-
 Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
Art of Wellness Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)11704 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 295, Los Angeles, CA, 90025
myartofwellness@gmail.com310-451-5522 Office Hours
MonClosedTue7:30 am --4 pmWed7:30 am --4 pmThu7:30 am -- 4 pmFri7:30 am -- 4 pmSat7:30 am -- 4 pmSunClosedOur office opens from Tuesdays to Saturdays 7:30 am to 4 pm, will be closed on Memorial day, Independent day, Labor day, Thanksgiving day, Christmas and New year.
-
Recent Posts
- Acupuncture for Sciatica Pain
- Can Acupuncture Help With Bladder Control?
- How to Treat De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Chinese New Year 2026: Year of the Horse
- Acupuncture and TCM Treatment for Perimenopause Symptoms
- How to Treat Insulin Resistance With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Metabolic Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Syncope With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Thoracic Outlet Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Dupuytren’s Contracture With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Nutcracker Syndrome With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Rosacea With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Perioral Dermatitis With Acupuncture and TCM
- Lymphatic Drainage With Acupuncture and TCM
- How to Treat Turf Toe With Acupuncture
- How to Treat Nerve Pain With Acupuncture and TCM
- Sign up to receive news and updates and get my free report:“The Top 10 Reasons to Try Acupuncture”

February 2026 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
Nutrition
Can Acupuncture Help Bad Breath?
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Dry mouth, coated tongue? Bad taste in your mouth, breath is always bad? There may be a deeper reason behind halitosis. Acupuncture and TCM can help correct the internal imbalances that are the root cause of bad breath.
How To Get Rid of Bad Breath
Looking for how to get rid of bad breath? Conventional medicine often sees bad breath as a dental issue, related to oral hygiene, gum disease, and bacteria on your tongue and in your mouth.
Recommendations for treating bad breath typically include using antibacterial mouth rinses and toothpastes, scraping your tongue, and flossing.
But what causes bad breath and dry mouth?
Bad Breath Causes
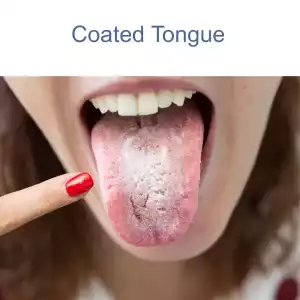
There are many health conditions that can cause bad breath, including:
- GERD – with acid reflux, some of the contents of the stomach come back up into the esophagus, which can smell strong.
- Diabetes – contributes to gum disease and bacterial growth in the mouth because of high glucose levels and poor blood flow to gums.
- Liver disease – breath may have a sulfurous, rotten egg smell, because toxins are not being adequately filtered by the liver.
- Kidney disease – can cause a metallic taste in the mouth, because minerals are not being filtered out through the kidneys.
- Sjogren’s Syndrome – parotid gland dysfunction leads to dry mouth.
- Sinusitis – mucus from sinus infection can smell bad as it drips into the back of the throat.
- Tonsillitis or tonsil stones – infected pus around the membranes of the tonsils can smell.
Other symptoms that often accompany bad breath include:
- Burning sensation on the tongue
- Need to clear your throat all the time
- Buildup on teeth, coated tongue
- Thick saliva
- Bad taste in mouth: metallic taste, sour taste, or bitter taste
Addressing these health issues can help clear up halitosis. But, what if you are experiencing frequent bad breath, and none of these health problems are the cause?
Underlying Causes of Bad Breath

According to TCM theory, bad breath usually arises from imbalances in the internal organ systems. Acupuncture treatment and herbal remedies can address the root causes of bad breath, so that it doesn’t come back.
In TCM, we consider “heat,” “wind,” “dampness,” “dryness,” and so on to be pathogenic factors that can either get into the body from external causes, or arise within the organ systems due to imbalances in Yin and Yang energies, or the obstruction or stagnation of Qi (life force energy).
Dryness and heat are the primary pathogenic factors that might lead to bad breath becoming a problem.
