affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed, leading to pain and tenderness, particularly during movements that involve gripping or pinching. This condition is often the result of repetitive thumb movements, such as those used in typing or texting. De Quervain’s disease tenosynovitis can cause sharp pain on the radial (thumb) side of the wrist, and people may find it difficult to grasp or hold objects.
- Tendonitis (or Tendinitis) of the Wrist – Tendonitis of the wrist refers to inflammation of the tendons that cross the wrist joint. It is commonly caused by repetitive motion, excessive strain, or sudden injury. Tendonitis can affect various tendons depending on the type of movement that led to the condition. Pain and swelling are typical symptoms, and the affected area may feel warm to the touch. Wrist tendonitis is often seen in athletes and individuals who perform repetitive tasks with their hands and can result in decreased wrist function and grip strength.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – Carpal tunnel syndrome is a type of neuropathy, or nerve pain, caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. This compression leads to pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is often associated with repetitive wrist movements and can be exacerbated by activities that involve gripping or bending the wrist. If left untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to permanent nerve damage and reduced hand function.
Other possible causes of wrist pain could include: bursitis (small, fluid-filled sacs that form between bones), ganglion cysts (fluid-filled cysts that form near joints), or Kienbock’s disease (in which the lunate bone of the wrist begins to break down).
Treatment for Wrist Pain
When a patient presents with wrist pain, diagnosis usually begins with a physical examination to identify the specific cause of pain. The doctor will assess the patient’s range of motion, grip strength, and any areas of tenderness or swelling in the wrist. Imaging via X-rays, MRI or ultrasound may be used to confirm a diagnosis, especially if a fracture, ligament tear, or nerve compression is suspected.
For nerve-related issues like carpal tunnel syndrome, a nerve conduction study (NCS) or electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to assess the functionality of the median nerve. This can help differentiate between arthritis, repetitive strain injuries, or specific tendon and nerve issues.
Conventional treatments for wrist pain depend on the specific diagnosis. In cases of arthritis, anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, or physical therapy are commonly recommended to manage pain and improve joint mobility.
For fractures, immobilization with a cast or splint is typically required, and surgery may be necessary for more severe breaks. Repetitive stress injuries like tendonitis or De Quervain’s tenosynovitis often respond to rest, ergonomic modifications, and anti-inflammatory treatments.
Physical therapy exercises to strengthen and stretch the affected muscles and tendons can be helpful. In cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, wrist splints are often used to keep the wrist in a neutral position, particularly at night, and corticosteroid injections may be administered, aimed to reduce inflammation.
If these methods do not relieve symptoms, surgical intervention, such as carpal tunnel release, might be recommended to decompress the median nerve.
While typical treatment usually involves pain medication, rest, and possibly physical therapy, acupuncture treatment can be an excellent adjunct or alternative treatment to relieve wrist pain.
Can Acupuncture Help Wrist Pain?

Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) can offer natural pain relief for injuries and chronic pain conditions, by reducing pain and inflammation, improving circulation, and supporting the body’s healing process.
According to TCM theory, the health of the internal organ systems is related to the rest of the body parts. For example, the spleen is responsible for transforming Qi and blood. If the spleen is weak, it can cause blockages in blood flow that create stasis, stiffness and pain in the limbs and joints. The liver governs the tendons of the body. When the liver is not functioning well, often due to emotional stress, than there may be pain and dysfunction in the tendons and joints.
Therefore, an acupuncturist does not only treat the painful area, but also looks at the deeper root cause and addresses them with acupuncture treatment, Chinese herbs, and other therapeutic modalities, to help relieve pain and inflammation and bring about healing.
A systematic review of trials showed that acupuncture treatment led to significant pain reduction for patients treated for rheumatoid arthritis affecting the wrist. It also concluded that acupuncture brought about pain relief and functional improvement for patients with tenosynovitis and carpal tunnel syndrome.
One study separated patients with carpal tunnel syndrome into two groups: one group received pain medication for wrist pain and the other group had 12 acupuncture treatments. Comparatively, the acupuncture group had greater reduction in pain, tingling, and numbness and greater functional improvement.
Studies of MRI results after acupuncture have suggested that acupuncture for carpal tunnel syndrome actually has a positive impact on nerve function in the wrist and changes the way the brain and nerves are signaling pain.
A trial involving patients treated for De Quervain’s disease tenosynovitis with five acupuncture sessions over the course of two weeks showed improvement in pain and grip strength, and the results were still maintained at a ten week follow up visit.