These words sound metaphorical, but they describe the nature of how problems occur within the human body and produce various symptoms. “Fire” or “heat” produces redness, swelling, eruptions of red bumps, thirst, excessive acid, etc.
When we say that pathogenic factors can arise from within, we are also acknowledging that emotions affect our physical and mental health, and vice versa.
Liver fire, or excess Yang energy in the Liver, for example, can arise due to dietary habits, like too much spicy food, or changes in weather, like warming temperatures in the springtime.
Liver heat is also related to feelings of anger and frustration. So, a lot of emotional stress and repressed anger can lead to liver fire problems.
Hot weather can contribute to feeling irritable. We must look at all sides of the problem in order to treat Liver fire and reduce uncomfortable symptoms, like trouble sleeping, and dry mouth.
Patterns of disharmony that can lead to bad breath as a symptoms include:
- Dry Intestine – leads to constipation and dry stool, dry throat and mouth, dizziness, hemorrhoids
- Stomach heat – thirsty all the time, craving for cold drinks, hungry all the time, canker sores, stomach pain, acid reflux, vomiting, feeling hot, acne breakouts
- Excess phlegm – tightness in chest, brain fog, dizziness
Sometimes one imbalance can lead to another. For example, liver fire can lead to fire in the lungs, causing chest pains and respiratory problems. Liver fire moving into the heart can cause angry outbursts, dry throat, and a bitter taste in your mouth.
TCM Nutrition to Address Bad Breath
Rather than simply telling you not to eat garlic, your acupuncturist will talk with you about eating the right foods to cool down the specific type of heat that is affecting your health. In TCM, we view certain foods as being “warming” or “cooling.” Eating more cool and neutral foods and avoiding heat-producing foods can help with halitosis.
An acupuncture practitioner will also assemble an herbal formula designed to address the organ system imbalances that seem to be causing problems.
Acupuncture Near Me for Bad Breath in West Los Angeles
Having bad breath can impede your social life and even your career. Experiencing dry mouth on a regular basis is very uncomfortable. It is important to address these issues, as they are likely an indication that there is something happening deeper under the surface. Please do not hesitate to reach out to us at Art of Wellness Acupuncture in Los Angeles, so that we can resolve this issue and help you feel better and more confident in your day to day life.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Cirrhosis With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Tired all the time? Upper right abdominal pain? Itchy skin? Muscle cramps? These can be cirrhosis of the liver symptoms. Acupuncture and TCM can help relieve liver pain due to cirrhosis and help to improve liver function.
Cirrhosis of the liver is a serious and progressive condition characterized by the scarring of liver tissue, which can lead to liver failure over time. This condition can be caused by various factors, like chronic viral hepatitis infections, primary biliary cirrhosis, and long-term alcohol overuse (alcoholic cirrhosis).
Other conditions that cause cirrhosis include: cystic fibrosis, autoimmune hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hemochromatosis (iron buildup), and primary biliary cholangitis (hardening of the bile ducts).
The liver is a vital organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances from the body, producing bile to aid in digestion, and storing nutrients. When cirrhosis of the liver occurs, these functions are significantly impaired, which can lead to a wide range of health problems.
Cirrhosis of the liver symptoms can vary depending on the severity and progression of the disease. Many people have liver cirrhosis without realizing it, as it is possible to have cirrhosis for years without being symptomatic.
Top 10 Symptoms of Cirrhosis of the Liver
Cirrhosis symptoms include:
- Bruise easily, bleed easily
- Nausea
- Fatigue, drowsiness
- Lack of appetite
- Itchy skin, pruritus
- Edema in legs, edema in ankles, edema in feet
- Jaundice – yellow eyes, yellow skin
- Spider veins
- Pale fingernails, clubbed fingers, red palms
- Cognitive difficulties, slurred speech
Cirrhosis can affect menstruation, causing irregular periods or no period, and cause female infertility. Cirrhosis can also affect sexual function (erectile dysfunction/ED), libido and male fertility.
In its early stages, cirrhosis may present with mild or no symptoms, making it challenging to diagnose without medical testing.
An enlarged spleen can be a symptom of liver cirrhosis.