The combination of acupuncture and moxibustion can be particularly helpful for treating Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
Overall, the evidence shows that acupuncture and other TCM modalities can be a relatively low cost, non-invasive way of helping to treat wrist pain, without surgery or the unwanted side effects of pain medications or steroid injections.
Acupuncture Near Me for Wrist Pain in Los Angeles
Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in West L.A. have over 35 years of experience helping people recover from sports injuries, repetitive stress injuries, and orthopedic pain conditions of all kinds. Acupuncture treatment for wrist pain can be used in addition to your medical protocol to help speed recovery and bring about pain relief.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Edema With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Swollen feet and ankles? Fluid retention in legs? These are signs of edema. Acupuncture and TCM offer natural diuretic herbs and alternative treatment for swelling in legs and feet.
Edema refers to when excess fluid in body tissues, or water retention, leads to swelling. Edema most commonly causes swollen ankles and swollen feet. But edema can occur in many parts of the body.
Blood vessels have tiny valves that work to push blood from the lower body back up to the heart. When this process isn’t working properly, blood and other fluids will gather in the legs and cause swollen feet and ankles.
Edema causes puffiness under the skin, and when you press on the skin, it leaves an imprint. The skin may be shiny and stretched because of water retention.
Other edema symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness in the legs, and a swollen belly or distended abdomen.
Everyone experiences edema once in a while; for example, after a long airplane flight, which causes fluids to pool in the legs and feet, or the day after eating particularly salty foods, which can cause water retention. Edema is also common during pregnancy, when increased blood volume and pressure from the growing uterus can cause edema in the legs.
Occasional edema can often be prevented or remedied by reducing salt intake, drinking more water, and wearing compression garments.
Some health conditions can cause edema, in which case, both the underlying issue and the edema itself need to be addressed.
Acupuncture and Chinese herbs can help relieve swollen ankles and feet due to water retention, as well as helping to address the root cause of edema.
Causes of Edema

Edema can happen when a person stays in one position for a long time and fluids build up in the lower body due to gravity. This type of swelling can be helped by getting up and moving around regularly and/or wearing compression socks that prevent water retention from causing swollen ankles and feet.
Cardiovascular issues having to do with heart function or the health of blood vessels can cause edema. When the heart doesn’t pump blood effectively, it can cause fluid buildup in the legs, ankles, and feet. Venous insufficiency, or weakness in the veins, can prevent blood from being pushed back to the heart properly, which leads to varicose veins and blood buildup in the legs.
Kidney disease and liver disease can contribute to edema. Damaged kidneys are less able to remove excess fluid, leading to swelling. Conditions like cirrhosis can increase pressure in blood vessels and reduce proteins that keep fluid in the bloodstream, causing edema.
Blocked or damaged lymph nodes can prevent lymph fluid from draining well, causing localized edema. This is known as lymphedema. Lymphedema can be related to cancer treatments, when lymph nodes are removed.
People may experience edema after a stroke or cardiac event like a heart attack.
Side effects from some drugs, including those for high blood pressure and corticosteroids, can cause fluid retention.
Conditions such as cellulitis or arthritis can cause inflammation and localized swelling.
When there are underlying conditions like cirrhosis, kidney problems, and vascular issues, they must be addressed in order to resolve the edema.
Treatment for Swollen Legs and Feet
Conventional medical treatments for edema typically focus on addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms. Typical medical treatment for edema may include:
- Diuretics to help the body expel excess fluid through urine.
- Compression stockings to help reduce swelling by promoting fluid movement in the legs.
- Elevating the affected limbs above the level of the heart can help reduce swelling.
- Lowering sodium in the diet can help prevent fluid retention.
- Regular exercise to improve circulation and help reduce swelling.
- Addressing heart, kidney, or liver issues can help manage edema.
Using diuretic medications may seem to alleviate swelling in the short term, but these drugs create a kind of dependency. As soon as a person stops taking the diuretics, the water retention will return.
Chinese herbal formulations can act as natural diuretics, while addressing the root cause of edema.
By integrating acupuncture and TCM into your treatment plan, you may find a holistic approach that addresses not only the symptoms of edema but also its cause, providing lasting relief from edema swelling.
Can Acupuncture Help Edema?

TCM theory for the treatment of edema goes back over 2000 years. The Yellow Emperor wrote about edema treatment in his medical text before 100 B.C., describing the disruption of fluid movement in the body. In the second century A.D., another well-known Chinese doctor Zhang Zhong-Jing detailed treatments for edema with herb formulas, which are still considered classics today.
Edema can be related to imbalances in Yin and Yang. Yin edema affects the spleen and kidneys, while Yang edema affects the spleen and lungs. Yin edema symptoms tend to start in the lower body, with swollen feet and ankles, while Yang edema symptoms tend to start in the upper body, with the tendency to have tight, shiny skin.