As the condition advances, cirrhosis symptoms will usually worsen, signaling the need for intervention.
4 Stages of Liver Disease
It is important to recognize the stages of cirrhosis of the liver. Early intervention can help slow down the progression of liver disease.
- Stage I: Steatosis (Fatty Liver) – The first stage involves inflammation of the bile duct or liver. Abdominal pain is often the first sign. If not treated, the inflammation can damage the liver. Symptoms and inflammation are usually treatable at this stage, preventing progression to stage II.
- Stage II: Fibrosis (Liver Scarring) – Many people don’t notice symptoms until stage II or III. In this stage, scarring begins to block the normal blood flow in the liver. The liver doesn’t function properly, but with treatment, it can still recover and slow down the disease.
- Stage III: Cirrhosis – Cirrhosis occurs when scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This happens over several years due to untreated disease or infection. The liver becomes hard and lumpy, making it difficult for blood to flow through it. The blocked blood flow can also affect the spleen, causing additional issues.
- Stage IV: Liver Failure – At this final stage, the liver stops functioning. Immediate medical intervention is needed to prevent fatal outcomes.
Early diagnosis and treatment for cirrhosis are crucial to prevent further liver damage and manage cirrhosis effectively. Acupuncture and TCM offer an alternative treatment for cirrhosis to help restore liver function.
Medical Treatment for Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis treatment focuses on slowing the progression of the disease, managing liver cirrhosis symptoms, and preventing complications. The specific approach can vary depending on the underlying cause of cirrhosis, such as hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Common conventional treatments and strategies used to manage liver cirrhosis include medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
For cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis B or C, antiviral medications can help reduce liver inflammation and prevent further liver damage.
Diuretics are often prescribed to reduce fluid retention and swelling (edema) in the legs and abdomen (ascites). Paracentesis is a procedure that drains excess fluid from the abdomen in cases of severe ascites.
Beta-blockers decrease the risk of bleeding from esophageal varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus) by lowering blood pressure in the portal vein.

Frequent blood tests, imaging studies (such as ultrasounds), and endoscopies to monitor liver function and detect complications early.
In cases where cirrhosis progresses to end-stage liver disease and liver function is severely compromised, a liver transplant is sometimes the only option. This involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy one from a donor.
For alcoholic cirrhosis, abstaining from alcohol is crucial. Medical support, counseling, and rehabilitation programs can aid in alcohol cessation.
Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, weight loss, and regular exercise, are essential for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) related cirrhosis. Eating a balanced diet low in sodium to reduce fluid retention and avoiding alcohol and substances that can further harm the liver.
By combining these treatments, healthcare providers aim to manage cirrhosis effectively, improve the quality of life, and extend the lifespan of individuals with this chronic condition. However, some of the medications recommended for cirrhosis, such as antiviral drugs and diuretics, can potentially cause harm to other organ systems and do not serve to address the deeper root causes of liver dysfunction. Acupuncture and TCM offer a holistic treatment for cirrhosis that takes the whole body into account.
Can Acupuncture Help Cirrhosis?
According to TCM theory, the liver is responsible not only for removing toxins from the bloodstream and body; it also disperses nutrients and medicinal substances throughout the body.
In modern life, people’s livers have to work much harder to process all of the chemicals and other toxins to which we are exposed on a daily basis. When the liver is overtaxed, it cannot provide adequate energy and nutrition, and it may not be able to eliminate all of the toxins.
This buildup of chemicals and unhealthy “food” substances in the liver contributes to the formulation of scar tissue in the liver.
Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, itchy skin or skin rashes indicate that the liver is trying to purge toxins. When the liver cannot expel enough of the toxins, they will begin to affect the kidneys, too.
Medical treatments that aim to get rid of rashes or other symptoms may help the person feel more comfortable, but they do not help the root cause of the problems in the liver; they only cover them up. The use of antiviral and antibiotic medications, likewise, may seem to be taking care of infections, but they are potentially causing further damage to the organs.
In TCM, internal pathogens like cold, damp, and stagnation affecting the organ systems contribute to disease. Liver disease is not only about the liver, but also the kidneys, heart, stomach, and spleen. Symptoms like stomach distension, edema in the legs and feet, varicose veins or spider veins, and jaundice occur because of deficiencies in the various organs.
An acupuncturist will listen and observe each individual’s symptoms carefully to see which organs are affected. The TCM treatment plan will then involve acupuncture treatment and herbs to help strengthen all of the organs (heart, kidney, spleen and stomach), not just the liver.
A review of 15 studies in China in which TCM was used to treat liver cirrhosis concluded that acupuncture is effective both as a primary treatment and an adjunct treatment for chronic liver disease, helping to relieve symptoms and improve liver function.
If acupuncture treatment is sought before there is too much liver damage, TCM can help slow the progression of the disease and reduce painful symptoms.
One study showed that four weeks of electro-acupuncture treatment helped to reduce muscle cramps in liver cirrhosis patients.
Acupuncture helps to treat the underlying conditions that cause cirrhosis, including hepatitis, and fatty liver disease.
Another study showed that patients who received acupuncture treatment in addition to conventional treatment for liver cirrhosis showed less liver fibrosis (scarring) and fewer gastrointestinal symptoms than patients who only received conventional treatment.
Most doctors will advise patients with liver disease to quit drinking and cut out certain foods. Acupuncturists have expertise in nutrition that allows them to give each patient personalized care when deciding what dietary changes need to be made. Acupuncture treatment can also be very helpful when people are ready to cut out alcohol and eat the right foods to help improve liver health.
Acupuncture Near Me for Cirrhosis in West Los Angeles
TCM has been used to help improve liver health for many centuries. Acupuncture and Chinese herbs can help address liver problems of all kinds. At Art of Wellness, we are able to help patients improve liver function and feel better through acupuncture, customized herbal formulas, and individualized nutritional counseling.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat SIBO With Acupuncture and TCM
by Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac., Ph.D.

Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea? These can be SIBO symptoms. SIBO, or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, can cause bloated stomach, abdominal cramps and pain. Acupuncture and TCM can offer alternative SIBO treatment and bloating relief.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition in which an abnormal increase in the population of bacteria occurs in the small intestine.
Unlike the large intestine, which is rich in bacterial flora essential for digestion and immune function, the small intestine typically contains relatively few bacteria. When these bacteria proliferate excessively in the small intestine, they can disrupt normal digestion and nutrient absorption, leading to a variety of uncomfortable and sometimes debilitating symptoms.
Problems with gut motility also contribute to SIBO symptoms. Peristalsis is the process by which the smooth muscle tissues in the intestine move food matter through the gastrointestinal tract. When peristalsis isn’t happening the way it should, this is known as dysmotility. This can lead to stagnation of food matter in the intestine, which allows for an overgrowth of bacteria to build up. This in turn can causes hydrogen and methane gas to be produced by the fermentation of carbohydrates that are stagnant in the small intestine. This excess gas causes painful bloating and distension of the abdomen.
SIBO can cause a range of digestive symptoms, such as bloated stomach, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, and malabsorption of nutrients from food, which can result in unwanted weight loss and nutritional deficiencies. Vitamin B12 deficiency is particularly common among people suffering from SIBO.
Other symptoms, seemingly unrelated to the gastrointestinal system, can include: fatigue, headache, low fever, and rosacea.
SIBO is often associated with other health issues, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, and diabetes.
Acupuncture and TCM can work as an adjunct or alternative treatment for SIBO symptoms.
This can lead to hydrogen and methane gas being produced by the fermentation of carbohydrates that are stagnant in the small intestine. This excess gas can cause painful bloating and a distended abdomen.
What Causes SIBO?

A wide variety of different issues can play a role in the development of SIBO. Many conditions may cause problems with the secretion of gastric acids, with motility of the small intestine, gut immune function, and structural issues related to surgeries, injuries, or other abnormalities of the intestine.