According to TCM, the organ systems of the Spleen, Kidneys, and Lungs must be balanced in order to restore proper functioning of fluid metabolism. An acupuncture treatment protocol would be directed towards clearing wind, heat, dampness, and other pathogenic forces, while balancing Yin and Yang, and regulating Qi and Blood.
Different pathologies of edema can be described by TCM diagnoses, including:
- Blood stasis
- Qi stagnation
- Damp heat
- Heat toxins
- Wind-cold or Wind-heat in the lungs
Recent research shows that ancient herb formulas can help regulate fluids and have a positive effect on vascular function.
Moxibustion, a TCM modality that involves warming acupoint areas by burning mugwort herb near the skin, is often used to help relieve edema. Moxa treatment can help improve blood flow by warming and dispersing dampness and phlegm and invigorating the spleen and kidneys.
One study of patients suffering from swelling in legs and ankles showed that moxibustion helped relieve swelling in the legs.
Breast cancer treatment often involves radiation treatment that affects the lymph nodes, or the removal of lymph nodes, which can lead to lymphedema. This type of lymphedema often affects one arm, or both arms. It can also affect other parts of the body.
One study involved using acupuncture treatment twice a week to help relieve lymphedema after cancer treatment. More than half of the patients experienced a significant improvement in lymphedema, as measured by arm circumference. The conclusion was that acupuncture is a safe treatment that can help reduce swelling.
Acupuncture treatment improves blood flow and the movement of fluids in general, while nourishing the kidneys and spleen. Moxibustion can be used to further stimulate the flow of blood and Qi.
Acupuncture Near Me for Edema in West Los Angeles
Edema is a common problem, but it requires an individualized approach, as it can have many different root causes. Experienced acupuncture practitioners like Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in Westwood, CA can help patients find relief from edema swelling and water retention in legs through a combination of acupuncture, moxa, herbs, and personalized nutrition counseling.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Ankylosing Spondylitis With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.
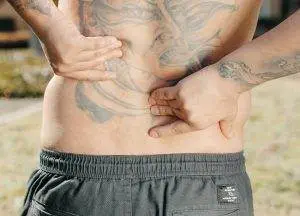
Low back pain, morning stiffness, hip pain? Fatigue, losing weight, poor vision, skin rashes? These can all be signs of Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS). Ankylosing Spondylitis is a type of autoimmune arthritis. Acupuncture can help relieve Ankylosing Spondylitis symptoms like lower back pain.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory arthritis condition that most often affects the spine, usually the lower back and pelvis is an inflammatory disease; the primary symptom is inflammation in the sacroiliac joints, the joints where the base of the spine (the ilium) meets the pelvis (the sacrum).
Similar to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis is an arthritic condition triggered by a person’s immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues. Arthritis generally refers to pain and swelling in joint tissues.
Ankylosing spondylitis can also affect the hips, knees, shoulder joints, and/or the ribcage. When the body tries to heal affected bones, extra bone tissue begins to grow. This new bone growth is what causes joint stiffness and lack of flexibility. When the ribs are affected, it can restrict normal breathing.
Ankylosing spondylitis can, over time, weaken bones to the extent that they begin to collapse; these compression fractures can ultimately lead to curvature of the spine and a stooped posture. These fractures of the vertebrae can potentially affect the spinal cord and nerves.
“Ankylosis” is a term for the stiffening and fusion of bones. A “fused spine” can be the eventual outcome of Ankylosing spondylitis.
AS can also cause inflammation in the GI tract, causing gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea. In this sense, it is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
In some cases, ankylosing spondylitis can cause eye inflammation, leading to vision problems like blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and painful eyes.
AS can also cause inflammation in the heart, which affects the function of the aortic valve and increases risk of heart disease.
As with other autoimmune disorders, modern medicine research has yet to discover what causes Ankylosing Spondylitis. Some gene mutations have been linked to ankylosing spondylitis, which is sometimes called axial spondyloarthritis.
Medical treatment for ankylosing spondylitis helps manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Acupuncture is widely recognized as an effective adjunct treatment for ankylosing spondylitis that can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
Top 10 Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms

The initial onset of symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis often includes episodes of lower back pain and stiffness or hip pain, which then may get more severe over time. But symptoms can vary widely from person to person, depending on which parts of the body are affected.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis include:
- Persistent lower back pain and stiffness, typically worse in the morning and after periods of inactivity; back pain that improves with movement and exercise
- Pain and stiffness that radiate from the lower back to the buttocks, hips, and thighs, reduced flexibility and range of motion in the spine
- Hip pain, shoulder pain, chest pain, rib pain, knee pain, and/or ankle pain
- Difficulty taking deep breaths due to stiffness in the chest and ribcage
- Fatigue
- Bony fusion of vertebrae, leading to a stooped posture and loss of spinal mobility
- Eye inflammation (uveitis) causes eye pain, sensitivity to light, and blurred vision
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
- Psoriasis, skin rash
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea
There is usually a gradual progression of AS symptoms over time, potentially leading to severe spinal deformity and disability.
Conventional treatment, with acupuncture and TCM used as a complementary treatment, can be helpful for symptomatic relief.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment
While there is no cure for AS, conventional medical treatments aim to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life for individuals with the condition.
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation associated with AS. They can help relieve symptoms and improve mobility, particularly during flare-ups.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) like sulfasalazine and methotrexate may be prescribed to slow the progression of AS and reduce inflammation. These medications work by suppressing the immune system’s abnormal response, which contributes to inflammation, the formation of extra bone tissue, and damage to the joints.
Biologic drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors like adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab, target specific components of the immune system involved in inflammation. They are often prescribed for individuals with moderate to severe AS who do not respond adequately to NSAIDs or DMARDs.
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management of AS by helping to improve flexibility, posture, and range of motion. Exercise programs tailored to the individual’s needs can help strengthen muscles, reduce pain, and maintain spinal mobility.
Orthopedic interventions, such as braces and orthotics, may be recommended to support proper posture and prevent spinal deformities caused by AS. In severe cases, surgical procedures like spinal fusion may be considered to stabilize the spine and alleviate pain.
Individuals with AS require regular monitoring by healthcare providers to assess disease activity, monitor medication effectiveness, and detect any complications early. Adjustments to treatment plans may be necessary based on disease progression and individual response to therapy.
Can Acupuncture Help Ankylosing Spondylitis?
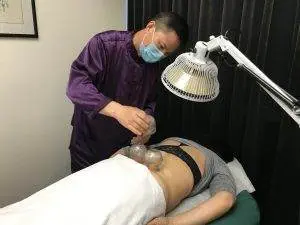
Acupuncture and moxibustion have been used for centuries to help relieve joint pain and stiffness due to inflammation. In Chinese, conditions that might involve bone fusion are called “zhu jie yang,” which means “bamboo spine.”
According to TCM theory, the bones are nourished by the kidney system; we observe that the formation of AS symptoms occurs along the Kidney Meridian and the Governing Vessel meridian. Weakness in bones may be due to deficiency of kidney Qi and blockage of the Governing Vessel.
Painful areas arise when there are blockages in Qi. Blockages occur due to pathogenic forces of phlegm accumulation, cold, and dampness.
Acupuncture treatment, herbs, and moxibustion may be used to strengthen the kidneys, address kidney yang deficiency, and clear dampness and wind from the channels.
One study found that patients who were diagnosed with ankylosing spondylitis and kidney yang deficiency and were given acupuncture treatment and moxibustion focused on the Governing Vessel meridian experienced significant reduction of pain.
Moxibustion warms and invigorates yang energy and can help improve immune function. In the case of AS, this treatment protocol can help slow the progression of the disease, preventing inappropriate bone formation and reducing inflammatory responses.
A review of 26 studies that involved moxibustion treatment as an adjunct therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. The conclusion was that patients who had moxibustion in addition to conventional treatment fared better than those who did not receive moxibustion.
The British Acupuncture Council recommends TCM treatment for AS, as it has been shown to be effective at relieving back pain, without side effects.
One study of patients with ankylosing spondylitis who received acupuncture treatment and Chinese herb supplements, including herbal soak baths, found that people experienced pain relief and functional improvement.
A study that looked at 22 patients who received cupping therapy along with acupuncture and infrared heat lamps. The vast majority of the patients reported significant improvement in their pain symptoms.
Tuina therapeutic massage may also be helpful for helping to improve mobility and circulation.
A review of studies showed that acupuncture offers “unique advantages” in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, including localized pain relief, reduced inflammation, improvement of joint mobility, prevention of spinal deformity, and overall better quality of life.
Acupuncture Near Me for Ankylosing Spondylitis in West Los Angeles
Acupuncture can be an effective complementary treatment for many autoimmune disorders, including Sjogren’s disease, Lupus, as well as difficult-to-treat chronic pain conditions like fibromyalgia and complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in West L.A. have over 35 years of experience helping patients find relief from all kinds of musculoskeletal pain.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.