Conditions that may contribute to SIBO include:
- Gastroparesis due to diabetes, or connective tissue disorders, viral infection, or ischemia
- Cirrhosis
- Chronic renal failure
- Scleroderma
- Crohn’s disease
- Celiac disease
- Recurrent rounds of antibiotics
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- GI tract surgeries that create structural abnormalities
- Immune deficiencies of T-cell or antibody responses
What’s the Difference Between IBS and SIBO?
Symptoms of SIBO are very similar to IBS symptoms, and it is possible for a person to have both IBS and SIBO at the same time. The difference between SIBO and irritable bowel syndrome is that IBS is a functional syndrome stemming from issues in the large intestine, whereas SIBO occurs in the small intestine.
One review of studies showed that the incidence of SIBO among patients with IBS is much higher than among people who don’t have IBS symptoms. The exact link between IBS and SIBO has not yet been clarified by medical science.
Medical Treatment for SIBO
In Western medicine, the treatment of SIBO typically involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at reducing the bacterial overgrowth, addressing the underlying causes, and managing symptoms.
Along with trying to find and address any underlying conditions that may be causing or contributing to SIBO, the mainstays of conventional treatment include antibiotics and medications to help improve gut motility.
The primary treatment for SIBO is the use of antibiotics to reduce the bacterial load in the small intestine. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include rifaximin, metronidazole, and ciprofloxacin. These antibiotics are chosen for their ability to target the small intestine bacteria while minimizing disruption to the rest of the gut microbiota.
Unfortunately, while antibiotics may help reduce bacteria, but they can also come with unwanted side effects. Rifaximin can cause bladder pain, urinary frequency, difficulty urinating, and cloudy urine. It can also contribute to feelings of anxiety, dizziness, headaches, fast breathing, fast heartbeat, and problems sleeping.
Antibiotics do not necessarily ease symptoms like gas and bloating, and can cause constipation and black, tarry stool.
Prokinetics are medications that help improve gut motility, ensuring that food and bacteria move efficiently through the digestive tract, which can help prevent bacterial stasis and overgrowth. Common prokinetics include erythromycin in low doses, prucalopride, and metoclopramide.
Dietary modifications will usually be recommended to help manage SIBO. Patients are often advised to follow specific diets such as the low FODMAP diet, which reduces the intake of fermentable carbohydrates that can feed bacterial overgrowth. Other dietary approaches may include the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) or an elemental diet, which involves consuming easily digestible, nutrient-rich formulas.
It can be difficult for people to follow a SIBO diet, and many physicians are not able to spend the time with patients that is required to properly support these behavioral changes. Without dietary support, the antibiotics and prokinetics may not do enough to get rid of SIBO.
Successful treatment of SIBO often requires addressing any underlying conditions that contribute to bacterial overgrowth. This could involve treating gastrointestinal motility disorders, managing chronic pancreatitis, or addressing structural abnormalities such as strictures or diverticula.
By understanding the underlying causes and employing a comprehensive treatment strategy, conventional medicine aims to alleviate symptoms and reduce the recurrence of SIBO. However, due to the chronic nature of the condition and the complexity of the gut microbiome, many patients seek complementary treatments such as acupuncture and herbal medicine to support their overall gut health and enhance the effectiveness of their treatment plan.
Can Acupuncture Help SIBO?

Chinese herbal medicine has its own way of helping to relieve SIBO, improve motility and digestion, and soothe uncomfortable stomach pain and bloating.
TCM theory views stagnation of Qi and blood as being one of the primary pathogenic forces in the body that causes pain and disease. In the case of SIBO, weakness or stagnation of organ systems, such as the stomach, liver, and spleen, is often part of the diagnostic pattern.
Diet, herbs, and supplements may all play an important role, in addition to acupuncture treatment for SIBO. Digestive enzymes and/or probiotics may be helpful in some cases. It may be necessary to eliminate some foods for a time to help control excessive fermentation and bacterial proliferation that is causing the gas and bloating.
There are foods and herbs that can work as natural prokinetics, to help improve gut motility and aid in proper absorption of nutrients. Ginger, turmeric, and peppermint oil are a few easy-to-find products that can help with digestion. There are also classic Chinese herbal preparations that can work even better than pharmaceutical prokinetics to help relieve constipation and indigestion.
A review of trials in China using Modified Runchang-Tang (MRCT) showed that in a sampling of over 2000 patients, this herbal formula worked better than conventional laxatives for relieving constipation.
Another review found that Modified Chaihu Shugan powder (MCSP) worked better than chemical prokinetics to help resolve symptoms of dyspepsia, or indigestion.
In addition to specific Chinese herb formulas that can help relieve digestive issues and work to get rid of unhealthy bacteria, there are other well-known common herbs that can also be helpful:
- Black cumin
- Garlic
- Cloves
- Cinnamon
- Thyme
- All-spice
- Bay leaves
- Mustard
- Rosemary
Acupuncture practitioners have generally received much more specialized training in nutrition than conventional doctors. Your acupuncturist will be able to make dietary recommendations that are specific to your symptoms and condition.
Acupuncture for SIBO Near Me in Los Angeles
Dr. Tan and Dr. Cai at Art of Wellness in West Los Angeles/Santa Monica have over 30 years of experience helping people with all types of gastrointestinal disorders. You do not have to suffer with gas pain and bloating, constipation or persistent diarrhea. Try Chinese medicine as an alternative or adjunct treatment for SIBO and IBS.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.
How to Treat Gastroparesis With Acupuncture and TCM
By Qineng Tan, L.Ac., Ph.D. and Xiaomei Cai, L.Ac. Ph.D.

Bloated stomach, indigestion? Acid reflux, regurgitating food? Abdominal pain or nausea? These can be signs of gastroparesis, also known as stomach paralysis. Acupuncture and TCM can help relieve gastroparesis symptoms.
What is gastroparesis? Gastric paralysis is a functional problem that occurs when the stomach muscles and the nerves that are connected to them aren’t activating normally. Weak stomach contractions lead to delayed emptying of the stomach into the small intestine.
Gastroparesis impacts your digestion, triggering uncomfortable symptoms, and limiting your ability to get proper nutrition and keep your blood sugar levels steady.
There are different types of gastroparesis.
- Diabetes-related gastroparesis – a side effect of diabetes
- Post-surgical gastroparesis – occurs after surgery, such as gallbladder or pancreas surgery, gastric bypass surgery, stomach surgery for ulcer, or hysterectomy
- Idiopathic gastroparesis – occurs without a clear explanation
Most people experience idiopathic gastroparesis, which means that doctors cannot necessarily identify what causes gastroparesis in many cases.
Some medications can delay stomach emptying, including narcotic pain medications like codeine, morphine, or oxycodone. Medications that work on nerve signals, such as those used to treat overactive bladder, can delay gastric emptying.
Scleroderma, an autoimmune condition that affects collagen production and smooth muscle tissues, can lead to gastroparesis. Parkinson’s disease, which affects nerve signals, can lead to delayed emptying of the stomach. Hypothyroidism can also affect nutrition and digestion, as can eating disorders, metabolic disorders, and/or chronic fatigue.
Acupuncture is a good modality for helping to relieve gastroparesis symptoms, because it works on the nervous system, to help restore the proper signaling to muscles.
Rumination Syndrome
Gastroparesis is sometimes confused with “rumination syndrome.” Rumination syndrome refers to the regular regurgitation of undigested food. People with this syndrome often regurgitate undigested food back up shortly after a meal. This condition is usually related to the functioning of muscles of the diaphragm and unconscious behaviors around chewing and swallowing.
Gastroparesis Symptoms

The most common signs of gastroparesis are bloating, pain, nausea, and feeling full quickly when you eat.
Other symptoms of gastroparesis include:
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Nausea, feeling nauseous after eating
- Vomiting, spitting up undigested food after eating
- Bloating, bloated stomach, abdominal bloating, abdominal cramping, stomach cramps, SIBO
- Belching, burping
- Acid reflux, heartburn
- High blood sugar, low blood sugar
- Lack of appetite
- Weight loss
- Malnutrition
Gastroparesis needs to be addressed, as it can compromise your overall health by blocking you from getting proper nutrition from your food.
Gastroparesis Treatment
Medical treatment for gastroparesis will depend on which type a person seems to have. If a person has diabetes-related gastroparesis, for example, treatment will necessitate better management of blood sugar levels.
Initial diagnosis usually involves imaging tests to see what is happening with the stomach and if there may be a blockage. Gastric motility tests help doctors see how your stomach muscles are working.
People will often be advised to change their dietary habits: possibly following a liquid diet for a period of time, or eating smaller meals throughout the day. You may be told to avoid fats and fiber, as these macronutrients can contribute to delayed stomach emptying.
In some cases, intravenous feeding or tube feeding may be necessary, if a person is severely undernourished due to gastroparesis.
Antiemetic medications may be prescribed to help with nausea and vomiting. Proton pump inhibitors may be recommended to help with acid reflux symptoms.
There are some medications that can help promote better gastric emptying by stimulating more muscular contractions. Erythromycin and metoclopramide are two drugs used to treat gastroparesis. These medications can have side effects, like stomach cramps, nausea and constipation. They can also have negative interactions with other medications.
If these treatments are not helping, surgical options may be offered. A gastrostomy or may be inserted to help drain the stomach. A jejunostomy tube can be placed to bypass the stomach, so that nutrition gets into the intestines. A pyloroplasty is an operation in which the muscular valve of the stomach is widened.
Newer, experimental treatments involve placing electrodes on the stomach to help activate contractions. Botox injections have also been tried, as a way to calm spasms in the stomach.
Acupuncture treatment can help relieve gastroparesis symptoms without side effects or invasive procedures.
Can Acupuncture Help Gastroparesis?

According to TCM theory, gastroparesis can be caused by a deficiency of stomach and/or spleen Qi. Part of the TCM treatment protocol for gastroparesis might involve using herbs and certain foods to help warm and nourish the spleen. Acupuncture treatment can help improve muscular function, as well help to relieve stomach pain.
The motility of the gastrointestinal system is controlled by nerve and electric impulses. Acupuncture, and in particular, electro-acupuncture, can have a positive effect on stimulating electrical activity and restoring neural pathways within the body.
Acupuncture has been shown to be helpful for relieving many GI symptoms, like nausea and bloating. This makes it a good treatment for many types of gastric disorders and stomach problems.
In one study, three different groups of people were all given acupuncture treatment, with emphasis on different acupoints used for each group. All three groups of patients had significant improvement in their gastroparesis symptoms.
Specifically, testing with barium meal showed that acupuncture helped improve the speed of stomach emptying. Patients also reported positive changes in their feeling of fullness after a meal and experienced less bloating.
One case study of a woman in her 60s who had been suffering for two years with gastroparesis symptoms showed significant improvement of nausea, timely stomach emptying, and energy levels after just four acupuncture treatments.
Another case study of a man in his 60s who presented with symptoms of fullness, stomach pain and distension, with delayed stomach emptying, ended with complete resolution of his symptoms after eleven acupuncture treatment sessions.
Acupuncture Near Me for Gastroparesis in Los Angeles
At Art of Wellness in West Los Angeles, Doctors Tan and Cai have over 35 years of experience helping people find relief from all kinds of gastrointestinal symptoms and stomach problems, including: IBS, stomach ulcer, colitis, Crohn’s disease, diverticulitis, nausea, diarrhea, and constipation. It’s worth trying acupuncture to see if it can help relieve gastroparesis symptoms for you.
*This article is for education from the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine only. The education provided by this article is not approved by FDA to diagnose, prevent, treat and cure human diseases. It should not stop you from consulting with your physician for your medical conditions. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on Qi, which is an invisible force that usually cannot be observed by modern science. Because science focuses on testing ideas about the natural world with evidence obtained through observation, these aspects of acupuncture can’t be studied by science. Therefore acupuncture and Chinese herbs are often not supported by double-blind, randomized trials, and they are considered alternative medicine therapies in the United States.


